編輯:關於Android編程
上篇剛好說到獲取到了簽名信息,下面進入安裝過程,直接上源碼:
private void installNewPackageLI(PackageParser.Package pkg,
int parseFlags, int scanMode, UserHandle user,
String installerPackageName, PackageInstalledInfo res) {
// Remember this for later, in case we need to rollback this install
String pkgName = pkg.packageName;
if (DEBUG_INSTALL) Slog.d(TAG, "installNewPackageLI: " + pkg);
boolean dataDirExists = getDataPathForPackage(pkg.packageName, 0).exists();
...................
mLastScanError = PackageManager.INSTALL_SUCCEEDED;
PackageParser.Package newPackage = scanPackageLI(pkg, parseFlags, scanMode,
System.currentTimeMillis(), user);
if (newPackage == null) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Package couldn't be installed in " + pkg.mPath);
if ((res.returnCode=mLastScanError) == PackageManager.INSTALL_SUCCEEDED) {
res.returnCode = PackageManager.INSTALL_FAILED_INVALID_APK;
}
} else {
updateSettingsLI(newPackage, installerPackageName, ull, null, res);
// delete the partially installed application. the data directory will have to be
// restored if it was already existing
if (res.returnCode != PackageManager.INSTALL_SUCCEEDED) {
// remove package from internal structures. Note that we want deletePackageX to
// delete the package data and cache directories that it created in
// scanPackageLocked, unless those directories existed before we even tried to
// install.
deletePackageLI(pkgName, UserHandle.ALL, false, null, null, dataDirExists ? PackageManager.DELETE_KEEP_DATA : 0,
res.removedInfo, true);
}
}
}主要邏輯是掃描當前的Package如果掃描成功然後更新Settings內容,更新失敗要刪除package信息。
scanPackageLI方法比較長,所以只列出了其中我認為比較重要的環節
private PackageParser.Package scanPackageLI(PackageParser.Package pkg,
int parseFlags, int scanMode, long currentTime, UserHandle user) {
//前面是一個APK完整性、是否重復的判斷以及針對SystemApp的特殊設置
........................
// Initialize package source and resource directories
File destCodeFile = new File(pkg.applicationInfo.sourceDir);
File destResourceFile = new File(pkg.applicationInfo.publicSourceDir);
SharedUserSetting suid = null;
PackageSetting pkgSetting = null;
// writer
// 這裡是一段針對SystemApp的修改安裝操作
....................................
//如果有設置shareUID的必須要判斷屬於同一個id的是否采用了同樣的簽名,首先獲取到這個簽名信息。
if (pkg.mSharedUserId != null) {
suid = mSettings.getSharedUserLPw(pkg.mSharedUserId, 0, true);
if (suid == null) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Creating application package " + pkg.packageName
+ " for shared user failed");
mLastScanError = PackageManager.INSTALL_FAILED_INSUFFICIENT_STORAGE;
return null;
}
}
// Just create the setting, don't add it yet. For already existing packages
// the PkgSetting exists already and doesn't have to be created.
pkgSetting = mSettings.getPackageLPw(pkg, origPackage, realName, suid, destCodeFile,
destResourceFile, pkg.applicationInfo.nativeLibraryDir,
pkg.applicationInfo.cpuAbi,
pkg.applicationInfo.flags, user, false);
if (pkgSetting == null) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Creating application package " + pkg.packageName + " failed");
mLastScanError = PackageManager.INSTALL_FAILED_INSUFFICIENT_STORAGE;
return null;
}
pkg.applicationInfo.uid = pkgSetting.appId;
pkg.mExtras = pkgSetting;
//這裡是對當前應用的簽名信息進行驗證,包括系統特殊組的特殊簽名
if (!verifySignaturesLP(pkgSetting, pkg)) {
if ((parseFlags&PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM_DIR) == 0) {
return null;
}
// The signature has changed, but this package is in the system
// image... let's recover!
pkgSetting.signatures.mSignatures = pkg.mSignatures;
// However... if this package is part of a shared user, but it
// doesn't match the signature of the shared user, let's fail.
// What this means is that you can't change the signatures
// associated with an overall shared user, which doesn't seem all
// that unreasonable.
