編輯:關於Android編程
上一篇文章《自定義viewgroup(2)》地址:http://www.jb51.net/article/100610.htm
代碼
package com.example.libingyuan.horizontallistview.ScrollViewGroup;
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.util.DisplayMetrics;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.view.WindowManager;
import android.widget.Scroller;
/**
* 自定義ViewGroup
* 在滾動的基礎上,增加了邊界限制
*/
public class ScrollViewGroup extends ViewGroup {
//滾動計算輔助類
private Scroller mScroller;
//手指落點的X坐標
private float mLastMotionX = 0;
//屏幕寬度
private int screenWidth;
/**
* 使用new關鍵字創建對象的時候調用
* @param context 上下文
*/
public ScrollViewGroup(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
/**
* 在XML文件中使用的時候調用
* @param context 上下文
* @param attrs 屬性:如 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
*/
public ScrollViewGroup(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
/**
* 在xml文件中調用,並且使用了自定義屬性的時候調用
* @param context 上下文
* @param attrs 屬性:如 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
* @param defStyleAttr 自定義屬性的id
*/
public ScrollViewGroup(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
init(context);
}
/**
* 初始化方法
* 初始化滾動輔助類Scroller以及計算出屏幕寬度
* @param context
*/
private void init(Context context) {
mScroller = new Scroller(context);
WindowManager manager = (WindowManager) context
.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE);
DisplayMetrics outMetrics = new DisplayMetrics();
manager.getDefaultDisplay().getMetrics(outMetrics);
screenWidth = outMetrics.widthPixels;
}
/**
* 滾動時需要重寫的方法,用於控制滾動
*/
@Override
public void computeScroll() {
//判斷滾動時候停止
if (mScroller.computeScrollOffset()) {
//滾動到指定的位置
scrollTo(mScroller.getCurrX(), mScroller.getCurrY());
//這句話必須寫,否則不能實時刷新
postInvalidate();
}
}
/**
* 手指觸屏事件監聽
* @param event
* @return
*/
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int action = event.getAction();
float x = event.getX();
switch (action) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
if (!mScroller.isFinished()) {
mScroller.abortAnimation();
}
mLastMotionX = event.getX();
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
float delt = mLastMotionX - x;
mLastMotionX = x;
scrollBy((int) delt, 0);
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
View lastChild=getChildAt(getChildCount()-1);
int finalyChild= (int) (lastChild.getX()+lastChild.getWidth()-screenWidth);
if (getScrollX()<0){
scrollTo(0,0);
}
if (getScrollX()>=finalyChild)
scrollTo(finalyChild,0);
invalidate();
break;
default:
break;
}
return true;
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
//重新設置寬高
this.setMeasuredDimension(measureWidth(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec), measureHeight(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec));
}
/**
* 測量寬度
*/
private int measureWidth(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
// 寬度
int sizeWidth = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int modeWidth = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
//父控件的寬(wrap_content)
int width = 0;
int childCount = getChildCount();
//重新測量子view的寬度,以及最大高度
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin;
width += childWidth;
}
return modeWidth == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ? sizeWidth : width;
}
/**
* 測量高度
*/
private int measureHeight(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
//高度
int sizeHeight = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int modeHeight = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
//父控件的高(wrap_content)
int height = 0;
int childCount = getChildCount();
//重新測量子view的寬度,以及最大高度
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin;
height += childHeight;
}
height = height / childCount;
return modeHeight == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ? sizeHeight : height;
}
/**
* 給子布局設定位置
*/
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int childLeft = 0;//子View左邊的間距
int childWidth;//子View的寬度
int height = getHeight();//屏幕的寬度
int childCount = getChildCount();//子View的數量
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin;
child.layout(childLeft, 0, childLeft + childWidth, height);
childLeft += childWidth;
}
}
@Override
public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
return new MarginLayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
}
}
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持本站。
 說說智能Android手機root的那些事
說說智能Android手機root的那些事
幫忙給朋友手機root ,是電信的定制機,試了很多軟件都沒有成,後來才發基帶版本是FB24,是不能root的,需要刷成EK21才能root,就在網上找刷機的
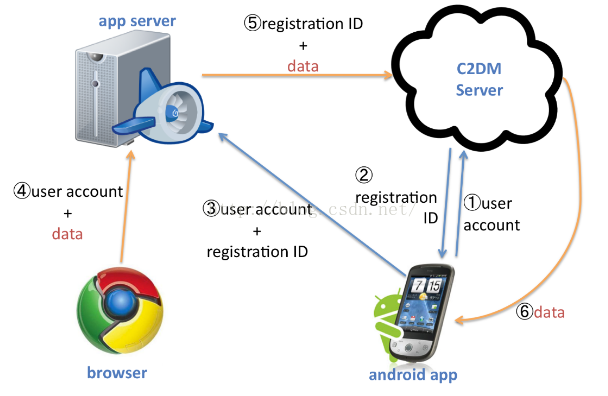 android後台信息推送調研
android後台信息推送調研
前言我們已經開發了一個應用,這裡稱為A應用,類似於天氣weather那種。現在的任務就是如果這些A應用有新版本了,或者天氣出現比較惡劣的狀況,要及時在手機上進行消息的推送
 Android熱補丁動態修復技術(完結篇):自動生成打包帶簽名的補丁,重構項目
Android熱補丁動態修復技術(完結篇):自動生成打包帶簽名的補丁,重構項目
一、關於前面四篇博文Android熱補丁動態修復技術(一):從Dex分包原理到熱補丁Android熱補丁動態修復技術(二):實戰!CLASS_ISPREVERIFIED問
 RecycleView刷新 齒輪轉動動畫效果
RecycleView刷新 齒輪轉動動畫效果
穿插一篇自定義view 的動畫效果,偶然看到的一個gif刷新齒輪效果圖片,原圖如下:感覺挺有意思的,就想自己也做一個,發費了一番功夫,算是做出了基本效果,但原諒我使其美觀