編輯:關於Android編程
Android系統中很早就有耗電量的API,只不過一直都是隱藏的,Android系統的設置-電池功能就是調用的這個API,該API的核心部分是調用了com.android.internal.os.BatteryStatsHelper類,利用PowerProfile類,讀取power_profile.xml文件,我們一起來看看具體如何計算耗電量,首先從最新版本6.0開始看
BatteryStatsHelper
其中計算耗電量的方法為490行的processAppUsage,下來一步一步來解釋該方法。
private void processAppUsage(SparseArray asUsers) {
方法的參數是一個SparseArray數組,存儲的對象是UserHandle,官方文檔給出的解釋是,代表一個用戶,可以理解為這個類裡面存儲了用戶的相關信息.
final boolean forAllUsers = (asUsers.get(UserHandle.USER_ALL) != null);
然後判斷該次計算是否針對所有用戶,通過UserHandle的USER_ALL值來判斷,該值為-1,源碼的地址在https://github.com/DoctorQ/platform_frameworks_base/blob/android-6.0.0_r1/core/java/android/os/UserHandle.java.
mStatsPeriod = mTypeBatteryRealtime;
然後給公共變量int類型的mStatsPeriod賦值,這個值mTypeBatteryRealtime的計算過程又在320行的refreshStats方法中:
mTypeBatteryRealtime = mStats.computeBatteryRealtime(rawRealtimeUs, mStatsType);
這裡面用到了BatteryStats(mStats)類中的computeBatteryRealtime方法,該方法計算出此次統計電量的時間間隔。好,歪樓了,回到BatteryStatsHelper中。
BatterySipper osSipper = null;
final SparseArray uidStats = mStats.getUidStats();
final int NU = uidStats.size();
首先創建一個BatterySipper對象osSipper,該對象裡面可以存儲一些後續我們要計算的值,然後通過BatteryStats類對象mStats來得到一個包含Uid的對象的SparseArray組數,然後計算了一下這個數組的大小,保存在變量NU中。
for (int iu = 0; iu < NU; iu++) {
final Uid u = uidStats.valueAt(iu);
final BatterySipper app = new BatterySipper(BatterySipper.DrainType.APP, u, 0);
然後for循環計算每個Uid代表的App的耗電量,因為BatterySipper可計算的類型有三種:應用, 系統服務, 硬件類型,所以這個地方傳入的是DrainType.APP,還有其他可選類型如下:
public enum DrainType {
IDLE,
CELL,
PHONE,
WIFI,
BLUETOOTH,
FLASHLIGHT,
SCREEN,
APP,
USER,
UNACCOUNTED,
OVERCOUNTED,
CAMERA
}
列舉了目前可計算耗電量的模塊。
mCpuPowerCalculator.calculateApp(app, u, mRawRealtime, mRawUptime, mStatsType);
mWakelockPowerCalculator.calculateApp(app, u, mRawRealtime, mRawUptime, mStatsType);
mMobileRadioPowerCalculator.calculateApp(app, u, mRawRealtime, mRawUptime, mStatsType);
mWifiPowerCalculator.calculateApp(app, u, mRawRealtime, mRawUptime, mStatsType);
mBluetoothPowerCalculator.calculateApp(app, u, mRawRealtime, mRawUptime, mStatsType);
mSensorPowerCalculator.calculateApp(app, u, mRawRealtime, mRawUptime, mStatsType);
mCameraPowerCalculator.calculateApp(app, u, mRawRealtime, mRawUptime, mStatsType);
mFlashlightPowerCalculator.calculateApp(app, u, mRawRealtime, mRawUptime, mStatsType);
其中mStatsType的值為BatteryStats.STATS_SINCE_CHARGED,代表了我們的計算規則是從上次充滿電後數據,還有一種規則是STATS_SINCE_UNPLUGGED是拔掉USB線後的數據。而mRawRealtime是當前時間,mRawUptime是運行時間。6.0的對各個模塊的消耗都交給了單獨的類去計算,這些類都繼承於PowerCalculator抽象類:
藍牙耗電:BluetoothPowerCalculator.java
攝像頭耗電:CameraPowerCalculator.java
Cpu耗電:CpuPowerCalculator.java
手電筒耗電:FlashlightPowerCalculator.java
無線電耗電:MobileRadioPowerCalculator.java
傳感器耗電:SensorPowerCalculator.java
Wakelock耗電:WakelockPowerCalculator.java
Wifi耗電:WifiPowerCalculator.java
這一部分我一會單獨拿出來挨個解釋,現在我們還是回到BatteryStatsHelper繼續往下走
final double totalPower = app.sumPower();
BatterySipper#sumPower方法是統計總耗電量,方法詳情如下,其中usagePowerMah這個值有點特殊,其他的上面都講過.
