編輯:關於android開發
Android編程實現圖標拖動效果的方法
本文實例講述了Android編程實現圖標拖動效果的方法。分享給大家供大家參考,具體如下:
最近優化圖標拖動時的速率,稍微有一點點效果,直接把代碼貼出來,有興趣一起討論的朋友可以給我留言。
代碼如下:
DragView.java
package com.android.dragtest;
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.FrameLayout;
public class DragView extends FrameLayout {
private static final String TAG = "DragView";
private float X;
private float Y;
private View mDragView;
public DragView(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public DragView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public DragView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
mDragView = new View(context);
mDragView.setLayoutParams(new LayoutParams(60, 60));
mDragView.setBackgroundDrawable(getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.gamecenter));
mDragView.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
addView(mDragView);
}
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
final int action = ev.getAction();
switch (action) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
Log.d(TAG, "===============>onInterceptTouchEvent ACTION_DOWN");
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
Log.d(TAG, "===============>onInterceptTouchEvent ACTION_MOVE");
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
Log.d(TAG, "===============>onInterceptTouchEvent ACTION_UP");
break;
}
return true;
}
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
final int action = ev.getAction();
X = ev.getX();
Y = ev.getY();
switch (action) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
Log.d(TAG, "onTouchEvent ACTION_DOWN");
mDragView.layout((int)X - 30, (int)Y - 30, (int)X + 30, (int)Y + 30);
mDragView.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
Log.d(TAG, "onTouchEvent ACTION_MOVE x:" + X + " Y:" + Y);
mDragView.layout((int)X - 30, (int)Y - 30, (int)X + 30, (int)Y + 30);
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
Log.d(TAG, "onTouchEvent ACTION_UP");
mDragView.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
break;
}
return true;
}
}
DragTestActivity.java
package com.android.dragtest;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
public class DragTestActivity extends Activity {
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
}
}
main.xml
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
希望本文所述對大家Android程序設計有所幫助。
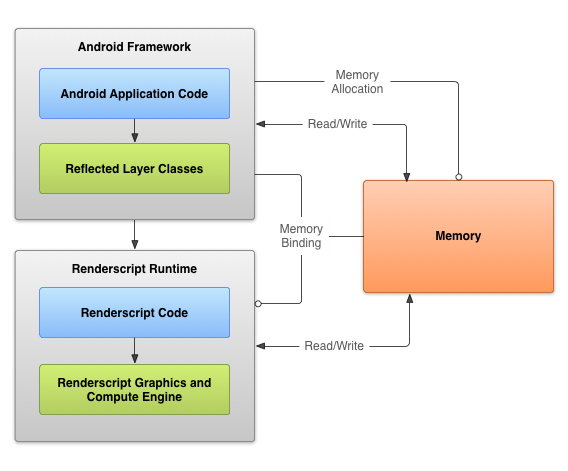 Android高效計算——RenderScript(一),androidrenderscript
Android高效計算——RenderScript(一),androidrenderscript
Android高效計算——RenderScript(一),androidrenderscript高效計算——RenderScript Render
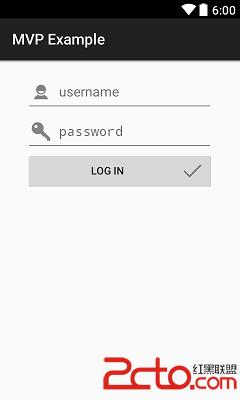 Android中MVP模式與MVC模式比較(含示例)
Android中MVP模式與MVC模式比較(含示例)
Android中MVP模式與MVC模式比較(含示例) MVP 介紹 MVP模式(Model-View-Presenter)是MVC模式的一個衍生。主要目的是為了解耦,使項
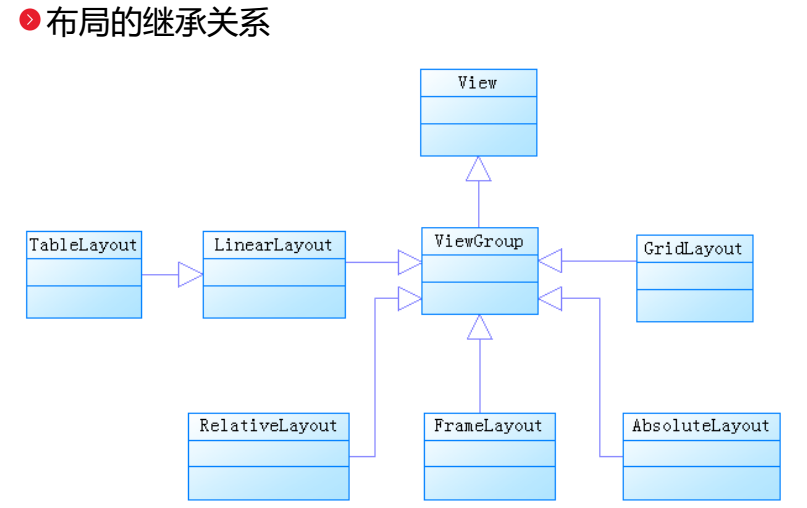 安卓的主要幾大布局,安卓布局
安卓的主要幾大布局,安卓布局
安卓的主要幾大布局,安卓布局今天我們的主要內容就是安卓的主要幾個基礎的布局方式。(主要布局如下:) 1.線性布局(LinerLayout) 2.相對布局(Relative
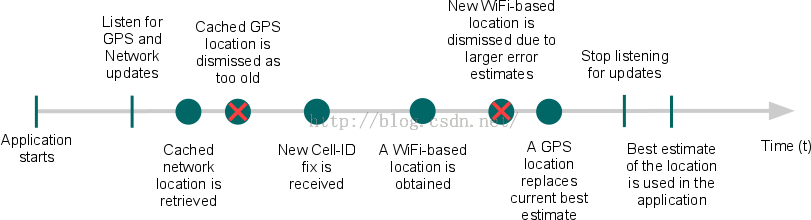 Android API Guides---Location Strategies
Android API Guides---Location Strategies
Android API Guides---Location Strategies Location Strategies 注:本指南中描述的策略適用於平台定位API中