編輯:關於Android編程
Content Provider管理著應用程序需要訪問的數據倉庫。這需要您在程序中繼承ContentProvider類,並在manifest中注冊組件。該類就是其他應用程序與您的應用程序數據庫之間的接口(interface between your provider and other applications)。通過ContentProvider,其他應用程序可以對本應用的數據庫進行方便的操作,這需要使用ContentResolver。
如您的程序需要向外界應用提供以下內容之一,那麼程序中需要創建ContentProvider:
需要向其他應用程序提供復雜的數據或文件( offer complex data or files to other applications);
希望用戶能從您的應用向其他應用復制復雜的數據(allow users to copy complex data from your app into other apps);
希望使用搜索框架提供提供定制的搜索建議( provide custom search suggestions using the search framework)。
!請注意:若只是應用需要訪問自身SQLite數據庫,那麼無需創建ContentProvider。
以下是創建provider的方法:
為您的應用程序設計原始存儲。ContentProvider以如下兩種方式提供數據:
文件數據(File data):在應用程序的的私有空間中,數據以不同形式的文件存儲,如照片(photos)、音頻(audio) 、視頻(videos)等。為了能讓其他應用程序讀取您的程序中的這些文件,需要provider作為媒介。
結構化數據(”Structured” data):數據存儲於數據庫、數據或其他類似的結構中。存儲的數據支持行列表的形式(Store the data in a form that’s compatible with tables of rows and columns)。每行代表一個實體(entity),如個人信息等。每列表示每個實體的不同屬性,如人的身高、體重等。這些表結構及其數據信息可以存儲於SQLite數據庫中。
實現ContentProvider中的方法;
為ContentProvider定義authority字符串,該字符串包含了content URI以及表中列的字段。若您希望ContentProvider可以處理intent,那麼還需定義intent的action、data、flag等。並為provider定義其他應用程序需要訪問它的權限。
Android中提供了如下存儲技術:
Android提供了SQLite數據庫API以訪問面向表的數據存儲(to store table-oriented data),SQLiteOpenHelper可幫助您創建數據庫,而SQLiteDatabase類是訪問數據庫的基礎類。provider提供給外界程序的內容表現為一張或多張表。
Android提供了多個面向文件存儲的API,關於文件存儲,您可以參考這個鏈接 Data Storage,若您希望創建一個訪問媒體文件(如音樂或多媒體)的provider,那麼該provider還能提供訪問表和其他文件的方法。
使用java.net或android.net包中的API可以訪問網絡數據,您可以將網絡數據同步到本地(如同步到本地的數據庫中),並將本地數據以表或文件的形式提供給程序。
BaseColumns._ID作為其字段。因為當需要將表中數據綁定到ListView上時,ListView需要一個列名為_ID的字段。
content URI是一個URI對象,它指定了provider中的某個數據(集、表),Content URIs 包含兩部分:authority和path,authority用於標識provider的唯一性,path用於指定該provider中的某張表或是某個文件。content URI還有一個id部分是可選的,它指定了表中的特定行。ContentProvider類中每一個訪問數據的方法(增刪改查)都會回傳一個URI參數,用於具體指定您需要訪問哪張表(哪一行)或是哪個文件。
一個provider通常只有一個authority,並且遵循android系統內部命名規范。為了防止authority之間的命名沖突,您應當使用公司的Internet域名的倒序來作為authority的前綴,或者使用應用的包名作為前綴。比如,您的應用程序包名為com.example.,那麼應當為provider的authority設置為com.example..provider。
path用於指定provider中的某張表。比如,繼續按上例來說,若provider中包含兩張表:table1、table2,其content URI應分別為com.example..provider/table1、com.example..provider/table2。您無需為每級path都設置一張表。
通常,在content URI後追加ID可以訪問該URI所指向的provider中的某張表的某一行數據信息。該ID將匹配表中名為“_ID”的字段中的值,並訪問該值所在的行( providers match the ID value to the table’s _ID column, and perform the requested access against the row that matches)。
其他應用程序訪問provider的常見情景是:app通過ContentResolver訪問content URI指定的ContentProvider中的某張表(或表中的某幾行),並返回一個Cursor對象,再利用CursorAdapter將Cursor對象作為數據源綁定至ListView上。而CursorAdapter要求綁定的Cursor必須包含_ID字段。
用戶可以在UI上查詢或修改ListView中的項,系統將查詢該項對應的Cursor中的行,並將該行的_ID追加至content URI後訪問provider中某張表的某一行,以達到查詢或修改該行數據的目的。
為了區分不同content URI 的訪問請求,系統提供了協助provider的UriMatcher類,並將content URI和特定的整型值一一對應(maps content URI “patterns” to integer values)。您可以使用switch語句處理不同整型值對應的content URI所需查詢的內容。content URI使用通配符查詢傳遞來的查詢URI:
比如說,您可能會使用如下content URI來查詢表中的某張表中的某些數據:
content://com.example.app.provider/table1: 查詢table1;
content://com.example.app.provider/table2/dataset1:查詢table2中的dataset1;
content://com.example.app.provider/table2/dataset2:查詢table2中的dataset2;
content://com.example.app.provider/table3: A table called table3:查詢table3;
content://com.example.app.provider/table3/1:查詢table3中行ID為1的條目;
在provider中,下面的寫法可以匹配第一個URI:
content://com.example.app.provider/*
在provider中,下面的寫法可以匹配第二個和第三個URI:
content://com.example.app.provider/table2/*
在provider中,下面的寫法可以匹配第五個URI:
content://com.example.app.provider/table3/#
下面演示了UriMatcher的用法,addURI()方法將傳入的URI與一個唯一的整型標識對應,match()方法將返回URI對應的整型值,示例如下:
public class ExampleProvider extends ContentProvider {
...