/**
* Sum all the powers and store the value into `value`.
* @return the sum of all the power in this BatterySipper.
*/
public double sumPower() {
return totalPowerMah = usagePowerMah + wifiPowerMah + gpsPowerMah + cpuPowerMah +
sensorPowerMah + mobileRadioPowerMah + wakeLockPowerMah + cameraPowerMah +
flashlightPowerMah;
}
然後根據是否是DEBUG版本打印信息,這個沒啥可說的,然後會把剛才計算的電量值添加到列表中:
// Add the app to the list if it is consuming power.
if (totalPower != 0 || u.getUid() == 0) {
//
// Add the app to the app list, WiFi, Bluetooth, etc, or into Other Users list.
//
final int uid = app.getUid();
final int userId = UserHandle.getUserId(uid);
if (uid == Process.WIFI_UID) {
mWifiSippers.add(app);
} else if (uid == Process.BLUETOOTH_UID) {
mBluetoothSippers.add(app);
} else if (!forAllUsers && asUsers.get(userId) == null
&& UserHandle.getAppId(uid) >= Process.FIRST_APPLICATION_UID) {
// We are told to just report this user's apps as one large entry.
List list = mUserSippers.get(userId);
if (list == null) {
list = new ArrayList<>();
mUserSippers.put(userId, list);
}
list.add(app);
} else {
mUsageList.add(app);
}
if (uid == 0) {
osSipper = app;
}
}
首先判斷totalPower的值和當前uid號是否符合規則,規則為總耗電量不為0或者用戶id為0.當uid表明為WIFI或者藍牙時,添加到下面對應的列表中,一般情況下正常的應用我們直接保存到下面的mUsageList中就行就行,但是也有一些例外:
/**
* List of apps using power.
*/
private final List mUsageList = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* List of apps using wifi power.
*/
private final List mWifiSippers = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* List of apps using bluetooth power.
*/
private final List mBluetoothSippers = new ArrayList<>();
如果我們的系統是單用戶系統,且當前的userId號不在我們的統計范圍內,且其進程id號是大於Process.FIRST_APPLICATION_UID(10000,系統分配給普通應用的其實id號),我們就要將其存放到mUserSippers數組中,定義如下:
private final SparseArray> mUserSippers = new SparseArray<>();
最後判斷uid為0的話,代表是Android操作系統的耗電量,賦值給osSipper(494行定義)就可以了,這樣一個app的計算就完成了,遍歷部分就不說了,保存這個osSipper是為了最後一步計算:
if (osSipper != null) {
// The device has probably been awake for longer than the screen on
// time and application wake lock time would account for. Assign
// this remainder to the OS, if possible.
