編輯:關於Android編程
其實寫分析源碼文章總會顯得很復雜很乏味,但是梳理自己看源碼時的一些總結也是一種提高。這篇博客分析下Activity啟動過程源碼,我會盡量說得簡單點。個人的觀點是看源碼不能看得太細,否則就會花費很多時間並很難理清整個過程。所以本次分析重在理清activity的一個啟動流程。
首先大概總結下activity啟動的整個流程,這個過程涉及到Instrumentation,ActivityThread,和ActivityManagerService(AMS)。通過Binder向AMS發請求,AMS內部有一個ActivityStack,它負責棧內的Activity同步,AMS去通過ActivityThread去調用Activity的生命周期方法完成Activity的啟動。如果對Binder進程間通信不了解可看下IPC——android進程間通信
先上一張總圖,等看完博客可以再回頭來看下這圖:
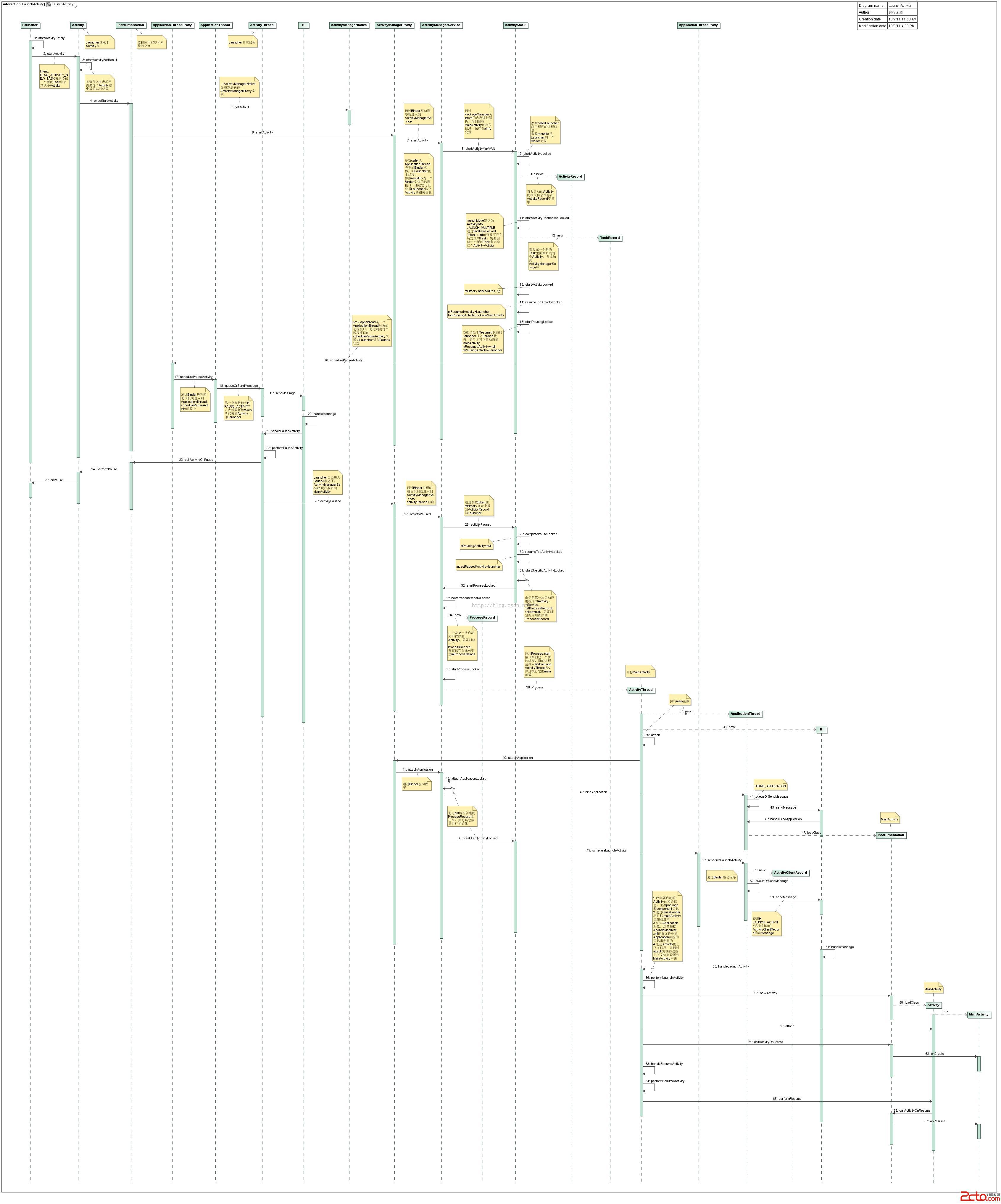
啟動一個activity最常用的方法就是startActivityForResult或者startActivity,而startActivity也是調用startActivityForResult,所以此次分析入口當然是startActivityForResult。
public void startActivityForResult(Intent intent, int requestCode, @Nullable Bundle options) {
if (mParent == null) {
Instrumentation.ActivityResult ar =
mInstrumentation .execStartActivity(
this, mMainThread .getApplicationThread() , mToken, this,
intent, requestCode, options) ;
if (ar != null) {
mMainThread .sendActivityResult(
mToken, mEmbeddedID, requestCode , ar.getResultCode(),
ar.getResultData());
}
if (requestCode >= 0) {
// If this start is requesting a result, we can avoid making
// the activity visible until the result is received. Setting
// this code during onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) or onResume() will keep the
// activity hidden during this time, to avoid flickering.
