編輯:關於Android編程
前言
相信大家都知道知道,在AndroidOS中,提供了五中數據存儲方式,分別是:ContentProvider存儲、文件存儲、SharedPreference存儲、SQLite數據庫存儲、網絡存儲。那麼這一篇,我們介紹文件存儲。
1.Android文件的操作模式
學過Java的同學都知道,我們新建文件,然後就可以寫入數據了,但是Android卻不一樣,因為Android是 基於Linux的,我們在讀寫文件的時候,還需加上文件的操作模式,Android中的操作模式如下:
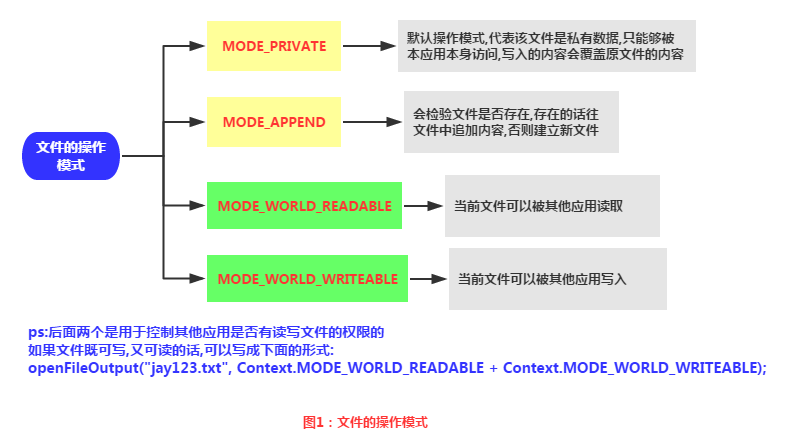
2、文件的操作模式
我們在學Java的時候都知道,Java中的IO操作來進行文件的保存和讀取,Android是基於Linux的,與Java不同的是Android在Context類中封裝好了輸入流和輸出流的獲取方法,分別是: FileInputStream openFileInput(String name); FileOutputStream(String name , int mode),這兩個方法第一個參數 用於指定文件名,第二個參數指定打開文件的模式。Android提供的文件模式有:
1.MODE_PRIVATE:Android提供的默認操作模式,代表該文件是私有數據,只能被應用本身訪問,在該模式下,寫入的內容會覆蓋原文件的內容。
2.MODE_APPEND:模式會檢查文件是否存在,存在就往文件追加內容,否則就創建新文件。
3.MODE_WORLD_READABLE:表示當前文件可以被其他應用讀取;
4.MODE_WORLD_WRITEABLE:表示當前文件可以被其他應用寫入。
此外,Android還提供了其它幾個重要的文件操作的方法:
1.getDir(String name , int mode):在應用程序的數據文件夾下獲取或者創建name對應的子目錄
2.File getFilesDir():獲取app的data目錄下的絕對路徑
3.String[] fileList():返回app的data目錄下數的全部文件
4.deleteFile(String fileName):刪除app的data目錄下的指定文件
3、讀寫文件
Android的讀寫文件和Java一樣,也是一樣通過IO操作實現,下面我們通過一個簡單的例子走一下這個流程:
布局文件代碼:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" android:padding="16dp"> <EditText android:id="@+id/ed_file_save" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> <Button android:id="@+id/btn_file_save" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginTop="10dp" android:text="保存內容" /> <Button android:id="@+id/btn_file_read" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginTop="10dp" android:text="讀取內容" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/tv_read_file" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginTop="10dp" android:textColor="#000" android:textSize="14sp" /> </LinearLayout>
Activity代碼:
package com.example.datasave;
import android.content.Context;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.annotation.Nullable;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.TextView;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* Created by Devin on 2016/7/19.
