編輯:關於Android編程
在Android中復雜的圖形的繪制絕大多數是通過path來實現,比如繪制一條曲線,然後讓一個物體隨著這個曲線運動,比如搜索按鈕,比如一個簡單時鐘的實現:
那麼什麼是path呢!
定義:path 就是路徑,就是圖形的路徑的集合,它裡邊包含了路徑裡邊的坐標點,等等的屬性。我們可以獲取到任意點的坐標,正切值。
那麼要獲取Path上邊所有點的坐標還需要用到一個類,PathMeasure;
PathMesure:
PathMeasure是一個用來測量Path的類,主要有以下方法:
構造方法

公共方法
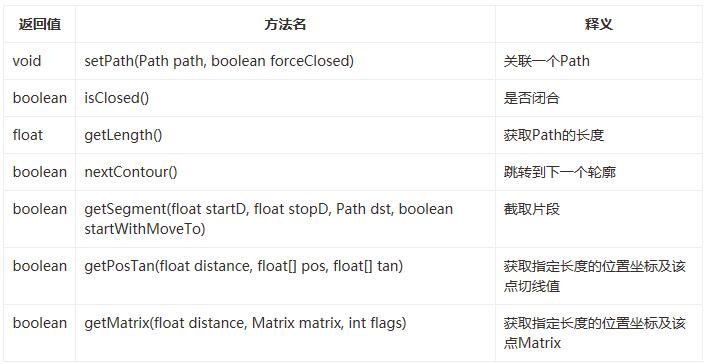
可以看到,這個就等於是一個Path的一個工具類,方法很簡單,那麼就開始我們所要做的按鈕跟時鐘的開發吧
(1)搜索按鈕,首先上圖:

要實現這個功能首先要把他分解開來做;
創建搜索按鈕的path路徑,然後創建外圈旋轉的path,
public void initPath(){
mPath_search = new Path();
mPath_circle = new Path();
mMeasure = new PathMeasure();
// 注意,不要到360度,否則內部會自動優化,測量不能取到需要的數值
RectF oval1 = new RectF(-50, -50, 50, 50); // 放大鏡圓環
mPath_search.addArc(oval1, 45, 359.9f);
RectF oval2 = new RectF(-100, -100, 100, 100); // 外部圓環
mPath_circle.addArc(oval2, 45, -359.9f);
float[] pos = new float[2];
mMeasure.setPath(mPath_circle, false); // 放大鏡把手的位置
mMeasure.getPosTan(0, pos, null);
mPath_search.lineTo(pos[0], pos[1]); // 放大鏡把手
Log.i("TAG", "pos=" + pos[0] + ":" + pos[1]);
}
我們要的效果就是點擊搜索按鈕的時候開始從按鈕變為旋轉,然後搜索結束以後變為搜索按鈕。
所以我們可以確定有四種狀態:
public enum Seach_State{
START,END,NONE,SEARCHING
}
然後根據狀態來進行動態繪制path,動態繪制path就要使用到PathMeasure測量當前path的坐標,然後進行繪制。
private void drawPath(Canvas c) {
c.translate(mWidth / 2, mHeight / 2);
switch (mState){
case NONE:
c.drawPath(mPath_search,mPaint);
break;
case START:
mMeasure.setPath(mPath_search,true);
Path path = new Path();
mMeasure.getSegment(mMeasure.getLength() * curretnAnimationValue,mMeasure.getLength(),path, true);
c.drawPath(path,mPaint);
break;
case SEARCHING:
mMeasure.setPath(mPath_circle,true);
Path path_search = new Path();
mMeasure.getSegment(mMeasure.getLength()*curretnAnimationValue -30,mMeasure.getLength()*curretnAnimationValue,path_search,true);
c.drawPath(path_search,mPaint);
break;
case END:
mMeasure.setPath(mPath_search,true);
Path path_view = new Path();
mMeasure.getSegment(0,mMeasure.getLength()*curretnAnimationValue,path_view,true);
c.drawPath(path_view,mPaint);
break;
}
}
然後就是需要通過使用屬性動畫來返回當前該繪制的百分百,通過這個值來進行計算要繪制的path。
下邊是整個代碼:
package com.duoku.platform.demo.canvaslibrary.attract.view;
import android.animation.Animator;
import android.animation.ValueAnimator;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.graphics.Paint;
import android.graphics.Path;
import android.graphics.PathMeasure;
import android.graphics.RectF;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
/**
* Created by chenpengfei_d on 2016/9/7.
