編輯:關於Android編程
Android中,Activity和Fragment之間傳遞對象,可以通過將對象序列化並存入Bundle或者Intent中進行傳遞,也可以將對象轉化為JSON字符串,進行傳遞。
序列化對象可以使用Java的Serializable的接口、Parcelable接口。轉化成JSON字符串,可以使用Gson等庫。
1.Serializable
public class Author implements Serializable{
private int id;
private String name;
//...
}
public class Book implements Serializable{
private String title;
private Author author;
//...
}
傳遞數據
Book book=new Book();
book.setTitle("Java編程思想");
Author author=new Author();
author.setId(1);
author.setName("Bruce Eckel");
book.setAuthor(author);
Intent intent=new Intent(this,SecondActivity.class);
intent.putExtra("book",book);
startActivity(intent);
接收數據
Book book= (Book) getIntent().getSerializableExtra("book");
Log.d(TAG,"book title->"+book.getTitle());
Log.d(TAG,"book author name->"+book.getAuthor().getName());
2.轉化為JSON字符串
public class Author{
private int id;
private String name;
//...
}
public class Book{
private String title;
private Author author;
//...
}
傳遞數據
Book book=new Book();
book.setTitle("Java編程思想");
Author author=new Author();
author.setId(1);
author.setName("Bruce Eckel");
book.setAuthor(author);
Intent intent=new Intent(this,SecondActivity.class);
intent.putExtra("book",new Gson().toJson(book));
startActivity(intent);
接收數據
String bookJson=getIntent().getStringExtra("book");
Book book=new Gson().fromJson(bookJson,Book.class);
Log.d(TAG,"book title->"+book.getTitle());
Log.d(TAG,"book author name->"+book.getAuthor().getName());
3.使用Parcelable
實現Parcelable接口需要實現兩個方法
除了要實現這兩個方法還必須創建一個Parcelable.Creator接口的實例,用於讀取Parcel容器中的數據
public class Author implements Parcelable{
private int id;
private String name;
//setter & getter...
@Override
public int describeContents() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public void writeToParcel(Parcel dest, int flags) {
//該方法將類的數據寫入外部提供的Parcel中.即打包需要傳遞的數據到Parcel容器保存,
// 以便從parcel容器獲取數據
dest.writeString(name);
dest.writeInt(id);
}
public static final Creator<Author> CREATOR=new Creator<Author>() {
@Override
public Author createFromParcel(Parcel source) {
//從Parcel容器中讀取傳遞數據值,封裝成Parcelable對象返回邏輯層。
Author author=new Author();
author.setName(source.readString());
author.setId(source.readInt());
return author;
}
@Override
public Author[] newArray(int size) {
//創建一個類型為T,長度為size的數組,僅一句話(return new T[size])即可。方法是供外部類反序列化本類數組使用。
return new Author[size];
}
};
}
public class Book implements Parcelable{
private String title;
private Author author;
//setter & getter...