// This can only be done when a result is requested because
// that guarantees we will get information back when the
// activity is finished, no matter what happens to it.
mStartedActivity = true;
}
final View decor = mWindow != null ? mWindow .peekDecorView() : null;
if (decor != null) {
decor.cancelPendingInputEvents();
}
// TODO Consider clearing/flushing other event sources and events for child windows.
} else {
if (options != null) {
mParent .startActivityFromChild( this, intent, requestCode, options) ;
} else {
// Note we want to go through this method for compatibility with
// existing applications that may have overridden it.
mParent .startActivityFromChild( this, intent, requestCode);
}
}
if (options != null && !isTopOfTask()) {
mActivityTransitionState .startExitOutTransition( this, options);
}
}
Intrumentation它用來監控應用程序和系統的交互。而mMainThread.getApplicationThread()獲取ApplicationThread,它是ActivityThread的一個內部類,是一個Binder對象,後面我們會看到,ActivityManagerService會使用它來和ActivityThread來進行進程間通信。上面的代碼最終調用了execStartActivity方法。
public ActivityResult execStartActivity(
Context who, IBinder contextThread, IBinder token , Activity target,
Intent intent , int requestCode, Bundle options) {
IApplicationThread whoThread = (IApplicationThread) contextThread;
if ( mActivityMonitors != null ) {
synchronized (mSync) {
final int N = mActivityMonitors.size() ;
for ( int i=0 ; i= 0 ? am.getResult() : null;
}
break;
}
}
}
}
try {
intent.migrateExtraStreamToClipData();
intent.prepareToLeaveProcess() ;
int result = ActivityManagerNative. getDefault()
.startActivity(whoThread, who.getBasePackageName() , intent,
intent.resolveTypeIfNeeded(who.getContentResolver()),
token, target != null ? target.mEmbeddedID : null,
requestCode, 0, null, options) ;
checkStartActivityResult(result, intent) ;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
return null;
}
這裡的intent.resolveTypeIfNeeded返回這個intent的MIME類型,如果沒有在AndroidManifest.xml設置MainActivity的MIME類型那就返回null。啟動的真正實現類由ActivityManagerNative.getDefault()的startActivity方法完成。先分析下ActivityManagerNative.getDefault()。
public abstract class ActivityManagerNative extends Binder implements IActivityManager{
…………
private static final Singleton gDefault = new Singleton() {
protected IActivityManager create() {
IBinder b = ServiceManager.getService("activity") ;
if ( false) {
Log.v ("ActivityManager" , "default service binder = " + b);
}
IActivityManager am = asInterface (b);
if ( false) {
Log.v ("ActivityManager" , "default service = " + am);
}
return am;
}
};
}
可以看到ActivityManagerNative是一個抽象類,它繼承Binder,並實現了IActivityManager接口,ActivityManagerService(下稱AMS)繼承著ActivityManagerNative,所以它是IActivityManager的具體實現類。ActivityManagerNative.getDefault是一個IActivityManager類型的Binder對象,因此它的具體實現是AMS。獲取的AMS的Binder對象是一個單例。ActivityManagerNative就相當於AIDL文件自動生成的那個類。ActivityManagerProxy是ActivityManagerNative中的一個代理方法,看下它的startActivity代碼:
class ActivityManagerProxy implements IActivityManager
{
public ActivityManagerProxy(IBinder remote)
{
mRemote = remote;
}
public IBinder asBinder()
{
return mRemote;
}
public int startActivity(IApplicationThread caller, String callingPackage, Intent intent,
String resolvedType, IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode,
int startFlags, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle options) throws RemoteException {
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
Parcel reply = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken(IActivityManager.descriptor);
data.writeStrongBinder(caller != null ? caller.asBinder() : null);
data.writeString(callingPackage);
intent.writeToParcel(data, 0);
data.writeString(resolvedType);
data.writeStrongBinder(resultTo);
data.writeString(resultWho);
data.writeInt(requestCode);
data.writeInt(startFlags);
if (profilerInfo != null) {
data.writeInt(1);
profilerInfo.writeToParcel(data, Parcelable.PARCELABLE_WRITE_RETURN_VALUE);
} else {
data.writeInt(0);
}
if (options != null) {
data.writeInt(1);
options.writeToParcel(data, 0);
} else {
data.writeInt(0);
}
mRemote.transact(START_ACTIVITY_TRANSACTION, data, reply, 0);
reply.readException();
int result = reply.readInt();
reply.recycle();
data.recycle();
return result;
}
public int startActivityAsUser(IApplicationThread caller, String callingPackage, Intent intent,