*/
public class SearchView extends View {
private Paint mPaint;
private Context mContext;
private Path mPath_circle;
private Path mPath_search;
private PathMeasure mMeasure;
private ValueAnimator mValueAnimator_search;
private long defaultduration=3000;
private float curretnAnimationValue;
private Seach_State mState = Seach_State.SEARCHING;
public SearchView(Context context) {
super(context);
init(context);
}
public SearchView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init(context);
}
public SearchView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
init(context);
}
public void init(Context context){
this.mContext = context;
initPaint();
initPath();
initAnimation();
}
public void initPaint(){
mPaint = new Paint();
mPaint.setDither(true);
mPaint.setStrokeCap(Paint.Cap.ROUND);//設置筆頭效果
mPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mPaint.setColor(Color.RED);
mPaint.setStrokeWidth(3);
mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
}
public void initPath(){
mPath_search = new Path();
mPath_circle = new Path();
mMeasure = new PathMeasure();
// 注意,不要到360度,否則內部會自動優化,測量不能取到需要的數值
RectF oval1 = new RectF(-50, -50, 50, 50); // 放大鏡圓環
mPath_search.addArc(oval1, 45, 359.9f);
RectF oval2 = new RectF(-100, -100, 100, 100); // 外部圓環
mPath_circle.addArc(oval2, 45, -359.9f);
float[] pos = new float[2];
mMeasure.setPath(mPath_circle, false); // 放大鏡把手的位置
mMeasure.getPosTan(0, pos, null);
mPath_search.lineTo(pos[0], pos[1]); // 放大鏡把手
Log.i("TAG", "pos=" + pos[0] + ":" + pos[1]);
}
public void initAnimation(){
mValueAnimator_search = ValueAnimator.ofFloat(0f,1.0f).setDuration(defaultduration);
mValueAnimator_search.addUpdateListener(updateListener);
mValueAnimator_search.addListener(animationListener);
}
private ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener updateListener = new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) {
curretnAnimationValue = (float) animation.getAnimatedValue();
invalidate();
}
};
private Animator.AnimatorListener animationListener = new Animator.AnimatorListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationStart(Animator animation) {
}
@Override
public void onAnimationEnd(Animator animation) {
if(mState ==Seach_State.START){