@Override
public int describeContents() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public void writeToParcel(Parcel dest, int flags) {
dest.writeString(title);
dest.writeParcelable(author,flags);
}
public static final Creator<Book> CREATOR=new Creator<Book>() {
@Override
public Book createFromParcel(Parcel source) {
Book book=new Book();
book.setTitle(source.readString());
book.setAuthor(source.<Author>readParcelable(Author.class.getClassLoader()));
return book;
}
@Override
public Book[] newArray(int size) {
return new Book[0];
}
};
}
傳遞數據
Book book=new Book();
book.setTitle("Java編程思想");
Author author=new Author();
author.setId(1);
author.setName("Bruce Eckel");
book.setAuthor(author);
Intent intent=new Intent(this,SecondActivity.class);
intent.putExtra("book",book);
startActivity(intent);
接收數據
Book book=getIntent().getParcelableExtra("book");
Log.d(TAG,"book title->"+book.getTitle());
Log.d(TAG,"book author name->"+book.getAuthor().getName());
4.性能分析
經過測試,我們得到下圖的效果
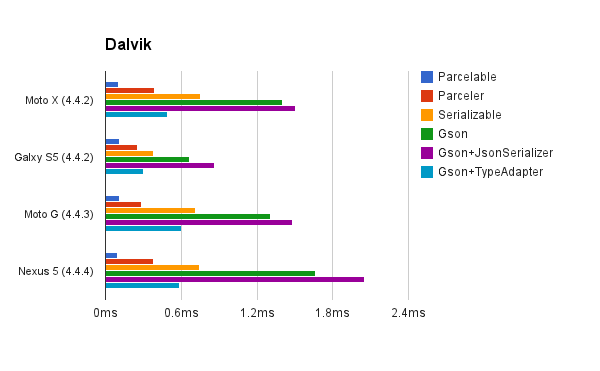
可以看出,通過轉換為字符串的速度是最慢的。Seralizable次之,Parcelable比Seralizable快10倍。所以從性能上考 慮,我們必定優先選擇Parcelable。但是Parcelable有大量重復的模板代碼,如何簡化這些操作,將是下面主要講解的內容。
5.簡化Parcel操作
如果你使用android Studio 可以通過安裝android-parcelable-intellij-plugin插件,或者自己配置模板進行操作。
5.1 parceler
除了上面的操作,還有大量的第三方庫來簡化Parcelable操作。當然使用這些庫也許會降低Parcelable的性能。Parceler就是這樣一個庫。
Parceler使用非常簡單,在定義Model時用@Parcel進行注解,在傳遞數據的時候使用Parcels的wrap方法來包裝成一個Parcelable對象。獲取數據時用Parcels的unwrap方法來獲取對象。
@Parcel
public class Author {
int id;
String name;
//setter & getter...
}
@Parcel
public class Book {
String title;
Author author;
//setter & getter
}
傳遞對象
Book book=new Book();
book.setTitle("Java編程思想");
Author author=new Author();
author.setId(1);
author.setName("Bruce Eckel");
book.setAuthor(author);
Intent intent=new Intent(this,SecondActivity.class);
intent.putExtra("book", Parcels.wrap(book));
startActivity(intent);
接收對象
Book book= Parcels.unwrap(getIntent().getParcelableExtra("book"));
Log.d(TAG,"book title->"+book.getTitle());
Log.d(TAG,"book author name->"+book.getAuthor().getName());
除了Parceler之外,還有如auto-parcel,ParcelableCodeGenerator,ParcelableGenerator等第三方庫,這裡我將不進行講解,有興趣的朋友,可以自行研究。
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持本站。
 Android性能優化之常見的內存洩漏
Android性能優化之常見的內存洩漏
前言對於內存洩漏,我想大家在開發中肯定都遇到過,只不過內存洩漏對我們來說並不是可見的,因為它是在堆中活動,而要想檢測程序中是否有內存洩漏的產生,通常我們可以借助LeakC
 使用Cordova來解決HTML5制作的WebView手機不兼容的問題
使用Cordova來解決HTML5制作的WebView手機不兼容的問題
一:Android 4.0WebView分析(1)WebView API三:Android 4.4 WebView的結構在Android 4.4系統上 Google已經將
 Android實現底部支付彈窗效果
Android實現底部支付彈窗效果
Android底部支付彈窗實現的效果:實現的思路:1.通過繼承PopupWindow自定義View來達到彈窗的彈出效果;2.通過回調將輸入的密碼由彈窗傳入到主界面中;2.
 Android主線程、子線程通信(Thread+handler)
Android主線程、子線程通信(Thread+handler)
Android是基於Java的,所以也分主線程,子線程!主線程:實現業務邏輯、UI繪制更新、各子線程串連,類似於將軍;子線程:完成耗時(聯網取數據、SD卡數據加載、後台長