String resolvedType, IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode,
int startFlags, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle options,
int userId) throws RemoteException {
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
Parcel reply = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken(IActivityManager.descriptor);
data.writeStrongBinder(caller != null ? caller.asBinder() : null);
data.writeString(callingPackage);
intent.writeToParcel(data, 0);
data.writeString(resolvedType);
data.writeStrongBinder(resultTo);
data.writeString(resultWho);
data.writeInt(requestCode);
data.writeInt(startFlags);
if (profilerInfo != null) {
data.writeInt(1);
profilerInfo.writeToParcel(data, Parcelable.PARCELABLE_WRITE_RETURN_VALUE);
} else {
data.writeInt(0);
}
if (options != null) {
data.writeInt(1);
options.writeToParcel(data, 0);
} else {
data.writeInt(0);
}
data.writeInt(userId);
mRemote.transact(START_ACTIVITY_AS_USER_TRANSACTION, data, reply, 0);
reply.readException();
int result = reply.readInt();
reply.recycle();
data.recycle();
return result;
…………
}
看到這就會發現,其實就是AIDL來進行進程間通信。它是真正實現類還應該是AMS中的startActivity。
public int startActivity(IBinder whoThread, String callingPackage,
Intent intent, String resolvedType, Bundle options) {
checkCaller();
int callingUser = UserHandle.getCallingUserId();
TaskRecord tr;
IApplicationThread appThread;
synchronized (ActivityManagerService.this) {
tr = recentTaskForIdLocked(mTaskId);
if (tr == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to find task ID " + mTaskId);
}
appThread = ApplicationThreadNative.asInterface(whoThread);
if (appThread == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Bad app thread " + appThread);
}
}
return mStackSupervisor.startActivityMayWait(appThread, -1, callingPackage, intent,
resolvedType, null, null, null, null, 0, 0, null, null,
null, options, callingUser, null, tr);
}
最後調用了 mStackSupervisor.startActivityMayWait,主要看兩部分: 1.解析Intent。
下面語句對參數intent的內容進行解析,得到MainActivity的相關信息,保存在aInfo變量中:
ActivityInfo aInfo;
try {
ResolveInfo rInfo =
AppGlobals.getPackageManager().resolveIntent(
intent, resolvedType,
PackageManager.MATCH_DEFAULT_ONLY
| ActivityManagerService.STOCK_PM_FLAGS);
aInfo = rInfo != null ? rInfo.activityInfo : null;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
......
}
2.:調用startActivityLocked。
int res = startActivityLocked(caller, intent, resolvedType, aInfo,
voiceSession, voiceInteractor, resultTo, resultWho,
requestCode, callingPid, callingUid, callingPackage,
realCallingPid, realCallingUid, startFlags, options,
componentSpecified, null, container, inTask);
最的返回了startActivityLocked,它在ActivityStackSupervisor中,再看下它的代碼:
final int startActivityLocked(IApplicationThread caller,
Intent intent, String resolvedType, ActivityInfo aInfo,
IVoiceInteractionSession voiceSession, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,
IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode,
int callingPid, int callingUid, String callingPackage,
int realCallingPid, int realCallingUid, int startFlags, Bundle options,
boolean componentSpecified, ActivityRecord[] outActivity, ActivityContainer container,
TaskRecord inTask) {
int err = ActivityManager.START_SUCCESS;
ProcessRecord callerApp = null;
if (caller != null) {
callerApp = mService.getRecordForAppLocked(caller);
if (callerApp != null) {
callingPid = callerApp.pid;
callingUid = callerApp.info.uid;
} else {
Slog.w(TAG, "Unable to find app for caller " + caller
+ " (pid=" + callingPid + ") when starting: "
+ intent.toString());
err = ActivityManager.START_PERMISSION_DENIED;
}
}
…………
ActivityRecord sourceRecord = null;
ActivityRecord resultRecord = null;
if (resultTo != null) {
sourceRecord = isInAnyStackLocked(resultTo);
if (DEBUG_RESULTS) Slog.v(
TAG, "Will send result to " + resultTo + " " + sourceRecord);
if (sourceRecord != null) {
if (requestCode >= 0 && !sourceRecord.finishing) {
resultRecord = sourceRecord;
}
}
}
final int launchFlags = intent.getFlags();
if ((launchFlags&Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_FORWARD_RESULT) != 0 && sourceRecord != null) {
// Transfer the result target from the source activity to the new
// one being started, including any failures.