*/
public class FileDataActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private EditText ed_file_save;
private Button btn_file_save;
private Button btn_file_read;
private TextView tv_read_file;
private String fileName = " hello.txt";
@Override
protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_file);
ed_file_save = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.ed_file_save);
btn_file_save = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_file_save);
btn_file_read = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_file_read);
tv_read_file = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv_read_file);
btn_file_save.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
String fileContent = ed_file_save.getText().toString();
try {
save(fileContent);
ToastUtils.showToast(FileDataActivity.this, "文件寫入成功");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
ToastUtils.showToast(FileDataActivity.this, "文件寫入失敗");
}
}
});
btn_file_read.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
try {
String content = read();
tv_read_file.setText("文件的內容是:" + content);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
ToastUtils.showToast(FileDataActivity.this, "讀取文件失敗!");
}
}
});
}
public void save(String fileContent) throws Exception {
FileOutputStream output = this.openFileOutput(fileName, Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
output.write(fileContent.getBytes());
output.close();
}
public String read() throws IOException {
//打開文件輸入流
FileInputStream input = this.openFileInput(fileName);
byte[] temp = new byte[1024];
StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer("");
int len = 0;
while ((len = input.read(temp)) > 0) {
stringBuffer.append(new String(temp, 0, len));
}
//關閉輸入流
input.close();
return stringBuffer.toString();
}
}
最後是實現效果圖:
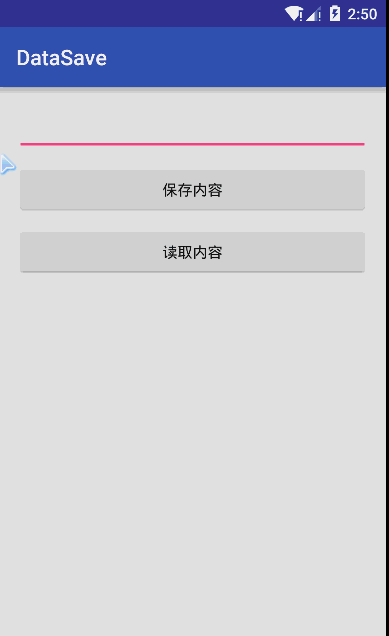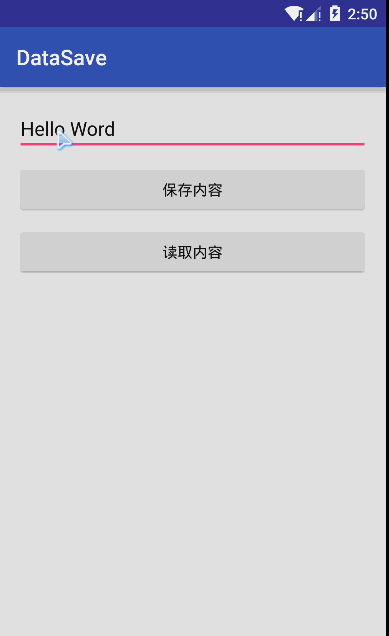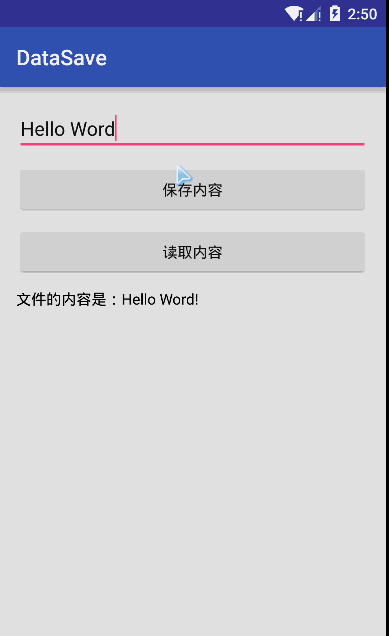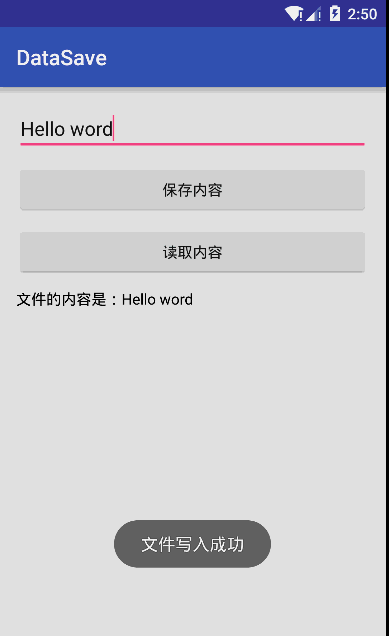
這裡文件使用的模式是私有模式,只能本應用讀取還會覆蓋原文件,這樣就可以實現簡單的文件讀寫。
4、讀寫SDcard的文件
讀寫SDCard需要權限:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.MOUNT_UNMOUNT_FILESYSTEMS" /> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" />
對設備讀寫SDCard的時候需要判斷SDCard是否存在,很多手機是不存在SDcard的,下面我們對SDCard的讀寫中會有體現,下面我們一起通過例子實現SDCard的讀寫操作
首先是布局文件代碼:
<EditText android:id="@+id/ed_file_save_sd" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginTop="20dp" /> <Button android:id="@+id/btn_file_save_sd" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginTop="10dp" android:text="寫入到SDcard" /> <Button android:id="@+id/btn_file_read_sd" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginTop="10dp" android:text="從SDcard讀取" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/tv_read_file_sd" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginTop="10dp" android:textColor="#000" android:textSize="14sp" />
Activity代碼:
ed_file_save_sd = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.ed_file_save_sd);