//這裡完成相同shareUid的簽名判斷
if (pkgSetting.sharedUser != null) {
if (compareSignatures(pkgSetting.sharedUser.signatures.mSignatures,
pkg.mSignatures) != PackageManager.SIGNATURE_MATCH) {
Log.w(TAG, "Signature mismatch for shared user : " + pkgSetting.sharedUser);
mLastScanError = PackageManager.INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_INCONSISTENT_CERTIFICATES;
return null;
}
}
// File a report about this.
String msg = "System package " + pkg.packageName
+ " signature changed; retaining data.";
reportSettingsProblem(Log.WARN, msg);
}
// Verify that this new package doesn't have any content providers
// that conflict with existing packages. Only do this if the
// package isn't already installed, since we don't want to break
// things that are installed.
if ((scanMode&SCAN_NEW_INSTALL) != 0) {
final int N = pkg.providers.size();
int i;
for (i=0; i= 0; i--) {
final String origName = pkg.mAdoptPermissions.get(i);
final PackageSetting orig = mSettings.peekPackageLPr(origName);
if (orig != null) {
if (verifyPackageUpdateLPr(orig, pkg)) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Adopting permissions from " + origName + " to "
+ pkg.packageName);
mSettings.transferPermissionsLPw(origName, pkg.packageName);
}
}
}
}
}
final String pkgName = pkg.packageName;
final long scanFileTime = scanFile.lastModified();
final boolean forceDex = (scanMode&SCAN_FORCE_DEX) != 0;
//進程名,如果配置了進程名就以配置為准,沒有就是默認包名
pkg.applicationInfo.processName = fixProcessName(
pkg.applicationInfo.packageName,
pkg.applicationInfo.processName,
pkg.applicationInfo.uid);
//下面都是針對安裝APK的data目錄進行處理
File dataPath;
if (mPlatformPackage == pkg) {
// The system package is special.
dataPath = new File (Environment.getDataDirectory(), "system");
pkg.applicationInfo.dataDir = dataPath.getPath();
} else {
// This is a normal package, need to make its data directory.
dataPath = getDataPathForPackage(pkg.packageName, 0);
boolean uidError = false;
//處理應用數據存儲路徑存在的情況
if (dataPath.exists()) {
int currentUid = 0;
try {
StructStat stat = Os.stat(dataPath.getPath());
currentUid = stat.st_uid;
} catch (ErrnoException e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Couldn't stat path " + dataPath.getPath(), e);
}
// If we have mismatched owners for the data path, we have a problem.
if (currentUid != pkg.applicationInfo.uid) {
boolean recovered = false;
//這裡是處理同樣的APK修改了UID的情況
if (currentUid == 0) {
// The directory somehow became owned by root. Wow.
// This is probably because the system was stopped while
// installd was in the middle of messing with its libs
// directory. Ask installd to fix that.
int ret = mInstaller.fixUid(pkgName, pkg.applicationInfo.uid,
pkg.applicationInfo.uid);
if (ret >= 0) {
recovered = true;
String msg = "Package " + pkg.packageName
+ " unexpectedly changed to uid 0; recovered to " +
+ pkg.applicationInfo.uid;
reportSettingsProblem(Log.WARN, msg);
}
}
//系統APK需要刪除Data目錄後重新創建
if (!recovered && ((parseFlags&PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM) != 0
|| (scanMode&SCAN_BOOTING) != 0)) {
// If this is a system app, we can at least delete its
// current data so the application will still work.
int ret = removeDataDirsLI(pkgName);
if (ret >= 0) {
// TODO: Kill the processes first
// Old data gone!
String prefix = (parseFlags&PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM) != 0
? "System package " : "Third party package ";
String msg = prefix + pkg.packageName
+ " has changed from uid: "
+ currentUid + " to "
+ pkg.applicationInfo.uid + "; old data erased";
reportSettingsProblem(Log.WARN, msg);
recovered = true;
// And now re-install the app.
ret = createDataDirsLI(pkgName, pkg.applicationInfo.uid,
pkg.applicationInfo.seinfo);
if (ret == -1) {
// Ack should not happen!
msg = prefix + pkg.packageName
+ " could not have data directory re-created after delete.";
reportSettingsProblem(Log.WARN, msg);
mLastScanError = PackageManager.INSTALL_FAILED_INSUFFICIENT_STORAGE;
return null;
}
}
if (!recovered) {
mHasSystemUidErrors = true;
}
} else if (!recovered) {
// If we allow this install to proceed, we will be broken.
