經常看到Android的消息用法大概為:
Looper.prepare()
Looper.myLooper();
xxxHandler = new Handler() {
handleMessage(Message msg){...}
};
Looper.loop();
剛開始搞不清楚狀況, 根據名字完全看不出有什麼關系的兩個類,到底如何進行消息傳遞呢? 只是知道就這麼用就沒問題的, 應該不少人跟我一樣吧.
如然有興趣來解刨一下吧.
Looper.prepare(); 裡面有一句 sThreadLocal.set(new Looper());
這裡就new 了一個Looper了, 然後放到ThreadLocal裡面, 這是個線程數據共享的一個類.
private Looper() {
mQueue = new MessageQueue();
mRun = true;
mThread = Thread.currentThread();
}
在這裡面就傳遞了當前的工作線程的信息,並且new了一個message queue,就是消息隊列嘛, 用來接收消息的容器.
public static Looper myLooper() {
return sThreadLocal.get();
}
這個函數就返回了上面創建的那個new Looper();
public Handler() {
...
mLooper = Looper.myLooper();
mQueue = mLooper.mQueue;
...
}
在這裡就把當前線程的Looper賦給Handler了, 這就發生關系了.
可能有同學還會有疑問, 上面是兩個類的不同的語句Looper.myLooper();怎麼得到的是同一個呢?
那就分析一下吧;
在Looper類裡面有個全局的靜態容器
static final ThreadLocal<Looper> sThreadLocal = new ThreadLocal<Looper>();
再進入ThreadLocal類裡面看
public void set(T value) {
Thread currentThread = Thread.currentThread();
Values values = values(currentThread);
if (values == null) {
values = initializeValues(currentThread);
}
values.put(this, value);
}
在這裡就把當前的線程的相關信息設進去了.
看看get()函數;
public T get() {
// Optimized for the fast path.
Thread currentThread = Thread.currentThread();
Values values = values(currentThread);
if (values != null) {
Object[] table = values.table;
int index = hash & values.mask;
if (this.reference == table[index]) {
return (T) table[index + 1];
}
} else {
values = initializeValues(currentThread);
}
return (T) values.getAfterMiss(this);
}
再這裡就返回了當前線程的相關信息.
因為ThreadLocal是個模板容器, 聲明為ThreadLocal<T>
在Looper中聲明為ThreadLocal<Looper> , 所以 T == Looper .
簡單的翻譯一下上面的get()和set()吧;
public void set(Looper value) {
values.put(this, value);
}
public void Looper get() {
return values.get(this);
}
這樣就很清晰了, 關系就是這麼發生的. 回頭梳理一下吧.
Looper.prepare()
Looper.myLooper();
xxxHandler = new Handler(){ handleMessage(Message msg){...} };
Looper.loop();
等價於
Looper.prepare() { sThreadLocal.set(currentThread, new Looper(); }
Looper.myLooper() { sThreadLocal.get(currentThread) }
new Handle(){
...
mLooper = sThreadLocal.get(currentThread);
mQueue = mLooper.mQueue;
...}
關系發生了,這時候就可以通過Message進行通信了, 這就不多說了.
 Android個人中心的頭像上傳,圖片編碼及截取實例
Android個人中心的頭像上傳,圖片編碼及截取實例
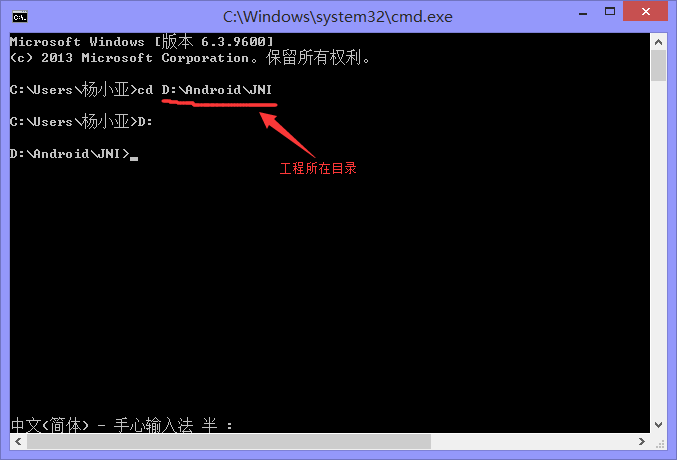 Android NDK開發簡單程序分享(Hello Word!)
Android NDK開發簡單程序分享(Hello Word!)
 Android 清楚程序緩存
Android 清楚程序緩存
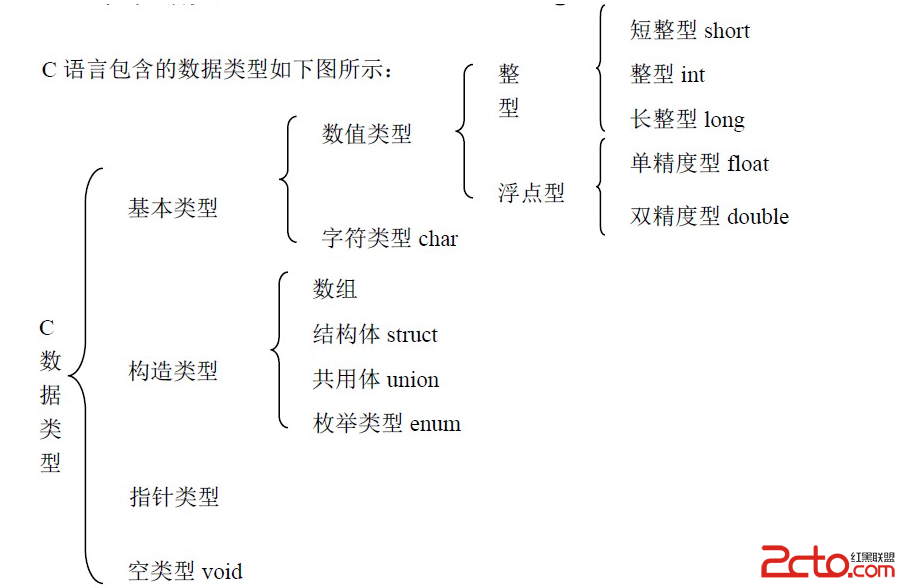 Android For JNI(二)——C語言中的數據類型,輸出,輸入函數以及操作內存地址,內存修改器
Android For JNI(二)——C語言中的數據類型,輸出,輸入函數以及操作內存地址,內存修改器