setState(Seach_State.SEARCHING);
}
}
@Override
public void onAnimationCancel(Animator animation) {
}
@Override
public void onAnimationRepeat(Animator animation) {
}
};
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
drawPath(canvas);
}
private int mWidth,mHeight;
@Override
protected void onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh) {
super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh);
mWidth = w;
mHeight = h;
}
private void drawPath(Canvas c) {
c.translate(mWidth / 2, mHeight / 2);
switch (mState){
case NONE:
c.drawPath(mPath_search,mPaint);
break;
case START:
mMeasure.setPath(mPath_search,true);
Path path = new Path();
mMeasure.getSegment(mMeasure.getLength() * curretnAnimationValue,mMeasure.getLength(),path, true);
c.drawPath(path,mPaint);
break;
case SEARCHING:
mMeasure.setPath(mPath_circle,true);
Path path_search = new Path();
mMeasure.getSegment(mMeasure.getLength()*curretnAnimationValue -30,mMeasure.getLength()*curretnAnimationValue,path_search,true);
c.drawPath(path_search,mPaint);
break;
case END:
mMeasure.setPath(mPath_search,true);
Path path_view = new Path();
mMeasure.getSegment(0,mMeasure.getLength()*curretnAnimationValue,path_view,true);
c.drawPath(path_view,mPaint);
break;
}
}
public void setState(Seach_State state){
this.mState = state;
startSearch();
}
public void startSearch(){
switch (mState){
case START:
mValueAnimator_search.setRepeatCount(0);
break;
case SEARCHING:
mValueAnimator_search.setRepeatCount(ValueAnimator.INFINITE);
mValueAnimator_search.setRepeatMode(ValueAnimator.REVERSE);
break;
case END:
mValueAnimator_search.setRepeatCount(0);
break;
}
mValueAnimator_search.start();
}
public enum Seach_State{
START,END,NONE,SEARCHING
}
}
(學習的點:path可以組合,可以把不同的path放置到一個path裡邊,然後進行統一的繪制)
(2)時鐘效果:

說一下時鐘的思路啊,網上很多時鐘都是通過Canvas繪制基本圖形實現的,沒有通過path來實現的,使用path實現是為了以後更加靈活的控制時鐘的繪制效果,比如我們要讓最外邊的圓圈逆時針旋轉,還比如在上邊添加些小星星啥的,用path的話會更加靈活。
時鐘的實現分部分:
1、創建外圈path路徑
2、創建刻度path路徑,要區分整點,繪制時間點
3、繪制指針,(這個使用的是canvas繪制的線段,也可以使用Path,可以自己測試)
需要計算當前時針,分針,秒針的角度,然後進行繪制
整體代碼:
package com.duoku.platform.demo.canvaslibrary.attract.view;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.graphics.Paint;
import android.graphics.Path;