// Abort, abort!
mLastScanError = PackageManager.INSTALL_FAILED_UID_CHANGED;
return null;
}
if (!recovered) {
pkg.applicationInfo.dataDir = "/mismatched_uid/settings_"
+ pkg.applicationInfo.uid + "/fs_"
+ currentUid;
pkg.applicationInfo.nativeLibraryDir = pkg.applicationInfo.dataDir;
String msg = "Package " + pkg.packageName
+ " has mismatched uid: "
+ currentUid + " on disk, "
+ pkg.applicationInfo.uid + " in settings";
// writer
synchronized (mPackages) {
mSettings.mReadMessages.append(msg);
mSettings.mReadMessages.append('\n');
uidError = true;
if (!pkgSetting.uidError) {
reportSettingsProblem(Log.ERROR, msg);
}
}
}
}
pkg.applicationInfo.dataDir = dataPath.getPath();
//如果需要恢復seinfo執行恢復操作
if (mShouldRestoreconData) {
Slog.i(TAG, "SELinux relabeling of " + pkg.packageName + " issued.");
mInstaller.restoreconData(pkg.packageName, pkg.applicationInfo.seinfo,
pkg.applicationInfo.uid);
}
} else {
//如果應用數據存儲路徑不存在則直接創建
if (DEBUG_PACKAGE_SCANNING) {
if ((parseFlags & PackageParser.PARSE_CHATTY) != 0)
Log.v(TAG, "Want this data dir: " + dataPath);
}
//invoke installer to do the actual installation
int ret = createDataDirsLI(pkgName, pkg.applicationInfo.uid,
pkg.applicationInfo.seinfo);
if (ret < 0) {
// Error from installer
mLastScanError = PackageManager.INSTALL_FAILED_INSUFFICIENT_STORAGE;
return null;
}
if (dataPath.exists()) {
pkg.applicationInfo.dataDir = dataPath.getPath();
} else {
Slog.w(TAG, "Unable to create data directory: " + dataPath);
pkg.applicationInfo.dataDir = null;
}
}
/*
* Set the data dir to the default "/data/data//lib"
* if we got here without anyone telling us different (e.g., apps
* stored on SD card have their native libraries stored in the ASEC
* container with the APK).
*
* This happens during an upgrade from a package settings file that
* doesn't have a native library path attribute at all.
*/
if (pkg.applicationInfo.nativeLibraryDir == null && pkg.applicationInfo.dataDir != null) {
if (pkgSetting.nativeLibraryPathString == null) {
setInternalAppNativeLibraryPath(pkg, pkgSetting);
} else {
pkg.applicationInfo.nativeLibraryDir = pkgSetting.nativeLibraryPathString;
}
}
pkgSetting.uidError = uidError;
}
String path = scanFile.getPath();
/* Note: We don't want to unpack the native binaries for
* system applications, unless they have been updated
* (the binaries are already under /system/lib).
* Also, don't unpack libs for apps on the external card
* since they should have their libraries in the ASEC
* container already.
*
* In other words, we're going to unpack the binaries
* only for non-system apps and system app upgrades.
*/
if (pkg.applicationInfo.nativeLibraryDir != null) {
//這裡面的操作針對APK的本地Lib文件的處理,包括拷貝文件以及對CPU ABI支持進行判斷
}
pkg.mScanPath = path;
if ((scanMode&SCAN_BOOTING) == 0 && pkgSetting.sharedUser != null) {
// We don't do this here during boot because we can do it all
// at once after scanning all existing packages.