if (requestCode >= 0) {
ActivityOptions.abort(options);
return ActivityManager.START_FORWARD_AND_REQUEST_CONFLICT;
}
resultRecord = sourceRecord.resultTo;
resultWho = sourceRecord.resultWho;
requestCode = sourceRecord.requestCode;
sourceRecord.resultTo = null;
…………
ActivityRecord r = new ActivityRecord(mService, callerApp, callingUid, callingPackage,
intent, resolvedType, aInfo, mService.mConfiguration, resultRecord, resultWho,
requestCode, componentSpecified, this, container, options);
^………………
err = startActivityUncheckedLocked(r, sourceRecord, voiceSession, voiceInteractor,
startFlags, true, options, inTask);
分三步:
1.從傳進來的參數caller得到調用者的進程信息,並保存在callerApp變量中,這裡就是Launcher應用程序的進程信息了。 前面說過,參數resultTo是Launcher這個Activity裡面的一個Binder對象,通過它可以獲得Launcher這個Activity的相關信息,保存在sourceRecord變量中。
final boolean launchSingleTop = r.launchMode == ActivityInfo.LAUNCH_SINGLE_TOP;
final boolean launchSingleInstance = r.launchMode == ActivityInfo.LAUNCH_SINGLE_INSTANCE;
final boolean launchSingleTask = r.launchMode == ActivityInfo.LAUNCH_SINGLE_TASK;
int launchFlags = intent.getFlags();
if ((launchFlags & Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_DOCUMENT) != 0 &&
(launchSingleInstance || launchSingleTask)) {
// We have a conflict between the Intent and the Activity manifest, manifest wins.
Slog.i(TAG, "Ignoring FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_DOCUMENT, launchMode is " +
"\"singleInstance\" or \"singleTask\"");
launchFlags &=
~(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_DOCUMENT | Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_MULTIPLE_TASK);
…………
if (doResume) {
resumeTopActivitiesLocked();
}
ActivityOptions.abort(options);
final boolean resumeTopActivityLocked(ActivityRecord prev, Bundle options) {
if (mStackSupervisor.inResumeTopActivity) {
// Don't even start recursing.
return false;
}
boolean result = false;
try {
// Protect against recursion.
mStackSupervisor.inResumeTopActivity = true;
if (mService.mLockScreenShown == ActivityManagerService.LOCK_SCREEN_LEAVING) {
mService.mLockScreenShown = ActivityManagerService.LOCK_SCREEN_HIDDEN;
mService.updateSleepIfNeededLocked();
}
result = resumeTopActivityInnerLocked(prev, options);
} finally {
mStackSupervisor.inResumeTopActivity = false;
}
return result;
}
通過上面的代碼可知,resumeTopActivitiesLocked調用了resumeTopActivityInnerLocked方法。來看下resumeTopActivityInnerLocked源代碼,由於這部分代碼很長,只貼出它的最主要流程:
if ((mService.mSleeping || mService.mShuttingDown)
&& mLastPausedActivity == next && next.state == ActivityState.PAUSED) {
......
return false;
}
.......
// We need to start pausing the current activity so the top one
// can be resumed...
if (mResumedActivity != null) {
if (mResumedActivity != null) {
if (DEBUG_STATES) Slog.d(TAG, "resumeTopActivityLocked: Pausing " + mResumedActivity);
pausing |= startPausingLocked(userLeaving, false, true, dontWaitForPause);
}
return true;
}
......
if (next.app != null && next.app.thread != null) {
......
} else {
......
