編輯:關於Android編程
Android總結篇系列:Android Service。Service通常總是稱之為“後台服務”,其中“後台”一詞是相對於前台而言的,具體是指其本身的運行並不依賴於用戶可視的UI界面,因此,從實際業務需求上來理解,Service的適用場景應該具備以下條件:
1.並不依賴於用戶可視的UI界面(當然,這一條其實也不是絕對的,如前台Service就是與Notification界面結合使用的);
2.具有較長時間的運行特性。
1.Service AndroidManifest.xml 聲明
一般而言,從Service的啟動方式上,可以將Service分為Started Service和Bound Service。無論哪種具體的Service啟動類型,都是通過繼承Service基類自定義而來。在使用Service時,要想系統能夠找到此自定義Service,無論哪種類型,都需要在AndroidManifest.xml中聲明,語法格式如下:
19 . . . 10
其中,android:exported屬性上一篇博文中對此已進行詳盡描述,android:name對應Service類名,android:permission是權限聲明,android:process設置具體的進程名稱。需要注意的是Service能否單獨使用一個進程與其啟動方式有關,本後下面會給出具體說明。其他的屬性此處與其他組件基本相同,不再過多描述。
注:如果自定義Service沒有在AndroidManifest.xml中聲明,當具體使用時,不會像Activity那樣直接崩潰報錯,對於顯式Intent啟動的Service,此時也會給出waring信息“IllegalArgumentException: Service not registered”,有時候不容易發現忘了聲明而一時定位不到問題。
2.Started Service
Started Service相對比較簡單,通過context.startService(Intent serviceIntent)啟動Service,context.stopService(Intent serviceIntent)停止此Service。當然,在Service內部,也可以通過stopSelf(...)方式停止其本身。
1)Started Service自定義
下面代碼片段顯示的是一個最基本的Started Service的自定義方式:
1 public class MyService extends Service {
2
3 public static final String TAG = "MyService";
4
5 @Override
6 public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
7 return null;
8 }
9
10 @Override
11 public void onCreate() {
12 super.onCreate();
13 Log.w(TAG, "in onCreate");
14 }
15
16 @Override
17 public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
18 Log.w(TAG, "in onStartCommand");
19 Log.w(TAG, "MyService:" + this);
20 String name = intent.getStringExtra("name");
21 Log.w(TAG, "name:" + name);
22 return START_STICKY;
23 }
24
25 @Override
26 public void onDestroy() {
27 super.onDestroy();
28 Log.w(TAG, "in onDestroy");
29 }
30 }
其中,onBind(...)函數是Service基類中的唯一抽象方法,子類都必須重寫實現,此函數的返回值是針對Bound Service類型的Service才有用的,在Started Service類型中,此函數直接返回 null 即可。onCreate(...)、onStartCommand(...)和onDestroy()都是Started Service相應生命周期階段的回調函數。
2) Started Service使用
1 public class MainActivity extends Activity {
2
3 public static final String TAG = "MainActivity";
4
5 private Button startServiceBtn;
6 private Button stopServideBtn;
7 private Button goBtn;
8
9 private Intent serviceIntent;
10
11 @Override
12 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
13 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
14 setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
15
16 startServiceBtn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.start_service);
17 stopServideBtn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.stop_service);
18 goBtn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.go);
19
20 startServiceBtn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
21 @Override
22 public void onClick(View v) {
23 serviceIntent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, MyService.class);
24 startService(serviceIntent);
25 }
26 });
27
28 stopServideBtn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
29 @Override
30 public void onClick(View v) {
31 stopService(serviceIntent);
32 }
33 });
34
35 goBtn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
36 @Override
37 public void onClick(View v) {
38 Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, BActivity.class);
39 startActivity(intent);
40 }
41 });
42
43 }
44
45 @Override
46 protected void onDestroy() {
47 super.onDestroy();
48 Log.w(TAG, "in onDestroy");
49 }
50 }
如上代碼片段,
當Client調用startService(Intent serviceIntent)後,如果MyService是第一次啟動,首先會執行 onCreate()回調,然後再執行onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId),當Client再次調用startService(Intent serviceIntent),將只執行onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId),因為此時Service已經創建了,無需執行onCreate()回調。無論多少次的startService,只需要一次stopService()即可將此Service終止,執行onDestroy()函數(其實很好理解,因為onDestroy()與onCreate()回調是相對的)。
下面重點關注下onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId)方法。