import android.graphics.PathMeasure;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.View;
import java.util.Calendar;
/**
* Created by chenpengfei_d on 2016/9/8.
*/
public class TimeView extends View {
private Paint mPaint,mPaint_time;
private Paint mPaint_h,mPaint_m,mPaint_s;
private Path mPath_Circle;
private Path mPath_Circle_h;
private Path mPath_Circle_m;
private Path mPath_h,mPath_m,mPath_s;
private Path mPath_duration;
private PathMeasure mMeasure;
private PathMeasure mMeasure_h;
private PathMeasure mMeasure_m;
private Handler mHandler = new Handler();
private Runnable clockRunnable;
private boolean isRunning;
public TimeView(Context context) {
super(context);
init();
}
public TimeView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init();
}
public TimeView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
init();
}
int t = 3;
public void init(){
//初始化畫筆
mPaint = new Paint();
mPaint.setDither(true);
mPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
mPaint.setStrokeWidth(2);
mPaint.setStrokeCap(Paint.Cap.ROUND);
mPaint.setStrokeJoin(Paint.Join.ROUND);
mPaint.setColor(Color.RED);
mPaint_time = new Paint();
mPaint_time.setDither(true);
mPaint_time.setAntiAlias(true);
mPaint_time.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
mPaint_time.setStrokeWidth(2);
mPaint_time.setTextSize(15);
mPaint_time.setStrokeCap(Paint.Cap.ROUND);
mPaint_time.setStrokeJoin(Paint.Join.ROUND);
mPaint_time.setColor(Color.RED);
mPaint_h = new Paint();
mPaint_h.setDither(true);
mPaint_h.setAntiAlias(true);
mPaint_h.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
mPaint_h.setStrokeWidth(6);
mPaint_h.setTextSize(15);
mPaint_h.setStrokeCap(Paint.Cap.ROUND);
mPaint_h.setStrokeJoin(Paint.Join.ROUND);
mPaint_h.setColor(Color.RED);
mPaint_m = new Paint();
mPaint_m.setDither(true);
mPaint_m.setAntiAlias(true);
mPaint_m.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
mPaint_m.setStrokeWidth(4);
mPaint_m.setTextSize(15);
mPaint_m.setStrokeCap(Paint.Cap.ROUND);
mPaint_m.setStrokeJoin(Paint.Join.ROUND);
mPaint_m.setColor(Color.RED);
mPaint_s = new Paint();
mPaint_s.setDither(true);
mPaint_s.setAntiAlias(true);
mPaint_s.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
mPaint_s.setStrokeWidth(2);
mPaint_s.setTextSize(15);