startSpecificActivityLocked(next, true, true);
}
return true;
}
由上可以清晰的看到,如果當前activity沒暫停,要先把它暫停。
if (prev.app != null && prev.app.thread != null) {
if (DEBUG_PAUSE) Slog.v(TAG, "Enqueueing pending pause: " + prev);
try {
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.AM_PAUSE_ACTIVITY,
prev.userId, System.identityHashCode(prev),
prev.shortComponentName);
mService.updateUsageStats(prev, false);
prev.app.thread.schedulePauseActivity(prev.appToken, prev.finishing,
userLeaving, prev.configChangeFlags, dontWait);
prev.app.thread是一個ApplicationThread對象的遠程接口,它的類型是IApplicationThread。通過調用這個遠程接口的schedulePauseActivity來通知Activity進入Paused狀態。先看下IApplicationThread接口。
public interface IApplicationThread extends IInterface {
void schedulePauseActivity(IBinder token, boolean finished, boolean userLeaving,
int configChanges, boolean dontReport) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleStopActivity(IBinder token, boolean showWindow,
int configChanges) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleWindowVisibility(IBinder token, boolean showWindow) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleSleeping(IBinder token, boolean sleeping) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleResumeActivity(IBinder token, int procState, boolean isForward, Bundle resumeArgs)
throws RemoteException;
void scheduleSendResult(IBinder token, List results) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleLaunchActivity(Intent intent, IBinder token, int ident,
ActivityInfo info, Configuration curConfig, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo,
String referrer, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor, int procState, Bundle state,
PersistableBundle persistentState, List pendingResults,
List pendingNewIntents, boolean notResumed, boolean isForward,
ProfilerInfo profilerInfo) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleRelaunchActivity(IBinder token, List pendingResults,
List pendingNewIntents, int configChanges,
boolean notResumed, Configuration config) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleNewIntent(List intent, IBinder token) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleDestroyActivity(IBinder token, boolean finished,
int configChanges) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleReceiver(Intent intent, ActivityInfo info, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo,
int resultCode, String data, Bundle extras, boolean sync,
int sendingUser, int processState) throws RemoteException;
static final int BACKUP_MODE_INCREMENTAL = 0;
static final int BACKUP_MODE_FULL = 1;
static final int BACKUP_MODE_RESTORE = 2;
static final int BACKUP_MODE_RESTORE_FULL = 3;
void scheduleCreateBackupAgent(ApplicationInfo app, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo,
int backupMode) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleDestroyBackupAgent(ApplicationInfo app, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo)
throws RemoteException;
void scheduleCreateService(IBinder token, ServiceInfo info,
CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, int processState) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleBindService(IBinder token,
Intent intent, boolean rebind, int processState) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleUnbindService(IBinder token,
Intent intent) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleServiceArgs(IBinder token, boolean taskRemoved, int startId,
int flags, Intent args) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleStopService(IBinder token) throws RemoteException;
static final int DEBUG_OFF = 0;
static final int DEBUG_ON = 1;
static final int DEBUG_WAIT = 2;
void bindApplication(String packageName, ApplicationInfo info, List providers,
ComponentName testName, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle testArguments,
IInstrumentationWatcher testWatcher, IUiAutomationConnection uiAutomationConnection,
int debugMode, boolean openGlTrace, boolean restrictedBackupMode, boolean persistent,
Configuration config, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, Map services,
Bundle coreSettings) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleExit() throws RemoteException;
void scheduleSuicide() throws RemoteException;
void scheduleConfigurationChanged(Configuration config) throws RemoteException;
void updateTimeZone() throws RemoteException;
void clearDnsCache() throws RemoteException;
void setHttpProxy(String proxy, String port, String exclList,
Uri pacFileUrl) throws RemoteException;
void processInBackground() throws RemoteException;
void dumpService(FileDescriptor fd, IBinder servicetoken, String[] args)
throws RemoteException;
void dumpProvider(FileDescriptor fd, IBinder servicetoken, String[] args)
throws RemoteException;
void scheduleRegisteredReceiver(IIntentReceiver receiver, Intent intent,
int resultCode, String data, Bundle extras, boolean ordered,
boolean sticky, int sendingUser, int processState) throws RemoteException;
void scheduleLowMemory() throws RemoteException;
void scheduleActivityConfigurationChanged(IBinder token) throws RemoteException;
void profilerControl(boolean start, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, int profileType)
throws RemoteException;
void dumpHeap(boolean managed, String path, ParcelFileDescriptor fd)
throws RemoteException;
由此猜測它與activity,service的開啟有關。IApplicationThread這個IBind實現者完成了大量和Activity以及service有關的功能。
而ApplicationThreadNative就是它的實現類。
public abstract class ApplicationThreadNative extends Binder
implements IApplicationThread {
/**
* Cast a Binder object into an application thread interface, generating
* a proxy if needed.