//
// We also do this *before* we perform dexopt on this package, so that
// we can avoid redundant dexopts, and also to make sure we've got the
// code and package path correct.
if (!adjustCpuAbisForSharedUserLPw(pkgSetting.sharedUser.packages,
pkg, forceDex, (scanMode & SCAN_DEFER_DEX) != 0)) {
mLastScanError = PackageManager.INSTALL_FAILED_CPU_ABI_INCOMPATIBLE;
return null;
}
}
//進行odex的優化
if ((scanMode&SCAN_NO_DEX) == 0) {
if (performDexOptLI(pkg, forceDex, (scanMode&SCAN_DEFER_DEX) != 0, false)
== DEX_OPT_FAILED) {
mLastScanError = PackageManager.INSTALL_FAILED_DEXOPT;
return null;
}
}
if (mFactoryTest && pkg.requestedPermissions.contains(
android.Manifest.permission.FACTORY_TEST)) {
pkg.applicationInfo.flags |= ApplicationInfo.FLAG_FACTORY_TEST;
}
ArrayList clientLibPkgs = null;
// writer
synchronized (mPackages) {
if ((pkg.applicationInfo.flags&ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM) != 0) {
// Only system apps can add new shared libraries.
if (pkg.libraryNames != null) {
for (int i=0; i UNAVAILABLE");
}
final int[] uidArray = new int[] { pkg.applicationInfo.uid };
final ArrayList pkgList = new ArrayList(1);
pkgList.add(pkg.applicationInfo.packageName);
sendResourcesChangedBroadcast(false, true, pkgList, uidArray, null);
}
// Post the request that it be killed now that the going-away broadcast is en route
killApplication(pkg.applicationInfo.packageName,
pkg.applicationInfo.uid, "update pkg");
}
// Also need to kill any apps that are dependent on the library.
if (clientLibPkgs != null) {
for (int i=0; i
總結一下這個過程,就是先檢查APK的合法性,包括文件合法性和簽名驗證;然後是對data的數據目錄做對應的處理,對lib目錄進行處理;下來是進行odex的優化;再接下來是重啟進程和通知資源改變;最後就是將安裝的APK的所有基本信息保存到服務的各類全局變量中,以便在系統運行時進行獲取和處理。解析成功之後,還需要更新一下Settings這個東東,這裡面干了不好有效的事情呢。注意一下這裡有兩個安裝的狀態:PKG_INSTALL_INCOMPLETE和PKG_INSTALL_COMPLETE兩種,沒有把dex文件移動成功還是會失敗的喲。下面把grantPermissionsLPw單獨拿出來看看。
private void updateSettingsLI(PackageParser.Package newPackage, String installerPackageName,
int[] allUsers, boolean[] perUserInstalled,
PackageInstalledInfo res) {
String pkgName = newPackage.packageName;
synchronized (mPackages) {
//write settings. the installStatus will be incomplete at this stage.
//note that the new package setting would have already been
//added to mPackages. It hasn't been persisted yet.
mSettings.setInstallStatus(pkgName, PackageSettingBase.PKG_INSTALL_INCOMPLETE);
mSettings.writeLPr();
}
if ((res.returnCode = moveDexFilesLI(newPackage))
!= PackageManager.INSTALL_SUCCEEDED) {
// Discontinue if moving dex files failed.
return;
}
if (DEBUG_INSTALL) Slog.d(TAG, "New package installed in " + newPackage.mPath);
synchronized (mPackages) {
updatePermissionsLPw(newPackage.packageName, newPackage,
UPDATE_PERMISSIONS_REPLACE_PKG | (newPackage.permissions.size() > 0
? UPDATE_PERMISSIONS_ALL : 0));
// For system-bundled packages, we assume that installing an upgraded version
// of the package implies that the user actually wants to run that new code,
// so we enable the package.
if (isSystemApp(newPackage)) {
// NB: implicit assumption that system package upgrades apply to all users
if (DEBUG_INSTALL) {
Slog.d(TAG, "Implicitly enabling system package on upgrade: " + pkgName);
}
PackageSetting ps = mSettings.mPackages.get(pkgName);
if (ps != null) {
if (res.origUsers != null) {
for (int userHandle : res.origUsers) {
ps.setEnabled(COMPONENT_ENABLED_STATE_DEFAULT,
userHandle, installerPackageName);
}
}
// Also convey the prior install/uninstall state
if (allUsers != null && perUserInstalled != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < allUsers.length; i++) {
if (DEBUG_INSTALL) {
Slog.d(TAG, " user " + allUsers[i]
+ " => " + perUserInstalled[i]);
}
ps.setInstalled(perUserInstalled[i], allUsers[i]);
}
// these install state changes will be persisted in the
// upcoming call to mSettings.writeLPr().