mPaint_s.setStrokeCap(Paint.Cap.ROUND);
mPaint_s.setStrokeJoin(Paint.Join.ROUND);
mPaint_s.setColor(Color.RED);
//初始化刻度
mPath_Circle = new Path();
mPath_Circle.addCircle(0,0,250, Path.Direction.CCW);
mPath_Circle_h = new Path();
mPath_Circle_h.addCircle(0,0,220, Path.Direction.CCW);
mPath_Circle_m = new Path();
mPath_Circle_m.addCircle(0,0,235, Path.Direction.CCW);
//初始化PathMeasure測量path坐標,
mMeasure = new PathMeasure();
mMeasure.setPath(mPath_Circle,true);
mMeasure_h = new PathMeasure();
mMeasure_h.setPath(mPath_Circle_h,true);
mMeasure_m = new PathMeasure();
mMeasure_m.setPath(mPath_Circle_m,true);
//獲取刻度path
mPath_duration = new Path();
for (int i = 60; i>0 ;i --){
Path path = new Path();
float pos [] = new float[2];
float tan [] = new float[2];
float pos2 [] = new float[2];
float tan2 [] = new float[2];
float pos3 [] = new float[2];
float tan3 [] = new float[2];
mMeasure.getPosTan(mMeasure.getLength()*i/60,pos,tan);
mMeasure_h.getPosTan(mMeasure_h.getLength()*i/60,pos2,tan2);
mMeasure_m.getPosTan(mMeasure_m.getLength()*i/60,pos3,tan3);
float x = pos[0];
float y = pos[1];
float x2 = pos2[0];
float y2 = pos2[1];
float x3 = pos3[0];
float y3 = pos3[1];
path.moveTo(x , y);
if(i% 5 ==0){
path.lineTo(x2,y2);
if(t>12){
t = t-12;
}
String time = t++ +"";
Path path_time = new Path();
mMeasure_h.getPosTan(mMeasure_h.getLength()*(i-1)/60,pos2,tan2);
mPaint.getTextPath(time,0,time.length(),(x2- (x2/15)),y2-(y2/15),path_time);
path.close();
path.addPath(path_time);
}else{
path.lineTo(x3,y3);
}
mPath_duration.addPath(path);
clockRunnable = new Runnable() {//裡面做的事情就是每隔一秒,刷新一次界面
@Override
public void run() {
//線程中刷新界面
postInvalidate();
mHandler.postDelayed(this, 1000);
}
};
}
mPath_h = new Path();
mPath_h.rLineTo(50,30);
mPath_m = new Path();
mPath_m.rLineTo(80,80);
mPath_s = new Path();
mPath_s.rLineTo(130,50);
}
private int mWidth,mHeight;
@Override
protected void onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh) {
super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh);
mWidth = w;
mHeight = h;
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
if(!isRunning){
isRunning = true;
mHandler.postDelayed(clockRunnable,1000);
}else{
canvas.translate(mWidth/2,mHeight/2);