// Creates a UriMatcher object.
private static final UriMatcher sUriMatcher;
...
/*
* The calls to addURI() go here, for all of the content URI patterns that the provider
* should recognize. For this snippet, only the calls for table 3 are shown.
*/
...
/*
* Sets the integer value for multiple rows in table 3 to 1. Notice that no wildcard is used
* in the path
*/
sUriMatcher.addURI("com.example.app.provider", "table3", 1);
/*
* Sets the code for a single row to 2. In this case, the "#" wildcard is
* used. "content://com.example.app.provider/table3/3" matches, but
* "content://com.example.app.provider/table3 doesn't.
*/
sUriMatcher.addURI("com.example.app.provider", "table3/#", 2);
...
// Implements ContentProvider.query()
public Cursor query(
Uri uri,
String[] projection,
String selection,
String[] selectionArgs,
String sortOrder) {
...
/*
* Choose the table to query and a sort order based on the code returned for the incoming
* URI. Here, too, only the statements for table 3 are shown.
*/
switch (sUriMatcher.match(uri)) {
// If the incoming URI was for all of table3
case 1:
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(sortOrder)) sortOrder = "_ID ASC";
break;
// If the incoming URI was for a single row
case 2:
/*
* Because this URI was for a single row, the _ID value part is
* present. Get the last path segment from the URI; this is the _ID value.
* Then, append the value to the WHERE clause for the query
*/
selection = selection + "_ID = " uri.getLastPathSegment();
break;
default:
...
// If the URI is not recognized, you should do some error handling here.
}
// call the code to actually do the query
}
ContentProvider用於處理其他應用程序的訪問請求,而最終將檢索結果傳給ContentResolver,ContentProvider的主要方法如下:
ContentProvider是抽象類,該類中包含6個抽象方法需要您實現,除了onCreate()方法外,其他應用程序欲訪問您定制的ContentProvider時,其余的5個方法均被調用(All of these methods except onCreate() are called by a client application that is attempting to access your content provider)。
query():從provider中查詢數據,並將結果以Cursor對象返回;
insert():向provider的某張表中插入一行新的數據,方法回傳的Uri參數用於指向需要插入的表,而ContentValue參數用於回傳插入的內容,該方法返回新插入行的Uri地址;
update():用於修改某些行,並返回修改的行數;
delete():刪除某些行,並返回刪除的行數。
getType():返回content URI對應的MIME 類型(Return the MIME type corresponding to a content URI),該方法的具體含義請您參考後續章節。
onCreate():該方法用於初始化ContentProvider,當ContentProvider被實例化後,該方法將被立刻回調。!請注意:只有ContentResolver試圖訪問您的ContentProvider,該實例才會被創建(Notice that your provider is not created until a ContentResolver object tries to access it)。
在ContentResolver中,包含著與上述同名的方法及方法簽名(these methods have the same signature as the identically-named ContentResolver methods)。
為了實現上述方法,您需要考慮這些事:
除了onCreate()方法外,其余方法均可在多個線程中同時調用,這就需要保證線程安全(can be called by multiple threads at once, so they must be thread-safe)。
避免在onCreate()方法中做耗時操作(Avoid doing lengthy operations in onCreate())。當方法中涉及的資源用到時再加載(Defer initialization tasks until they are actually needed)。
盡管您必須實現這些方法,但是您可以不做任何操作。比如說,當您需要向表中插入數據時,若只是在insert()中返回0,則數據插入操作不會成功。
ContentProvider.query()方法返回一個Cursor對象,若返回失敗,將方法將拋出一個異常。
若您是使用SQLite數據庫存儲數據,那麼調用SQLiteDatabase的query()方法返回的Cursor對象可以直接作為該方法的返回值(you can simply return the Cursor returned by one of the query() methods of the SQLiteDatabase class)。若未查詢到匹配結果,那麼返回的Cursor對象中,其getCount()方法應返回0。若出現異常,Cursor對象應返回null。