}
}
}
res.name = pkgName;
res.uid = newPackage.applicationInfo.uid;
res.pkg = newPackage;
mSettings.setInstallStatus(pkgName, PackageSettingBase.PKG_INSTALL_COMPLETE);
mSettings.setInstallerPackageName(pkgName, installerPackageName);
res.returnCode = PackageManager.INSTALL_SUCCEEDED;
//to update install status
mSettings.writeLPr();
}
} private void grantPermissionsLPw(PackageParser.Package pkg, boolean replace) {
final PackageSetting ps = (PackageSetting) pkg.mExtras;
if (ps == null) {
return;
}
final GrantedPermissions gp = ps.sharedUser != null ? ps.sharedUser : ps;
HashSet origPermissions = gp.grantedPermissions;
boolean changedPermission = false;
//如果是替換的話,先要保存原始的權限,然後清空。
if (replace) {
ps.permissionsFixed = false;
if (gp == ps) {
origPermissions = new HashSet(gp.grantedPermissions);
gp.grantedPermissions.clear();
gp.gids = mGlobalGids;
}
}
if (gp.gids == null) {
gp.gids = mGlobalGids;
}
//這裡是列出了所有當前應用請求授予的權限
final int N = pkg.requestedPermissions.size();
for (int i=0; i更新Settings中各個APK的信息和狀態,這些會同步寫到 "data/system/packages.xml"、"packages-backup.xml")、 "packages.list")、"packages-stopped.xml")和 "packages-stopped-backup.xml"幾個系統配置文件中。其中比較重要的grantPermissionsLPw()拿出來看看,這裡是進行APK權限的授予,包括普通權限的直接授予,特殊權限的組(簽名)認證以及同組權限的共享。
Android在linux UID之上的權限管理及安全的核心就在這裡,主要是簽名、用戶組和權限級別控制,那麼它們之間有哪些關系了,這一部分我們單獨拿出來說一下:從ShareUserSettings和GrantedPermissions類的構成就可以看出一二了。用戶組在Android上的本質上就是一系列被授予權限集合的概念(當然了,它包含的UID是linux的用戶管理機制),可以用很多的Package采用相同的用戶組,並且它們必須具有相同的數字簽名。
final class SharedUserSetting extends GrantedPermissions {
final String name;
int userId;
// flags that are associated with this uid, regardless of any package flags
int uidFlags;
final HashSet packages = new HashSet();
final PackageSignatures signatures = new PackageSignatures();
SharedUserSetting(String _name, int _pkgFlags) {
super(_pkgFlags);
uidFlags = _pkgFlags;
name = _name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "SharedUserSetting{" + Integer.toHexString(System.identityHashCode(this)) + " "
+ name + "/" + userId + "}";
}
void removePackage(PackageSetting packageSetting) {
if (packages.remove(packageSetting)) {