tv_read_file_sd = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv_read_file_sd);
btn_file_read_sd = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_file_read_sd);
btn_file_read_sd.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
try {
String content = readFromSD();
tv_read_file_sd.setText("從SDCard讀取到的內容是:" + content);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
ToastUtils.showToast(FileDataActivity.this, "讀取文件失敗!");
}
}
});
btn_file_save_sd = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_file_save_sd);
btn_file_save_sd.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
String content = ed_file_save_sd.getText().toString();
try {
save2SDCard(content);
ToastUtils.showToast(FileDataActivity.this, "文件寫入SDCard成功");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
ToastUtils.showToast(FileDataActivity.this, "文件寫入SDCard失敗");
}
}
});
public void save2SDCard(String content) throws Exception {
if (Environment.getExternalStorageState().equals(Environment.MEDIA_MOUNTED)) { // 如果sdcard存在
String fileName3 = Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory().getCanonicalPath() + File.separator + "test" + File.separator + fileName2;
File file = new File(fileName3);
if (!file.getParentFile().exists()) {
file.getParentFile().mkdir();
}
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);
fileOutputStream.write(content.getBytes());
fileOutputStream.close();
} else {
ToastUtils.showToast(this, "SDCard不存在");
}
}
public String readFromSD() throws Exception {
StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer("");
if (Environment.getExternalStorageState().equals(Environment.MEDIA_MOUNTED)) {
String fileName3 = Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory().getCanonicalPath() + File.separator + "test" + File.separator + fileName2;
File file = new File(fileName3);
if (!file.getParentFile().exists()) {
file.getParentFile().mkdir();
}
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
byte[] temp = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while ((len = fileInputStream.read(temp)) > 0) {
stringBuffer.append(new String(temp, 0, len));
}
fileInputStream.close();
} else {
ToastUtils.showToast(this, "SDCard不存在");
}
return stringBuffer.toString();
}
SDCard的讀取和文件操作差不多,需要判斷SDCard是否存在,最後是效果圖:

5、讀取raw和assets文件的數據
raw/res中的文件會被映射到Android的R文件中,我們直接通過R文件就可以訪問,這裡就不在過多介紹了。
assets中的文件不會像raw/res中的文件一樣被映射到R文件中,可以有目錄結構,Android提供了一個訪問assets文件的AssetManager對象,我們訪問也很簡單:
AssetManager assetsManager = getAssets();
InputStream inputStream = assetsManager.open("fileName");
這樣就可以直接獲取到assets目錄下的資源文件。
AndroidOS的文件存儲就簡單介紹到這裡,下面提供一些文件存儲的工具方法:
package com.example.datasave.io;
import android.content.Context;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
/**
* IO流 工具類<br>
* 很簡單,僅支持文本操作
*/
public class IOUtils {
/**
* 文本的寫入操作
*
* @param filePath 文件路徑。一定要加上文件名字 <br>
* 例如:../a/a.txt
* @param content 寫入內容
* @param append 是否追加
*/
public static void write(String filePath, String content, boolean append) {