若您並沒有使用SQLite數據庫存儲數據,那麼應根據具體數據的結構,使用系統提供的Cursor子類對象作為返回值。比如,MatrixCursor是Cursor的一個子類,它可以指向每一行都是一個Object對象數組的矩陣結構(each row is an array of Object)。調用該類的addRow()方法可添加一行數據。
!請注意:Android 系統必須能夠跨進程邊界傳播 Exception,Android 可以為以下異常執行此操作,這些異常可能有助於處理查詢錯誤:1、IllegalArgumentException:您可以選擇在提供程序收到無效的內容 URI 時引發此異常;2、NullPointerException:空指針異常
insert()方法可為指定的表中添加一行數據,使用回傳參數ContentValues配置值。若ContentValues的鍵並沒有表中的任何字段與之對應,您應當設定一個默認值。
刪除指定表中的某一行或多行數據。方法返回int值,表示刪除的行數。
方法利用ContentValues以鍵值對的方式修改指定表中的數據。返回int型變量,表示修改的行數。
當初始化provider時,系統將回調onCreate()方法,在該方法中不要執行耗時操作,您可以在resolver訪問該provider時,再創建數據庫,並延遲數據加載。
比方說,您可以在ContentProvider.onCreate()方法中創建一個SQLiteOpenHelper對象,第一次打開數據庫時創建SQL表,實現方式是調用getWritableDatabase()方法,調用該方法會立即觸發SQLiteOpenHelper.onCreate()方法的回調,可以在該方法中創建數據庫和表。
下面將以代碼片段的方式展示上述實現過程:
public class ExampleProvider extends ContentProvider
/*
* Defines a handle to the database helper object. The MainDatabaseHelper class is defined
* in a following snippet.
*/
private MainDatabaseHelper mOpenHelper;
// Defines the database name
private static final String DBNAME = "mydb";
// Holds the database object
private SQLiteDatabase db;
public boolean onCreate() {
/*
* Creates a new helper object. This method always returns quickly.
* Notice that the database itself isn't created or opened
* until SQLiteOpenHelper.getWritableDatabase is called
*/
mOpenHelper = new MainDatabaseHelper(
getContext(), // the application context
DBNAME, // the name of the database)
null, // uses the default SQLite cursor
1 // the version number
);
return true;
}
...
// Implements the provider's insert method
public Cursor insert(Uri uri, ContentValues values) {
// Insert code here to determine which table to open, handle error-checking, and so forth
...
/*
* Gets a writeable database. This will trigger its creation if it doesn't already exist.
*
*/
db = mOpenHelper.getWritableDatabase();
}
}
以下是SQLiteOpenHelper.onCreate()中的代碼:
...
// A string that defines the SQL statement for creating a table
private static final String SQL_CREATE_MAIN = "CREATE TABLE " +
"main " + // Table's name
"(" + // The columns in the table
" _ID INTEGER PRIMARY KEY, " +
" WORD TEXT"
" FREQUENCY INTEGER " +
" LOCALE TEXT )";
...
/**
* Helper class that actually creates and manages the provider's underlying data repository.
*/
protected static final class MainDatabaseHelper extends SQLiteOpenHelper {
/*
* Instantiates an open helper for the provider's SQLite data repository
* Do not do database creation and upgrade here.
*/
MainDatabaseHelper(Context context) {
super(context, DBNAME, null, 1);
}
/*
* Creates the data repository. This is called when the provider attempts to open the
* repository and SQLite reports that it doesn't exist.
*/
public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase db) {
// Creates the main table
db.execSQL(SQL_CREATE_MAIN);
}
}
ContentProvider MIME Types)ContentProvider中包含了兩種返回MIME類型的方法:
getType():該方法必須實現(One of the required methods that you must implement for any provider);
getStreamTypes():若您的provider提供了文件訪問,需實現該方法(A method that you’re expected to implement if your provider offers files.