其中參數flags默認情況下是0,對應的常量名為START_STICKY_COMPATIBILITY。startId是一個唯一的整型,用於表示此次Client執行startService(...)的請求請求標識,在多次startService(...)的情況下,呈現0,1,2....遞增。另外,此函數具有一個int型的返回值,具體的可選值及含義如下:
START_NOT_STICKY:當Service因為內存不足而被系統kill後,接下來未來的某個時間內,即使系統內存足夠可用,系統也不會嘗試重新創建此Service。除非程序中Client明確再次調用startService(...)啟動此Service。
START_STICKY:當Service因為內存不足而被系統kill後,接下來未來的某個時間內,當系統內存足夠可用的情況下,系統將會嘗試重新創建此Service,一旦創建成功後將回調onStartCommand(...)方法,但其中的Intent將是null,pendingintent除外。
START_REDELIVER_INTENT:與START_STICKY唯一不同的是,回調onStartCommand(...)方法時,其中的Intent將是非空,將是最後一次調用startService(...)中的intent。
START_STICKY_COMPATIBILITY:compatibility version of {@link #START_STICKY} that does not guarantee that {@link #onStartCommand} will be called again after being killed。此值一般不會使用,所以注意前面三種情形就好。
以上的描述中,”當Service因為內存不足而被系統kill後“一定要非常注意,因為此函數的返回值設定只是針對此種情況才有意義的,換言之,當認為的kill掉Service進程,此函數返回值無論怎麼設定,接下來未來的某個時間內,即使系統內存足夠可用,Service也不會重啟。
小米手機針對此處做了變更:
另外,需要注意的是,小米手機針對此處做了一定的修改。在“自啟動管理”中有一個自啟動應用列表,默認情況下,只有少應用(如微信、QQ、YY、360等)默認是可以自啟動的,其他應用默認都是禁止的。用戶可以手動添加自啟動應用,添加後的應用中如果Started Service onStartCommand(...)回調返回值是START_STICKY或START_REDELIVER_INTENT,當用戶在小米手機上長按Home鍵結束App後,接下來未來的某個時間內,當系統內存足夠可用時,Service依然可以按照上述規定重啟。當然,如果用戶在 設置 >> 應用 >> 強制kill掉App進程,此時Service是不會重啟的。
注:以上實驗結論基於小米2S親測。
3)Started Service生命周期及進程相關
1.onCreate(Client首次startService(..)) >> onStartCommand >> onStartCommand - optional ... >> onDestroy(Client調用stopService(..))
注:onStartCommand(..)可以多次被調用,onDestroy()與onCreate()想匹配,當用戶強制kill掉進程時,onDestroy()是不會執行的。
2.對於同一類型的Service,Service實例一次永遠只存在一個,而不管Client是否是相同的組件,也不管Client是否處於相同的進程中。
3.Service通過startService(..)啟動Service後,此時Service的生命周期與Client本身的什麼周期是沒有任何關系的,只有Client調用stopService(..)或Service本身調用stopSelf(..)才能停止此Service。當然,當用戶強制kill掉Service進程或系統因內存不足也可能kill掉此Service。
4.Client A 通過startService(..)啟動Service後,可以在其他Client(如Client B、Client C)通過調用stopService(..)結束此Service。
5.Client調用stopService(..)時,如果當前Service沒有啟動,也不會出現任何報錯或問題,也就是說,stopService(..)無需做當前Service是否有效的判斷。
6.startService(Intent serviceIntent),其中的intent既可以是顯式Intent,也可以是隱式Intent,當Client與Service同處於一個App時,一般推薦使用顯示Intent。當處於不同App時,只能使用隱式Intent。
當Service需要運行在單獨的進程中,AndroidManifest.xml聲明時需要通過android:process指明此進程名稱,當此Service需要對其他App開放時,android:exported屬性值需要設置為true(當然,在有intent-filter時默認值就是true)。
15 6 7 8
4)Started Service Client與Service通信相關
當Client調用startService(Intent serviceIntent)啟動Service時,Client可以將參數通過Intent直接傳遞給Service。Service執行過程中,如果需要將參數傳遞給Client,一般可以通過借助於發送廣播的方式(此時,Client需要注冊此廣播)。
3.Bound Service
相對於Started Service,Bound Service具有更多的知識點。Bound Service的主要特性在於Service的生命周期是依附於Client的生命周期的,當Client不存在時,Bound Service將執行onDestroy,同時通過Service中的Binder對象可以較為方便進行Client-Service通信。Bound Service一般使用過程如下:
1.自定義Service繼承基類Service,並重寫onBind(Intent intent)方法,此方法中需要返回具體的Binder對象;
2.Client通過實現ServiceConnection接口來自定義ServiceConnection,並通過bindService (Intent service, ServiceConnection sc, int flags)方法將Service綁定到此Client上;
3.自定義的ServiceConnection中實現onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder binder)方法,獲取Service端Binder實例;
4.通過獲取的Binder實例進行Service端其他公共方法的調用,以完成Client-Service通信;
5.當Client在恰當的生命周期(如onDestroy等)時,此時需要解綁之前已經綁定的Service,通過調用函數unbindService(ServiceConnection sc)。
在Bound Service具體使用過程中,根據onBind(Intent intent)方法放回的Binder對象的定義方式不同,又可以將其分為以下三種方式,且每種方式具有不同的特點和適用場景:
1).Extending the Binder class
這是Bound Service中最常見的一種使用方式,也是Bound Service中最簡單的一種。
局限:Clinet與Service必須同屬於同一個進程,不能實現進程間通信(IPC)。否則則會出現類似於“android.os.BinderProxy cannot be cast to xxx”錯誤。
下面通過代碼片段看下具體的使用:
1 public class MyBindService extends Service {
2
3 public static final String TAG = "MyBindService";
4
5 private MyBinder mBinder = new MyBinder();
6
7 public class MyBinder extends Binder {
8 MyBindService getService() {
9 return MyBindService.this;
10 }
11 }
12
13 @Override
14 public void onCreate() {
15 super.onCreate();
16 Log.w(TAG, "in onCreate");
17 }
18
19 @Override
20 public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