// recalculate the pkgFlags for this shared user if needed
if ((this.pkgFlags & packageSetting.pkgFlags) != 0) {
int aggregatedFlags = uidFlags;
for (PackageSetting ps : packages) {
aggregatedFlags |= ps.pkgFlags;
}
setFlags(aggregatedFlags);
}
}
}
void addPackage(PackageSetting packageSetting) {
if (packages.add(packageSetting)) {
setFlags(this.pkgFlags | packageSetting.pkgFlags);
}
}
}
class GrantedPermissions {
int pkgFlags;
HashSet grantedPermissions = new HashSet();
int[] gids;
GrantedPermissions(int pkgFlags) {
setFlags(pkgFlags);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
GrantedPermissions(GrantedPermissions base) {
pkgFlags = base.pkgFlags;
grantedPermissions = (HashSet) base.grantedPermissions.clone();
if (base.gids != null) {
gids = base.gids.clone();
}
}
void setFlags(int pkgFlags) {
this.pkgFlags = pkgFlags
& (ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM
| ApplicationInfo.FLAG_PRIVILEGED
| ApplicationInfo.FLAG_FORWARD_LOCK
| ApplicationInfo.FLAG_EXTERNAL_STORAGE);
}
}
另外網上還有兩個經典的觀點這裡也摘過來,這都是上面分析可以得出的:
1、 兩個程序有相同的UID,並不意味著它們會運行在同一個進程中。一個程序運行在哪一個進程,一般是由它的Package名稱和UID來決定的,也就是說,UID相同但是Package名稱不同的兩個程序是運行兩個不同的進程中的(相同的UID和簽名並包名相同會覆蓋安裝)。這一點你可以看一下這篇文章:http://blog.csdn.net/luoshengyang/article/details/6689748
2、 給每一個程序都分配一個UID是用來控制權限的,因此,兩個程序具有相同的UID,就意味它們有相同的權限,可以進行資源共享。相同UID的資源共享只是針對linux文件系統的訪問權控制,不同進程間的數據是無法共享訪問的。
前面還有個細節問題在看的過程中忽略了,應用權限聲明和授予權限是如何生效的呢?其實對服務來說,權限只是一個字符串而已,一種是Framework定義好了的(其實也是系統應用或者服務要檢查用到了才定義),比如讀寫外部存儲的權限等等,還有一種是應用申明的(申明時還可以帶上權限的級別)。所有這些權限都會保存在settings中,然後呢,權限都有一個級別的概念,對於普通和以下級別權限只要應用在manifest文件中寫上並且在settings中有就可以授予,危險級別的就需要系統APK和簽名咯才會授予。至於具體起作用其實是在應用請求時會去比對當前請求是否需要權限並且你這個應用是否被授予了這種權限。很多地方都有類似於checkPermission的方法,最終都會調用到ActivityManager中的checkComponentPermission()這個方法。
/** @hide */
public static int checkComponentPermission(String permission, int uid,
int owningUid, boolean exported) {
// Root, system server get to do everything.
if (uid == 0 || uid == Process.SYSTEM_UID) {
return PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED;
}
// Isolated processes don't get any permissions.
if (UserHandle.isIsolated(uid)) {
return PackageManager.PERMISSION_DENIED;
