編輯:Android編程入門
Android建議我們不要在UI線程中執行耗時操作,因為這很容易導致ANR異常(在Android源碼中我們可以看到,UI如果對用戶的操作超過5秒無響應,就會報ANR異常)。因此,一些耗時操作都會在子線程中完成。當我們在子線程中獲取了數據,要將其顯示到UI中,如果沒有Handler,這將很難完成。因此,Android之所以提供Handler,就是為了解決子線程訪問UI的問題。
為什麼Android不允許在子線程中訪問UI呢?顯然這樣做不安全,多線程訪問UI是不安全的(學過操作系統的盆友應該都了解線程互斥,這裡我就不詳細介紹了)。有人就會說了,可以通過設置信號量來解決啊。這中方法不是不可以,因為這種方法會使訪問UI的邏輯變得復雜;其次這會降低UI的訪問效率。而使用Handler就比較簡單高效。Handler是同個Message來通訊的。
使用Handler時,需要重寫handleMessage方法,在handleMessage中接受新線程發來的Message,並做相應的處理。在新線程中則是通過Message來傳遞消息,Message中往往也攜帶著需要傳遞的數據以及消息的類型。還要強調一點,如果當前線程有Looper就不需要執行Looper.prepare(),如果沒有,就需要在新線程內執行Looper.prepare(),否則會報錯。具體使用代碼如下:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private Handler mHandler=new Handler(){
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what)
{
case 1:
//執行需要修改的UI操作
break;
default:
break;
}
}
};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {//在新線程中執行耗時操作
//如果當前線程有Looper就不需要執行Looper.prepare();
Looper.prepare();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);//睡眠1秒
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//操作完成之後通過發送Message,來通知Handler進行UI操作
Message msg=new Message();
msg.what=1;
/*這部分是偽代碼,value 是想通過Message傳遞的值
Bundle data=new Bundle();
data.putSerializable("key",value);
msg.setData(data);
*/
//設置好數據後,發送消息
mHandler.sendMessage(msg);
}
}).start();
}
}
Handler創建時會采用Looper來建立消息循環。所以,當前線程必須要有Looper。當Handler創建完成後,其內部的Looper以及MessageQueue既可以和Handler一起協同工作了。Handler通過sendMessage將消息發送給內部的MessageQueue,而MessageQueue會調用queue.enqueueMessage(msg, uptimeMillis)方法,它的源碼如下:
boolean enqueueMessage(Message msg, long when) {
if (msg.target == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Message must have a target.");
}
if (msg.isInUse()) {
throw new IllegalStateException(msg + " This message is already in use.");
}
synchronized (this) {
if (mQuitting) {
IllegalStateException e = new IllegalStateException(
msg.target + " sending message to a Handler on a dead thread");
Log.w(TAG, e.getMessage(), e);
msg.recycle();
return false;
}
msg.markInUse();
msg.when = when;
Message p = mMessages;
boolean needWake;
if (p == null || when == 0 || when < p.when) {
// New head, wake up the event queue if blocked.
msg.next = p;
mMessages = msg;
needWake = mBlocked;
} else {
// Inserted within the middle of the queue. Usually we don't have to wake
// up the event queue unless there is a barrier at the head of the queue
// and the message is the earliest asynchronous message in the queue.
needWake = mBlocked && p.target == null && msg.isAsynchronous();
Message prev;
for (;;) {
prev = p;
p = p.next;
if (p == null || when < p.when) {
break;
}
if (needWake && p.isAsynchronous()) {
needWake = false;
}
}
msg.next = p; // invariant: p == prev.next
prev.next = msg;
}
// We can assume mPtr != 0 because mQuitting is false.
if (needWake) {
nativeWake(mPtr);
}
}
return true;
}
通過源碼,我們發現,queue.enqueueMessage(msg, uptimeMillis)將消息放入了MessageQueue裡。Looper則會一直處理MessageQueue中的消息。
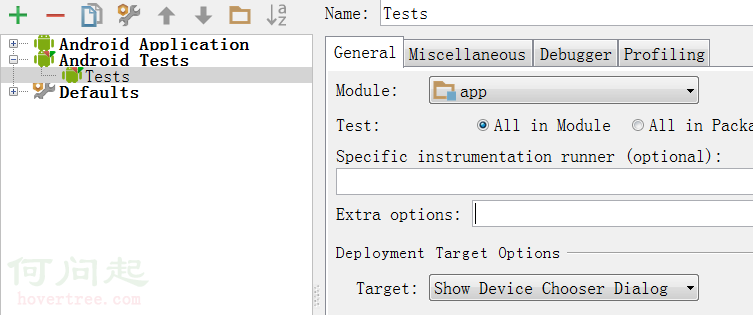 在Android Studio中進行單元測試
在Android Studio中進行單元測試
寫單元測試類1.創建單元測試文件夾,即新建一個用於單元測試的包,存放單元測試的類。2.創建一個類如 ExampleTest,注意要繼承自InstrumentationTe
 Android—自定義控件實現ListView下拉刷新
Android—自定義控件實現ListView下拉刷新
這篇博客為大家介紹一個android常見的功能——ListView下拉刷新(參考自他人博客,網址忘記了,閱讀他的代碼自己理解注釋的,希望能幫助到大
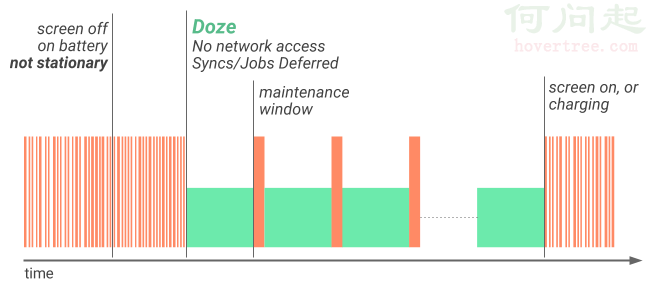 android 7.0 學習筆記(一)
android 7.0 學習筆記(一)
導讀增強的Doze模式後台優化Data Saver 一.增強的Doze模式Android N對Android M引進的Doze模式進行了進一步的增強,變化體現在
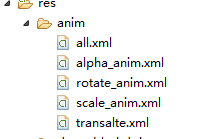 補間動畫TweenAnimation
補間動畫TweenAnimation
animation_translate = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(MainActivity.this, R.anim.transalt