*/
static public IApplicationThread asInterface(IBinder obj) {
if (obj == null) {
return null;
}
IApplicationThread in =
(IApplicationThread)obj.queryLocalInterface(descriptor);
if (in != null) {
return in;
}
return new ApplicationThreadProxy(obj);
}
public ApplicationThreadNative() {
attachInterface(this, descriptor);
}
@Override
public boolean onTransact(int code, Parcel data, Parcel reply, int flags)
throws RemoteException {
switch (code) {
case SCHEDULE_PAUSE_ACTIVITY_TRANSACTION:
{
data.enforceInterface(IApplicationThread.descriptor);
IBinder b = data.readStrongBinder();
boolean finished = data.readInt() != 0;
boolean userLeaving = data.readInt() != 0;
int configChanges = data.readInt();
boolean dontReport = data.readInt() != 0;
schedulePauseActivity(b, finished, userLeaving, configChanges, dontReport);
return true;
}
public final void schedulePauseActivity(IBinder token, boolean finished, boolean userLeaving, int configChanges, boolean dontReport) throws RemoteException { Parcel data = Parcel.obtain(); data.writeInterfaceToken(IApplicationThread.descriptor); data.writeStrongBinder(token); data.writeInt(finished ? 1 : 0); data.writeInt(userLeaving ? 1 :0); data.writeInt(configChanges); data.writeInt(dontReport ? 1 : 0); mRemote.transact(SCHEDULE_PAUSE_ACTIVITY_TRANSACTION, data, null, IBinder.FLAG_ONEWAY); data.recycle(); }
………………}
由上可見它就是一個Binder抽象類,ApplicationThreadProxy是代理類。真正實現類是ApplicationThread。直接看ApplicationThread的schedulePauseActivity方法。
public final void schedulePauseActivity(IBinder token, boolean finished,
boolean userLeaving, int configChanges, boolean dontReport) {
sendMessage(
finished ? H.PAUSE_ACTIVITY_FINISHING : H.PAUSE_ACTIVITY,
token,
(userLeaving ? 1 : 0) | (dontReport ? 2 : 0),
configChanges);
}
看到這,就知道接下來肯定是用Handler來發送消息了,發送消息的代碼如下:
private void sendMessage(int what, Object obj, int arg1, int arg2, boolean async) {
if (DEBUG_MESSAGES) Slog.v(
TAG, "SCHEDULE " + what + " " + mH.codeToString(what)
+ ": " + arg1 + " / " + obj);
Message msg = Message.obtain();
msg.what = what;
msg.obj = obj;
msg.arg1 = arg1;
msg.arg2 = arg2;
if (async) {
msg.setAsynchronous(true);
}
mH.sendMessage(msg);
}
就是在發送一個暫停Activity的消息給Handler處理,這個Handler名字為H。H在它的handlerMessage中處理相應的請求,它的實現如下:
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
…………
case PAUSE_ACTIVITY:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "activityPause");
handlePauseActivity((IBinder)msg.obj, false, (msg.arg1&1) != 0, msg.arg2,
(msg.arg1&2) != 0);
maybeSnapshot();
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
…………
}
看下handlePauseActivity的代碼:
private void handlePauseActivity(IBinder token, boolean finished,
boolean userLeaving, int configChanges, boolean dontReport) {
ActivityClientRecord r = mActivities.get(token);
if (r != null) {
//Slog.v(TAG, "userLeaving=" + userLeaving + " handling pause of " + r);
if (userLeaving) {
performUserLeavingActivity(r);
}
r.activity.mConfigChangeFlags |= configChanges;
performPauseActivity(token, finished, r.isPreHoneycomb());
// Make sure any pending writes are now committed.
if (r.isPreHoneycomb()) {
QueuedWork.waitToFinish();
}
// Tell the activity manager we have paused.
if (!dontReport) {
try {
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().activityPaused(token);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
}
}
mSomeActivitiesChanged = true;
}
函數首先將Binder引用token轉換成ActivityRecord的遠程接口ActivityClientRecord,然後做了三個事情:1. 如果userLeaving為true,則通過調用performUserLeavingActivity函數來調用Activity.onUserLeaveHint通知Activity,用戶要離開它了;2. 調用performPauseActivity函數來調用Activity.onPause函數,我們知道,在Activity的生命周期中,當它要讓位於其它的Activity時,系統就會調用它的onPause函數;3. 它通知ActivityManagerService,這個Activity已經進入Paused狀態了,ActivityManagerService現在可以完成未竟的事情,即啟動MainActivity了。
看下ActivityManagerService.activityPaused的代碼:
public final void activityPaused(IBinder token) {
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
synchronized(this) {
ActivityStack stack = ActivityRecord.getStackLocked(token);
if (stack != null) {
stack.activityPausedLocked(token, false);
}
}
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
繞了一大圈又回到了ActivityStack中,調用它的activityPauseLocked方法。
final void activityPausedLocked(IBinder token, boolean timeout) {
if (DEBUG_PAUSE) Slog.v(
TAG, "Activity paused: token=" + token + ", timeout=" + timeout);
final ActivityRecord r = isInStackLocked(token);
if (r != null) {
mHandler.removeMessages(PAUSE_TIMEOUT_MSG, r);
if (mPausingActivity == r) {
if (DEBUG_STATES) Slog.v(TAG, "Moving to PAUSED: " + r
+ (timeout ? " (due to timeout)" : " (pause complete)"));
completePauseLocked(true);
} else {
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.AM_FAILED_TO_PAUSE,
r.userId, System.identityHashCode(r), r.shortComponentName,
mPausingActivity != null
? mPausingActivity.shortComponentName : "(none)");
}
}
}
前一個Activity的信息保存在mPausingActivity中,因此,這裡mPausingActivity等於r,於是,執行completePauseLocked操作。
private void completePauseLocked(boolean resumeNext) {
…………
if (resumeNext) {
final ActivityStack topStack = mStackSupervisor.getFocusedStack();
if (!mService.isSleepingOrShuttingDown()) {
mStackSupervisor.resumeTopActivitiesLocked(topStack, prev, null);
} else {
mStackSupervisor.checkReadyForSleepLocked();
ActivityRecord top = topStack.topRunningActivityLocked(null);
if (top == null || (prev != null && top != prev)) {
// If there are no more activities available to run,
// do resume anyway to start something. Also if the top
// activity on the stack is not the just paused activity,
// we need to go ahead and resume it to ensure we complete
// an in-flight app switch.