21 Log.w(TAG, "in onBind");
22 return mBinder;
23 }
24
25 @Override
26 public boolean onUnbind(Intent intent) {
27 Log.w(TAG, "in onUnbind");
28 return super.onUnbind(intent);
29 }
30
31 @Override
32 public void onDestroy() {
33 super.onDestroy();
34 Log.w(TAG, "in onDestroy");
35 }
36 }
1 public class BActivity extends Activity {
2
3 public static final String TAG = "BActivity";
4
5 private Button bindServiceBtn;
6 private Button unbindServiceBtn;
7
8 private Button startIntentService;
9
10 private Intent serviceIntent;
11
12 private ServiceConnection sc = new MyServiceConnection();
13 private MyBinder mBinder;
14 private MyBindService mBindService;
15 private boolean mBound;
16
17 private class MyServiceConnection implements ServiceConnection {
18
19 @Override
20 public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder binder) {
21 Log.w(TAG, "in MyServiceConnection onServiceConnected");
22 mBinder = (MyBinder) binder;
23 mBindService = mBinder.getService();
24
25 mBound = true;
26 }
27
28 @Override
29 public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
30 // This is called when the connection with the service has been
31 // unexpectedly disconnected -- that is, its process crashed.
32 Log.w(TAG, "in MyServiceConnection onServiceDisconnected");
33 mBound = false;
34 }
35
36 }
37
38 @Override
39 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
40 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
41 setContentView(R.layout.b);
42
43 bindServiceBtn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.bind_service);
44 unbindServiceBtn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.unbind_service);
45 startIntentService = (Button) findViewById(R.id.start_intentservice);
46
47 bindServiceBtn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
48 @Override
49 public void onClick(View v) {
50 Intent intent = new Intent(BActivity.this, MyBindService.class);
51 bindService(intent, sc, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
52 }
53 });
54
55 unbindServiceBtn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
56 @Override
57 public void onClick(View v) {
58 excuteUnbindService();
59 }
60 });
61
62 startIntentService.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
63 @Override
64 public void onClick(View v) {
65 Intent intent = new Intent(BActivity.this, MyIntentService.class);
66 startService(intent);
67 }
68 });
69
70 }
71
72 private void excuteUnbindService() {
73 if (mBound) {
74 unbindService(sc);
75 mBound = false;
76 }
77 }
78
79 @Override
80 protected void onDestroy() {
81 super.onDestroy();
82 Log.w(TAG, "in onDestroy");
83 excuteUnbindService();
84 }
85 }
首次點擊bindServiceBtn進行bindService(..)時,依次回調順序如下:
1 MyBindService(13457): in onCreate 2 MyBindService(13457): in onBind 3 BActivity(13457): in MyServiceConnection onServiceConnected
再次點擊bindServiceBtn按鈕時,發現沒有任何輸出,說明MyBindService沒有進行任何回調。
點擊unbindServiceBtn進行unbindService(..)時,回調順序為:
1 MyBindService(13457): in onUnbind 2 MyBindService(13457): in onDestroy
注:在四大基本組件中,需要注意的的是BroadcastReceiver不能作為Bound Service的Client,因為BroadcastReceiver的生命周期很短,當執行完onReceive(..)回調時,BroadcastReceiver生命周期完結。而Bound Service又與Client本身的生命周期相關,因此,Android中不允許BroadcastReceiver去bindService(..),當有此類需求時,可以考慮通過startService(..)替代。
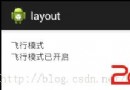 android的SharedPreferences使用
android的SharedPreferences使用
需求:模擬android系統應用設置中飛行模式的開啟與關閉,並記住設置的狀態 布局文件:fragment_main.xml 資源文件s
 ImageView的屬性android:scaleType作用
ImageView的屬性android:scaleType作用
在網上查了好多資料,大致都雷同,大家都是互相抄襲的,看著很費勁,不好理解,自己總結一下,留著需要看的話來查找。代碼中的例子如下 <ImageView
 【Android】如何寫一個JsBridge
【Android】如何寫一個JsBridge
JsBridge簡介Android JsBridge 就是用來在 Android app的原生 java 代碼與 javascript 代碼中架設通信(調用)橋梁的輔助工
 Android軟鍵盤遮擋的四種完美解決方案
Android軟鍵盤遮擋的四種完美解決方案
一、問題概述 在編輯框輸入內容時會彈出軟鍵盤,而手機屏幕區域有限往往會遮住輸入界面,我們先看一下問題效果圖: 輸入用戶名和密碼時,系統會彈出鍵盤,造成系統鍵盤會擋住文