編輯:關於Android編程
前文簡單介紹了Android中SurfaceView的基本使用,本文就來介紹一下SurfaceView與多線程的混搭。SurfaceView與多線程混搭,是為了防止動畫閃爍而實現的一種多線程應用。android的多線程用法與JAVA的多線程用法完全一樣,本文不做多線程方面的介紹了。直接講解SurfaceView與多線程的混合使用,即開一條線程專門讀取圖片,另外一條線程專門繪圖。
本文程序運行截圖如下,左邊是開單個線程讀取並繪圖,右邊是開兩個線程,一個專門讀取圖片,一個專門繪圖:
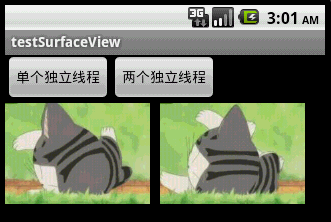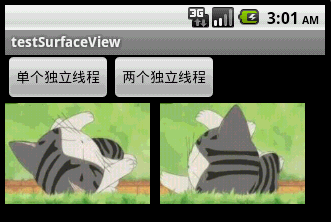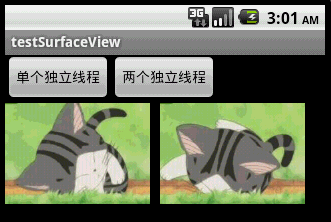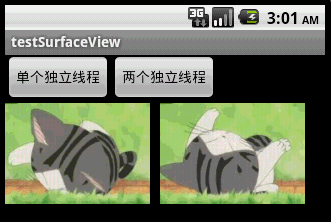
對比一下可以看出,右邊動畫的幀速明顯比左邊的快,左右兩者都沒使用Thread.sleep()。為什麼要開兩個線程一個讀一個畫,而不去開兩個線程像左邊那樣都“邊讀邊畫”呢?因為SurfaceView每次繪圖都會鎖定Canvas,也就是說同一片區域這次沒畫完下次就不能畫,因此要提高動畫播放的效率,就得開一條線程專門畫圖,開另外一條線程做預處理的工作。
main.xml的源碼如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:orientation="vertical"> <LinearLayout android:id="@+id/LinearLayout01" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"> <Button android:id="@+id/Button01" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="單個獨立線程"></Button> <Button android:id="@+id/Button02" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="兩個獨立線程"></Button> </LinearLayout> <SurfaceView android:id="@+id/SurfaceView01" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent"></SurfaceView> </LinearLayout>
Java程序的源碼如下:
package com.testSurfaceView;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import android.graphics.BitmapFactory;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Paint;
import android.graphics.Rect;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.SurfaceHolder;
import android.view.SurfaceView;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
public class testSurfaceView extends Activity {
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
Button btnSingleThread, btnDoubleThread;
SurfaceView sfv;
SurfaceHolder sfh;
ArrayList<Integer> imgList = new ArrayList<Integer>();
int imgWidth, imgHeight;
Bitmap bitmap;//獨立線程讀取,獨立線程繪圖
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
btnSingleThread = (Button) this.findViewById(R.id.Button01);
btnDoubleThread = (Button) this.findViewById(R.id.Button02);
btnSingleThread.setOnClickListener(new ClickEvent());
btnDoubleThread.setOnClickListener(new ClickEvent());
sfv = (SurfaceView) this.findViewById(R.id.SurfaceView01);
sfh = sfv.getHolder();
sfh.addCallback(new MyCallBack());// 自動運行surfaceCreated以及surfaceChanged
}
class ClickEvent implements View.OnClickListener {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
if (v == btnSingleThread) {
new Load_DrawImage(0, 0).start();//開一條線程讀取並繪圖
} else if (v == btnDoubleThread) {
new LoadImage().start();//開一條線程讀取
new DrawImage(imgWidth + 10, 0).start();//開一條線程繪圖
}
}
}
class MyCallBack implements SurfaceHolder.Callback {
@Override
public void surfaceChanged(SurfaceHolder holder, int format, int width,
int height) {
Log.i("Surface:", "Change");
}
@Override
public void surfaceCreated(SurfaceHolder holder) {
Log.i("Surface:", "Create");
// 用反射機制來獲取資源中的圖片ID和尺寸
Field[] fields = R.drawable.class.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
if (!"icon".equals(field.getName()))// 除了icon之外的圖片
{
int index = 0;
try {
index = field.getInt(R.drawable.class);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 保存圖片ID
imgList.add(index);
}
}
// 取得圖像大小
Bitmap bmImg = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(),
imgList.get(0));
imgWidth = bmImg.getWidth();
imgHeight = bmImg.getHeight();
}
@Override
public void surfaceDestroyed(SurfaceHolder holder) {
Log.i("Surface:", "Destroy");
}
}
/*
* 讀取並顯示圖片的線程
*/
class Load_DrawImage extends Thread {
int x, y;
int imgIndex = 0;
public Load_DrawImage(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public void run() {
while (true) {
Canvas c = sfh.lockCanvas(new Rect(this.x, this.y, this.x
+ imgWidth, this.y + imgHeight));
Bitmap bmImg = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(),
imgList.get(imgIndex));
c.drawBitmap(bmImg, this.x, this.y, new Paint());
imgIndex++;
if (imgIndex == imgList.size())
imgIndex = 0;
sfh.unlockCanvasAndPost(c);// 更新屏幕顯示內容
}
}
};
/*
* 只負責繪圖的線程
*/
class DrawImage extends Thread {
int x, y;
public DrawImage(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public void run() {
while (true) {
if (bitmap != null) {//如果圖像有效
Canvas c = sfh.lockCanvas(new Rect(this.x, this.y, this.x
+ imgWidth, this.y + imgHeight));
c.drawBitmap(bitmap, this.x, this.y, new Paint());
sfh.unlockCanvasAndPost(c);// 更新屏幕顯示內容
}
}
}
};
/*
* 只負責讀取圖片的線程
*/
class LoadImage extends Thread {
int imgIndex = 0;
public void run() {
while (true) {
bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(),
imgList.get(imgIndex));
imgIndex++;
if (imgIndex == imgList.size())//如果到盡頭則重新讀取
imgIndex = 0;
}
}
};
}
希望本文所述示例能對大家進行Android的SurfaceView與多線程的混搭編程有所幫助。
 Android App仿QQ制作Material Design風格沉浸式狀態欄
Android App仿QQ制作Material Design風格沉浸式狀態欄
一、概述近期注意到QQ新版使用了沉浸式狀態欄,ok,先聲明一下效果圖:恩,接下來正題。首先只有大於等於4.4版本支持這個半透明狀態欄的效果,但是4.4和5.0的顯示效果有
 谷歌推薦的Android圖片加載庫(Glide)介紹
谷歌推薦的Android圖片加載庫(Glide)介紹
在過去的谷歌開發者峰會,谷歌給我們介紹了一個圖片加載庫,bumptech開發的一個名字叫Glide 的Android圖像加載庫。它已被用於許多谷歌開源項目,到現在為止,包
 Android ORMLite數據庫詳解
Android ORMLite數據庫詳解
OrmLite是一個數據庫操作輔助的開源框架,底層還是Sqlite。O-R-M是Object relational mapping(對象關系映射)的縮寫,即業務實體對象與
 Android學習之——JAVA中的Object
Android學習之——JAVA中的Object
一、Object java.lang.Object 是所有類的根類,每個 Java 對象都是一個 Object。本文主要說明的是 Object 類中的一組方法,這些方法是