mWakelockPowerCalculator.calculateRemaining(osSipper, mStats, mRawRealtime,
mRawUptime, mStatsType);
osSipper.sumPower();
}
主流程我們已經介紹完了,下面來看各個子模塊耗電量的計算
CpuPowerCalculator.java
Cpu的計算要用到PowerProfile類,該類主要是解析power_profile.xml:
- 0
- 0.1
- 0.1
- 0.1
- 0.1
- 0.1
- 0.1
- 0.1
- 0.1
- 0.1
- 0.1
- 0.1
- 0.1
- 0.1
- 0.1
0.2
0.1
400000
- 0.1
0.1
- 1000
.0002
.002
.02
.2
2
這個裡面存儲了Cpu(cpu.speeds)的主頻等級,以及每個主頻每秒消耗的毫安(cpu.active),好,現在回到CpuPowerCalculator中,先來看構造方法
public CpuPowerCalculator(PowerProfile profile) {
final int speedSteps = profile.getNumSpeedSteps();
mPowerCpuNormal = new double[speedSteps];
mSpeedStepTimes = new long[speedSteps];
for (int p = 0; p < speedSteps; p++) {
mPowerCpuNormal[p] = profile.getAveragePower(PowerProfile.POWER_CPU_ACTIVE, p);
}
}
第一步獲得Cpu有幾個主頻等級,因為不同等級消耗的電量不一樣,所以要區別對待,根據主頻的個數,然後初始化mPowerCpuNormal和mSpeedStepTimes,前者用來保存不同等級的耗電速度,後者用來保存在不同等級上耗時,然後給mPowerCpuNormal的每個元素附上值。構造方法就完成了其所有的工作,現在來計算方法calculateApp,
final int speedSteps = mSpeedStepTimes.length;
long totalTimeAtSpeeds = 0;
for (int step = 0; step < speedSteps; step++) {
mSpeedStepTimes[step] = u.getTimeAtCpuSpeed(step, statsType);
totalTimeAtSpeeds += mSpeedStepTimes[step];
}
totalTimeAtSpeeds = Math.max(totalTimeAtSpeeds, 1);
首先得到Cpu主頻等級個數,然後BatteryStats.Uid得到不同主頻上執行時間,計算Cpu總耗時保存在totalTimeAtSpeeds中,
app.cpuTimeMs = (u.getUserCpuTimeUs(statsType) + u.getSystemCpuTimeUs(statsType)) / 1000;
Cpu的執行時間分很多部分,但是我們關注User和Kernal部分,也就是上面的SystemCpuTime,
 Android開發之Drag&Drop框架實現拖放手勢
Android開發之Drag&Drop框架實現拖放手勢
Android3.0提供了drag/drop框架,利用此框架可以實現使用拖放手勢將一個view拖放到當前布局中的另外一個view中。本文將介紹如何使用拖放框架。 一、實
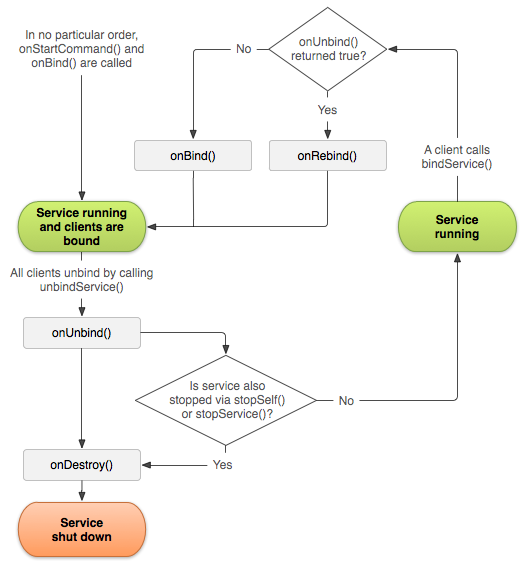 Android官方文檔之Bound Services
Android官方文檔之Bound Services
綁定式Service在CS結構中扮演著Server的角色。綁定式Service允許其他組件(如Activity)綁定該Service、發送請求、接收響應、甚至IPC通信(
 在 Android* 商務應用中實施地圖和地理圍欄特性
在 Android* 商務應用中實施地圖和地理圍欄特性
摘要 本案例研究討論了如何將地圖和地理定位特性構建到 Android* 商務應用中,包括在 Google Maps* 上覆蓋商店位置,以及在設備進入商店地理圍欄鄰近區
 qq厘米秀挑戰厘米神搶手怎麼玩
qq厘米秀挑戰厘米神搶手怎麼玩
QQ厘米秀是騰訊手機QQ新出的功能,玩家在手機QQ聊天中可以放上自己的厘米秀,也能發很多特定的帶有聲音的表情。QQ厘米秀讓用戶在手機QQ聊天中更有趣,而且目