canvas.drawPath(mPath_Circle,mPaint);
canvas.save();
canvas.drawPath(mPath_duration,mPaint_time);
canvas.drawPoint(0,0,mPaint_time);
drawClockPoint(canvas);
}
}
private Calendar cal;
private int hour;
private int min;
private int second;
private float hourAngle,minAngle,secAngle;
/**
* 繪制三個指針
* @param canvas
*/
private void drawClockPoint(Canvas canvas) {
cal = Calendar.getInstance();
hour = cal.get(Calendar.HOUR);//Calendar.HOUR獲取的是12小時制,Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY獲取的是24小時制
min = cal.get(Calendar.MINUTE);
second = cal.get(Calendar.SECOND);
//計算時分秒指針各自需要偏移的角度
hourAngle = (float)hour / 12 * 360 + (float)min / 60 * (360 / 12);//360/12是指每個數字之間的角度
minAngle = (float)min / 60 * 360;
secAngle = (float)second / 60 * 360;
//下面將時、分、秒指針按照各自的偏移角度進行旋轉,每次旋轉前要先保存canvas的原始狀態
canvas.save();
canvas.rotate(hourAngle,0, 0);
canvas.drawLine(0, 0, mWidth/6, getHeight() / 6 - 65, mPaint_h);//時針長度設置為65
canvas.restore();
canvas.save();
canvas.rotate(minAngle,0, 0);
canvas.drawLine(0, 0, mWidth/6, getHeight() / 6 - 90 , mPaint_m);//分針長度設置為90
canvas.restore();
canvas.save();
canvas.rotate(secAngle,0, 0);
canvas.drawLine(0, 0, mWidth/6, getHeight() / 6 - 110 , mPaint_s);//秒針長度設置為110
canvas.restore();
}
}
這其實還不算特別復雜的動畫,也許你有啥好的想法,可以自己通過Path + 屬性動畫來實現更好看的效果;
比如星空的效果,比如動態繪制文字 + 路徑實現類似ppt中播放的一些特效,比如電子書的自動翻頁。
(3)下邊再介紹一個知識,就是svg:
svg是什麼東西呢?
他的學名叫做可縮放矢量圖形,是基於可擴展標記語言(標准通用標記語言的子集),用於描述二維矢量圖形的一種圖形格式。
這種格式的圖形式可以加載到Android的Path裡邊。
既然可以加載到Path裡邊,那麼是不是就可以實現更復雜的效果呢,下邊看圖:(明天再寫了)
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持本站。
 Z Launcher怎麼用 Nokia Z Launcher桌面介紹
Z Launcher怎麼用 Nokia Z Launcher桌面介紹
下載安裝好應用後,第一次打開會出現隱私許可協議,點擊接受後就會進入教程頁面,選擇跳過教程進入主頁面,可以看到它非常簡潔,整個Launcher只有主屏幕和應用
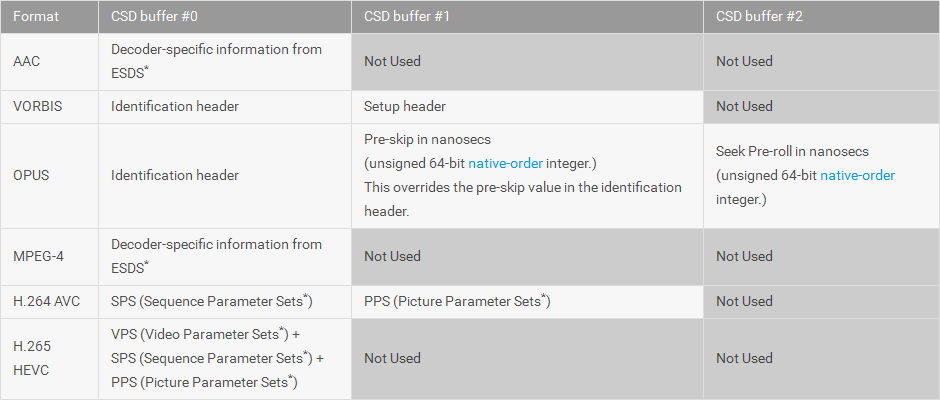 Android多媒體--MediaCodec 中文API文檔
Android多媒體--MediaCodec 中文API文檔
MediaCodecpublic final class MediaCodec extends ObjectJava.lang.Object → androi
 HDU 1849 Rabbit and Grass 簡單SG定理
HDU 1849 Rabbit and Grass 簡單SG定理
點擊打開鏈接 Rabbit and Grass Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 327
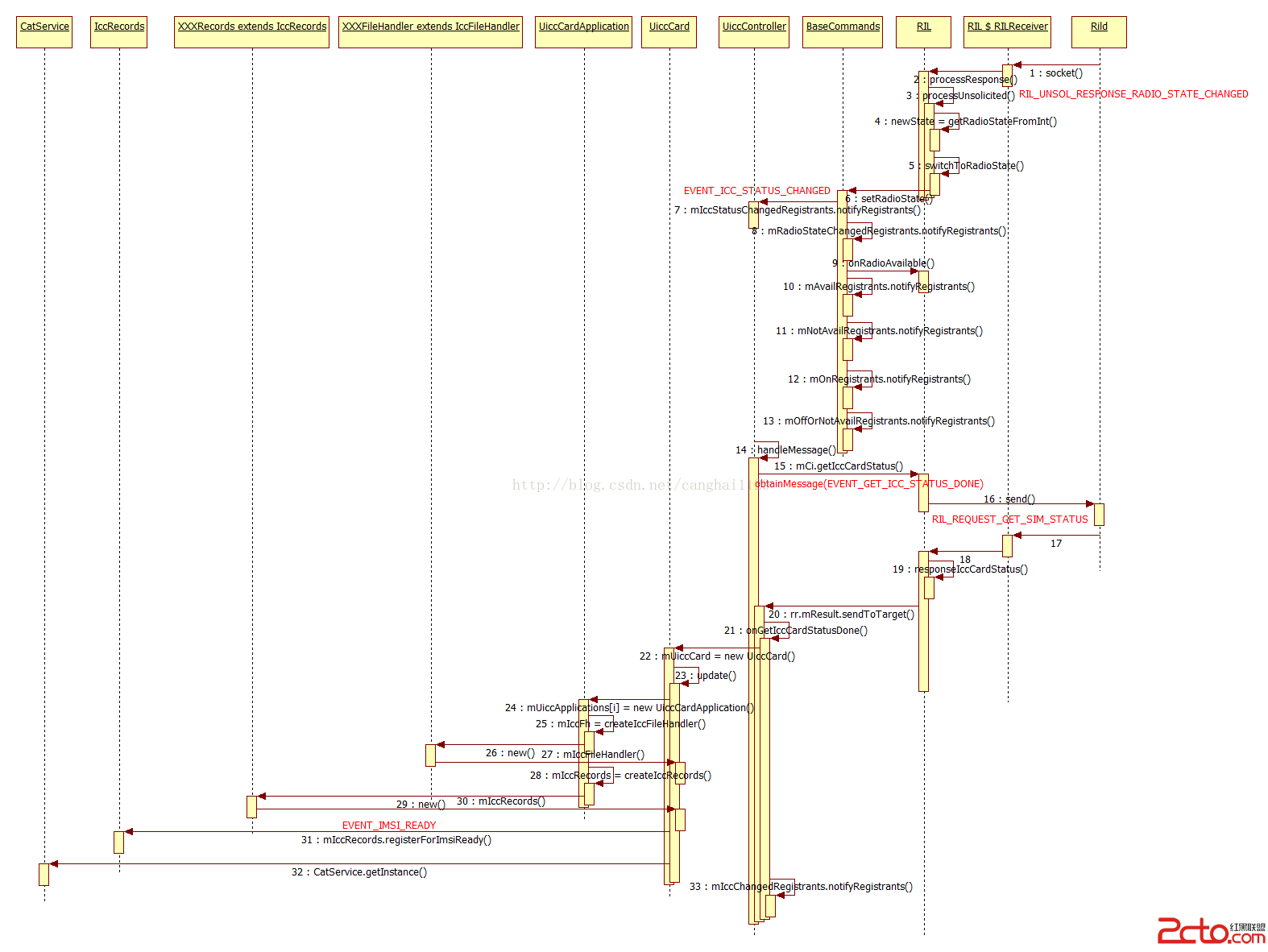 Android4.4 Telephony流程分析——SIM卡開機時的初始化
Android4.4 Telephony流程分析——SIM卡開機時的初始化
本文代碼以MTK平台Android 4.4為分析對象,與Google原生AOSP有些許差異,請讀者知悉。 本文主要介紹MTK Android開機時,SIM卡的Fram