mStackSupervisor.resumeTopActivitiesLocked(topStack, null, null);
}
}
}
…………
}
很顯然,又回到了resumeTopActivitiesLocked中,這次activity己經停止,所以它調用了ActivityStackSupervisor的StartSpecificActivityLocked方法。
void startSpecificActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r,
boolean andResume, boolean checkConfig) {
// Is this activity's application already running?
ProcessRecord app = mService.getProcessRecordLocked(r.processName,
r.info.applicationInfo.uid, true);
r.task.stack.setLaunchTime(r);
if (app != null && app.thread != null) {
try {
if ((r.info.flags&ActivityInfo.FLAG_MULTIPROCESS) == 0
|| !"android".equals(r.info.packageName)) {
// Don't add this if it is a platform component that is marked
// to run in multiple processes, because this is actually
// part of the framework so doesn't make sense to track as a
// separate apk in the process.
app.addPackage(r.info.packageName, r.info.applicationInfo.versionCode,
mService.mProcessStats);
}
realStartActivityLocked(r, app, andResume, checkConfig);
return;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Exception when starting activity "
+ r.intent.getComponent().flattenToShortString(), e);
}
// If a dead object exception was thrown -- fall through to
// restart the application.
}
mService.startProcessLocked(r.processName, r.info.applicationInfo, true, 0,
"activity", r.intent.getComponent(), false, false, true);
}
接下來重點看下realStartActivityLocked,它代碼中有以下一段
app.thread.scheduleLaunchActivity(new Intent(r.intent), r.appToken,
System.identityHashCode(r), r.info, new Configuration(mService.mConfiguration),
r.compat, r.launchedFromPackage, r.task.voiceInteractor, app.repProcState,
r.icicle, r.persistentState, results, newIntents, !andResume,
mService.isNextTransitionForward(), profilerInfo);
是不是有種似曾相識的感覺。接下來就是跟暫停一樣了,調用ApplicationThread中的scheduleLaunchActivity,最終調用H中的HandlerMessage。
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
if (DEBUG_MESSAGES) Slog.v(TAG, ">>> handling: " + codeToString(msg.what));
switch (msg.what) {
case LAUNCH_ACTIVITY: {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "activityStart");
final ActivityClientRecord r = (ActivityClientRecord) msg.obj;
r.packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck(
r.activityInfo.applicationInfo, r.compatInfo);
handleLaunchActivity(r, null);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
} break;
………………
再看下handleLaunchActivity()的實現,代碼比較長,只看核心的。
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(
TAG, "Handling launch of " + r);
// Initialize before creating the activity
WindowManagerGlobal.initialize();
Activity a = performLaunchActivity(r, customIntent);
if (a != null) {
r.createdConfig = new Configuration(mConfiguration);
Bundle oldState = r.state;
handleResumeActivity(r.token, false, r.isForward,
!r.activity.mFinished && !r.startsNotResumed);
performLaunchAcitvity中調用Activity的onCreate(),onStart()方法,handlerResumeActivity調用onResume()方法。重點看下performLaunchAcitvity,我們把它拆分來看,它總共完成以下幾個功能。
1.從ActivityClientRecord中獲取待啟動的Activity的組件信息
ActivityInfo aInfo = r.activityInfo;
if (r.packageInfo == null) {
r.packageInfo = getPackageInfo(aInfo.applicationInfo, r.compatInfo,
Context.CONTEXT_INCLUDE_CODE);
}
ComponentName component = r.intent.getComponent();
if (component == null) {
component = r.intent.resolveActivity(
mInitialApplication.getPackageManager());
r.intent.setComponent(component);
}
if (r.activityInfo.targetActivity != null) {
component = new ComponentName(r.activityInfo.packageName,
r.activityInfo.targetActivity);
}
2.通過Instrumentation 的newActivity方法使用類加載器創建Activity對象
Activity activity = null;
try {
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = r.packageInfo.getClassLoader();
activity = mInstrumentation.newActivity(
cl, component.getClassName(), r.intent);