)。
getType()方法返回值為String類型,表示傳入的Uri對象所對應的MIME類型。回傳的Uri參數既可以是帶有通配符的Uri,也可以是一個具體的Uri。
常見的MIME類型有 text,、HTML、JPEG 等。如需查看MIME的全部類型及解析,您可以點擊這個鏈接:《IANA MIME Media Types》。
對於getType()方法返回的MIME類型,應遵循以下格式:
Type 部分:vnd
Subtype 部分:
若回傳的Uri指向表的某一行,那麼格式應為:android.cursor.item/
若回傳的Uri指向表的多行(一行以上),那麼格式應為:android.cursor.dir/
Provider-specific 部分:vnd.。其中
如您的provider的authority是com.example.app.provider,若需要訪問table1中的多行,那麼MIME類型可以這樣寫:
vnd.android.cursor.dir/vnd.com.example.provider.table1
如需訪問table1中的單行,MIME類型可以這樣寫:
vnd.android.cursor.item/vnd.com.example.provider.table1
若provider可以訪問文件,應該實現String[] getStreamTypes (Uri uri,方法。該方法返回一個
String mimeTypeFilter)String數組,數組中的每一項表示傳入的Uri所指向的文件類型(for the files your provider can return for a given content URI),若其他應用程序只對某個特定類型的文件感興趣,那麼應給getStreamTypes()方法的第二個參數傳入感興趣的文件的MIME類型。
比如說,provider提供了 .jpg、.png 和 .gif類型的圖像文件,其他應用程序調用ContentResolver.getStreamTypes()方法並傳入過濾參數image/*,那麼系統將返回如下所示的String數組:
{ "image/jpeg", "image/png", "image/gif"}
若應用程序只對.jpg格式的文件感興趣,那麼可以傳入*\/jpeg作為過濾參數,則方法將返回
{"image/jpeg"}
若provider提供的文件類型無法匹配您傳入的過濾文件類型,那麼方法應返回null(If your provider doesn’t offer any of the MIME types requested in the filter string, getStreamTypes() should return null)。
Contract類是一個用public final關鍵字修飾的類,存在於provider所在的應用程序中,該類的內部定義了provider中需要使用到的URIs、column names、 MIME types、 meta-data等字符串常量。設置常量的好處是:當需要修改查詢的范圍或內容時,只需修改這個類中的字符串即可。
設置Contract類的另一個好處是協助開發者對字符串常量的記憶( mnemonic names for its constants)。
默認情況下,存儲在設備內部存儲的文件對您的應用貨provider是私有的;
程序中創建的SQLiteDatabase數據庫只有您自己的程序和provider可以操作;
默認情況下,外部存儲中的文件是公開的(data files that you save to external storage are public and world-readable),您無需使用provider訪問外存中的文件。因為這些文件使用系統提供的API就能訪問。
所有應用程序都可以訪問您的provider。默認情況下,您的provider沒有任何權限。可以在manifest文件的
這需要在manifest中設置android:name屬性指定,指定的權限應具有唯一性。如為provider添加只讀的權限:
com.example.app.provider.permission.READ_PROVIDER