BufferedWriter bufw = null;
try {
bufw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(
new FileOutputStream(filePath, append)));
bufw.write(content);
} catch (Exception e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (bufw != null) {
try {
bufw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
/**
* 文本的讀取操作
*
* @param path 文件路徑,一定要加上文件名字<br>
* 例如:../a/a.txt
* @return
*/
public static String read(String path) {
BufferedReader bufr = null;
try {
bufr = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(
new FileInputStream(path)));
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
String str = null;
while ((str = bufr.readLine()) != null) {
sb.append(str);
}
return sb.toString();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (bufr != null) {
try {
bufr.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* 文本的讀取操作
*
* @param is 輸入流
* @return
*/
public static String read(InputStream is) {
BufferedReader bufr = null;
try {
bufr = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is));
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
String str = null;
while ((str = bufr.readLine()) != null) {
sb.append(str);
}
return sb.toString();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (bufr != null) {
try {
bufr.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* @param context 上下文
* @param fileName 文件名
* @return 字節數組
*/
public static byte[] readBytes(Context context, String fileName) {
FileInputStream fin = null;
byte[] buffer = null;
try {
fin = context.openFileInput(fileName);
int length = fin.available();
buffer = new byte[length];
fin.read(buffer);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (fin != null) {
fin.close();
fin = null;
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return buffer;
}
/**
* 快速讀取程序應用包下的文件內容
*
* @param context 上下文
* @param filename 文件名稱
* @return 文件內容
* @throws IOException
*/
public static String read(Context context, String filename)
throws IOException {
FileInputStream inStream = context.openFileInput(filename);
ByteArrayOutputStream outStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while ((len = inStream.read(buffer)) != -1) {
outStream.write(buffer, 0, len);
}
byte[] data = outStream.toByteArray();
return new String(data);
}
}
好的,關於Android的數據存儲與訪問的文件讀寫就到這裡,如果在學習本文中遇到什麼問題,或者覺得有些纰漏的地方,歡迎提出,萬分感激,謝謝~
 Android 信息中URL地址識別問題
Android 信息中URL地址識別問題
ATCID主要用來處理PC端傳輸過來的AT命令,從AT命令實際處理的地方來說,主要分為3類: 1. 需要Modem來處理的AT命令; 2. 需要在nativ
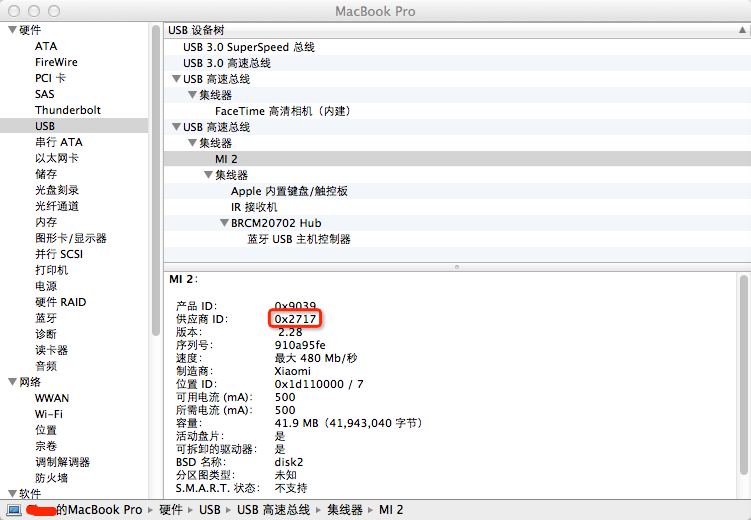 Android 手機無法連接mac解決辦法
Android 手機無法連接mac解決辦法
Android 手機無法連接mac解決辦法一般的android連接mac 很方便不用安裝驅動就可以啦,可是不知道為什麼二般情況下有的android手機(小米2,華為等)就
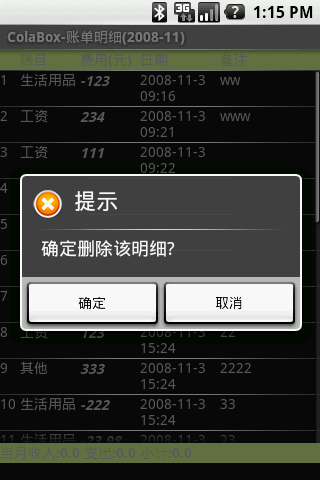 Android 個人理財工具六:顯示賬單明細 下
Android 個人理財工具六:顯示賬單明細 下
上一節的顯示賬單明細 上中,賬單明細的顯示已經基本實現,本文主要整理下代碼,實現此窗口的查詢和刪除功能;按下Menu菜單
 Android7.0 PackageManagerService (3) APK安裝
Android7.0 PackageManagerService (3) APK安裝
在本篇博客中,我們分析一下Android中的APK是如何安裝的,以及PKMS在這個過程中進行了哪些工作。APK的安裝方式有很多,我們先來看看如何用adb命令進行安裝。我們