StrictMode.incrementExpectedActivityCount(activity.getClass());
r.intent.setExtrasClassLoader(cl);
r.intent.prepareToEnterProcess();
if (r.state != null) {
r.state.setClassLoader(cl);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(activity, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to instantiate activity " + component
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
重點實現在newActivity中
public Activity newActivity(ClassLoader cl, String className,
Intent intent)
throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException,
ClassNotFoundException {
return (Activity)cl.loadClass(className).newInstance();
}
3.通過LoadedApk的makeApplication方法來嘗試創建Application
public Application makeApplication(boolean forceDefaultAppClass,
Instrumentation instrumentation) {
if (mApplication != null) {
return mApplication;
}
Application app = null;
String appClass = mApplicationInfo.className;
if (forceDefaultAppClass || (appClass == null)) {
appClass = "android.app.Application";
}
try {
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = getClassLoader();
if (!mPackageName.equals("android")) {
initializeJavaContextClassLoader();
}
ContextImpl appContext = ContextImpl.createAppContext(mActivityThread, this);
app = mActivityThread.mInstrumentation.newApplication(
cl, appClass, appContext);
appContext.setOuterContext(app);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mActivityThread.mInstrumentation.onException(app, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to instantiate application " + appClass
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
mActivityThread.mAllApplications.add(app);
mApplication = app;
if (instrumentation != null) {
try {
instrumentation.callApplicationOnCreate(app);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!instrumentation.onException(app, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to create application " + app.getClass().getName()
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
}
…………
如果Application被創建了,就不會再重復創建了。這也意味著一個應用只有一個Application,它的創建是通過Instrumentation來完成的。通過類加載載來實現。創建完通過callApplicationOnCreate來調用Application的onCreate()方法。
4,創建ContextImpl對象並通過Activity的attach方法來完成一些重要數據的初始化。
Context appContext = createBaseContextForActivity(r, activity);
CharSequence title = r.activityInfo.loadLabel(appContext.getPackageManager());
Configuration config = new Configuration(mCompatConfiguration);
if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG, "Launching activity "
+ r.activityInfo.name + " with config " + config);
activity.attach(appContext, this, getInstrumentation(), r.token,
r.ident, app, r.intent, r.activityInfo, title, r.parent,
r.embeddedID, r.lastNonConfigurationInstances, config,
r.referrer, r.voiceInteractor);
ContextImpl是通過Activity的attach方法與Acitivity建立關聯的。此外attach來完成window的創建並建立自己和window的關聯。這樣當window接收到外部輸入事件後就可以將事件傳遞給Activity。
到些Activity就啟動起來了。
1. 應用程序的MainActivity通過Binder進程間通信機制通知ActivityManagerService,它要啟動一個新的Activity;
2. :ActivityManagerService通過Binder進程間通信機制通知MainActivity進入Paused狀態;
3. MainActivity通過Binder進程間通信機制通知ActivityManagerService,它已經准備就緒進入Paused狀態,於是ActivityManagerService就准備要在MainActivity所在的進程和任務中啟動新的Activity了;
4. ActivityManagerService通過Binder進程間通信機制通知MainActivity所在的ActivityThread,現在一切准備就緒,它可以真正執行Activity的啟動操作了。
 Android筆記之:App列表之下拉刷新的使用
Android筆記之:App列表之下拉刷新的使用
Android的ListView是應用最廣的一個組件,功能強大,擴展性靈活(不局限於ListView本身一個類),前面的文章有介紹分組,拖拽,3D立體,游標,圓角,而今天
 Android Studio中的EditText控件使用詳解
Android Studio中的EditText控件使用詳解
一:新建HelloEditText工程創建設置如下:Project name:HelloEditText Build Target :android 2.2 Applic
 手把手圖文並茂教你發布Android開源庫
手把手圖文並茂教你發布Android開源庫
經常逛github,總看到別人的readme中寫著compile ‘com.xxx:1.0.xxx’,這個已經越來越普及,個人,團人,公司都在用,
 Android SlidingMenu使用和示例詳解
Android SlidingMenu使用和示例詳解
很多APP都有側滑菜單的功能,部分APP左右都是側滑菜單~SlidingMenu 這個開源項目可以很好幫助我們實現側滑功能,如果對SlidingMenu 還不是很了解的童