下面描述了provider權限的作用域,作用域越小的權限,優先級越高(More fine-grained permissions take precedence over ones with larger scope):
統一的讀寫provider級別權限(Single read-write provider-level permission):在android:permission屬性指定。
單獨的讀寫provider級別權限(Separate read and write provider-level permission):在android:readPermission 和android:writePermission屬性指定。該權限高於上面的統一讀寫權限(They take precedence over the permission required by android:permission)。
path級別的權限(Path-level permission):在provider的content URI中設置只讀、只寫、或可讀可寫的權限。在
您的程序中定義的ContentProvider需要在manifest中使用
Authority:使用android:authorities屬性配置。該屬性為provider提供一個唯一的標識。
Provider class name:使用android:name屬性定義。屬性值為定制的ContentProvider的全限定類名。
Permissions:指定了其他應用需要訪問該provider所需聲明的權限。
android:grantUriPermssions:臨時權限;
android:permission:provider范圍內的讀寫權限;
android:readPermission:provider范圍的只讀權限;
android:writePermission:provider范圍的只寫權限。
Startup and control attributes:下列屬性決定了系統何時以及如何啟動provider、provider的特性、以及運行時設置:
android:enabled:是否允許系統啟動provider;
android:exported:是否允許其他應用程序訪問provider;
android:initOrder:指定同一進程中,相對於其他provider的啟動順序;
android:multiProcess:是否允許在與client端相同的進程中啟動provider;
android:process:provider運行的進程名;
android:syncable:provider中的數據與服務器上的數據同步。
Informational attributes:為provider提供可選的圖標和標題。
android:icon:指定一個drawable資源,該圖標出現在設置 > 應用 > 全部 中應用列表內的provider標簽旁;
android:label:描述provider(和)或其數據的信息標簽。 該標簽出現在設置 > 應用 > 全部中的應用列表內。
 android:android Intent and IntentFilter
android:android Intent and IntentFilter
1,intentfilter說明:如果說是將一個activity有其他應用打開,或者是在webView 或者 bybird app中調用我們自己的activi
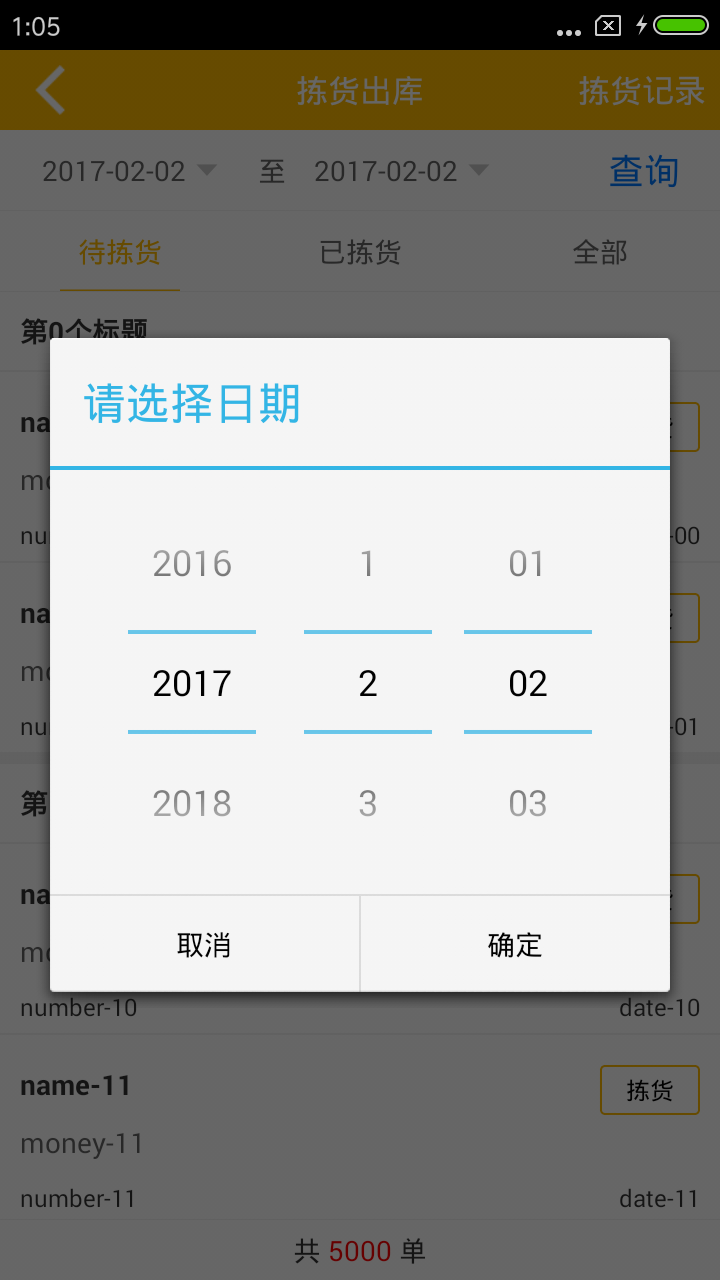 android學習記錄2:DatePicker的使用及設置其主題
android學習記錄2:DatePicker的使用及設置其主題
DatePickerDiaLog 在android 4.n的版本中,取消選擇日期時,會調用onDateSet ,確認選擇日期時會調用兩次onDateSet(但在高版本中不
 ES文件浏覽器怎麼添加其他雲
ES文件浏覽器怎麼添加其他雲
ES文件浏覽器怎麼添加其他雲。ES文件浏覽器是一個能管理手機本地、局域網共享、FTP和藍牙文件的管理器。他有自己的個人雲,那我想添加其他的雲,怎麼辦呢?是不
 Android學習筆記之六-圖片的修飾技術
Android學習筆記之六-圖片的修飾技術
1.ShapDrawable用途:圓角的輸入框 單色背景的按鈕開發步驟:1. 創建drawable文件夾2. 創建一個shap文件. 文件名:業務名_控件名縮寫_bg