}
// If there is a uid that owns whatever is being accessed, it has
// blanket access to it regardless of the permissions it requires.
if (owningUid >= 0 && UserHandle.isSameApp(uid, owningUid)) {
return PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED;
}
// If the target is not exported, then nobody else can get to it.
if (!exported) {
return PackageManager.PERMISSION_DENIED;
}
if (permission == null) {
return PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED;
}
try {
return AppGlobals.getPackageManager()
.checkUidPermission(permission, uid);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// Should never happen, but if it does... deny!
Slog.e(TAG, "PackageManager is dead?!?", e);
}
return PackageManager.PERMISSION_DENIED;
}最終還是調用到了PackageManagerService中的checkUidPermission方法:
@Override
public int checkUidPermission(String permName, int uid) {
synchronized (mPackages) {
Object obj = mSettings.getUserIdLPr(UserHandle.getAppId(uid));
if (obj != null) {
GrantedPermissions gp = (GrantedPermissions)obj;
if (gp.grantedPermissions.contains(permName)) {
return PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED;
}
} else {
HashSet perms = mSystemPermissions.get(uid);
if (perms != null && perms.contains(permName)) {
return PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED;
}
}
}
return PackageManager.PERMISSION_DENIED;
} 看到了吧,最終還是看gp.grantedPermissions中有沒有這個字符串的問題,這跟前面授予權限就對應上了吧。
這兩篇說的東西都很雜,看完對包管理服務框架還是沒有什麼整體的認識,接下來我就要在下篇開始站高度啦,開始講講整體架構。
 Android應用性能優化之使用SparseArray替代HashMap
Android應用性能優化之使用SparseArray替代HashMap
一、概述最近在項目中看到了SparseArray,好奇研究了下。 SparseArray是Android框架獨有的類,在標准的JDK中不存在這個類。它要比 HashMap
 刷機精靈adb怎麼刷機
刷機精靈adb怎麼刷機
很多人在用刷機精靈最新版時,除了看到很多確實可以用到的功能,也發現了一個根本沒想過會去用也並不了解的功能,那就是adb命令工具。如果你在刷機過程中有點閱歷,
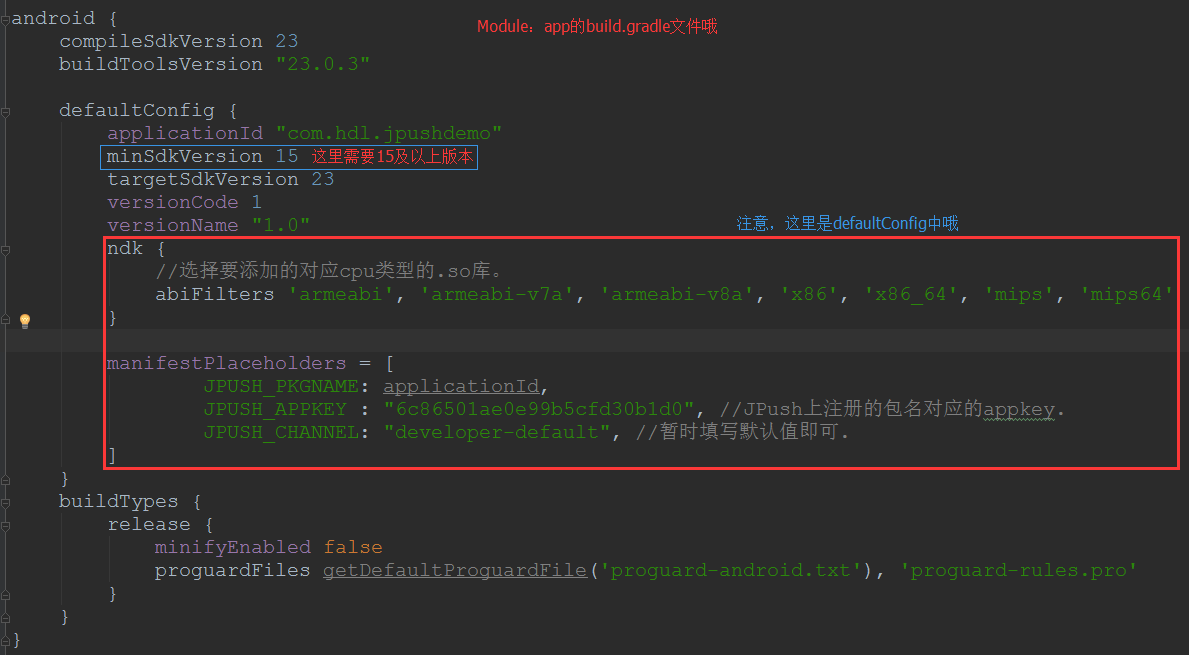 【快速搞定】2分鐘搞定極光推送(極光推送Android端集成)
【快速搞定】2分鐘搞定極光推送(極光推送Android端集成)
一、前言2分鐘只是一個虛數哈,不過只要你速度快,兩分鐘還真是能搞定的哦。在2.1.8版本以前,極光的配置還是非常麻煩的,需要在清單文件(AndroidManifest.x
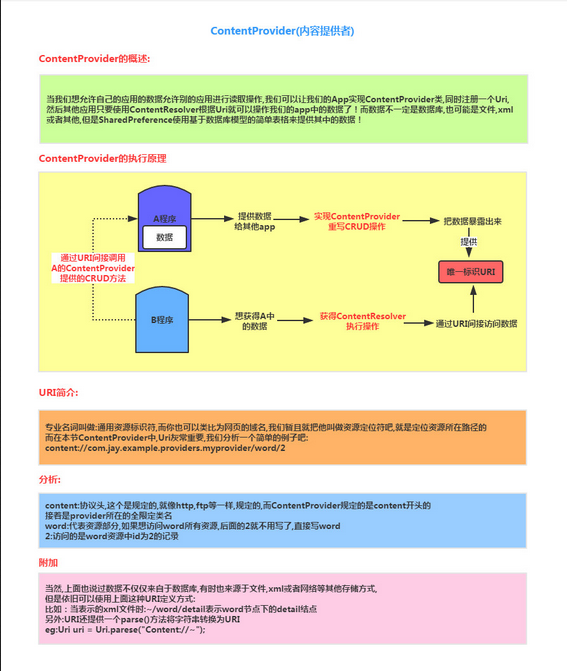 Android四大組件之ContentProvider(上)
Android四大組件之ContentProvider(上)
(一)概述本節給大家帶來的是Android四大組件中的最後一個——ContentProvider(內容提供者),可能部分讀者 有疑問了,&rdqu