本課將告訴你如何通過後台加載來加速應用啟動和降低應用耗電。
後台跑服務
除非你做了特殊指定,否則在應用中的大部分前台操作都是在一個特殊的UI線程裡面進行的。這有可能會導致一些問題,因為長時間運行的操作會影響到你應用的響應速度。為了避免這個問題,android框架提供了一系列幫助你在後台通過線程推遲加載的功能,被使用得最多的非IntentService莫屬了。
本課將向你描述如何實現一個IntentService,發送請求操作並向其它組件報告結果。
創建一個後台服務
本課將直觀地告訴你如何通過後台線程執行操作,通過它來執行耗時操作從而避免你的界面無法及時響應的問題。IntentService是不會受窗口生命周期回調的影響的,所以在繼續運行它之前,你需要關閉AsyncTask。
每個IntentService都是有限制條件的:
(1)它不可以直接和應用的界面進行交互,為了將操作結果返回給界面,你需要將他們發送到窗口;
(2) 工作請求是按順序進行的,當已經有一個操作在IntentService中運行時,如果這是你發送另外一個請求,需要等到第一個操作執行完畢後才會繼續後面的請求;
(3) 在IntentService中運行的操作是不可以被中斷的。
然而,多數情況下一個IntentService是後台操作最簡單的處理方式。
本課將告訴你如何創建你自己的IntentService子類,還會向你展示如何創建一個必要的onHandleIntent()回調。最後,將告訴你如何在清單文件中定義IntentService。
創建一個IntentService
為了在你的應用中創建一個IntentService組件,需要定義一個繼承於IntentService的類並復寫其onHandleIntent()方法,比如:
[java]
<span style="font-size:18px">public class RSSPullService extends IntentService {
@Override
protected void onHandleIntent(Intent workIntent) {
// Gets data from the incoming Intent
String dataString = workIntent.getDataString();
...
// Do work here, based on the contents of dataString
...
}
}
</span>
注意,對於任何一個Service都會回調的那些方法,比如onStartCommand(),都會自動地被IntentService引用。在一個IntentService中,你應該避免復寫這些回調方法。
在清單文件Manifest中定義IntentService
IntentService同樣需要在你應用的清單文件中有一個入口,通過在<application>標簽下聲明<service>的方式來為IntentService提供入口:
[java]
<span style="font-size:18px"><application
android:icon="@drawable/icon"
android:label="@string/app_name">
...
<!--
Because android:exported is set to "false",
the service is only available to this app.
-->
<service
android:name=".RSSPullService"
android:exported="false"/>
...
<application/>
</span>
上例中的“android:name”屬性指定了IntentService的類名。
注意,<service>標簽沒有包含IntentFilter過濾器。該窗口通過一個明確地Intent向服務發送工作請求,所以不需要任何過濾器。也就是說,只有在同一個應用內,或者是有相同ID的其它應用才可以訪問這個服務。
現在你有了基本的IntentService類,你可以通過Intent對象發送工作請求了。
向後台服務發送工作請求
之前的課程向我們展示了如何創建一個IntentService類。本課將告訴你如何通過發送Intent來觸發IntentService執行一個操作。這個Intent可以包含IntentService需要處理的可選數據。你可以在Activity或者Fragment的任何一個地方向IntentService傳遞Intent。
創建並發送一個工作請求給IntentService
為了創建一個工作請求並將其發送到IntentService,需要創建一個明確地Intent來添加工作請求數據,然後通過調用IntentService的StartService()方法來發送它。
具體請看下面實例:
1、為IntentService的子類RSSPullService創建一個新的、明確地Intent。
[java]
<span style="font-size:18px">/*
* Creates a new Intent to start the RSSPullService
* IntentService. Passes a URI in the
* Intent's "data" field.
*/
mServiceIntent = new Intent(getActivity(), RSSPullService.class);
mServiceIntent.setData(Uri.parse(dataUrl));
</span>
2、調用startService()方法
[java]
<span style="font-size:18px">// Starts the IntentService
getActivity().startService(mServiceIntent);
</span>
注意,你可以在Activity或者Fragment的任何地方發送工作請求。比如,如果你需要首先獲取用戶輸入,你可以在按鈕點擊或者類似於手勢操作的回調中來發送請求。
一旦你調用了startService()方法,IntentService會處理定義在onHandleIntent()方法中的工作,然後自己停止。
下一步是向原始的Activity或者Fragment報告工作請求的結果,下一個將告訴你如何通過BroadcastReceiver來實現這個功能。
報告工作狀態
本課將告訴你如何將後台服務的請求工作狀態報告給發送請求的組件。這將允許你,比如報告一個窗口對象的UI更新請求狀態。一般推薦使用LocalBroadcastManager來發送和接收這些狀態,但這僅限於在你自己應用的各組件中廣播Intent。
從IntentService報告狀態
為了在IntentService中向其他組件發送工作請求狀態,首先你需要創建一個包含狀態信息數據的Intent,作為了一個選項,你可以在Intent中添加一個操作或者數據URI。
下一步,通過調用LocalBroadcastManager.sendBroadcast()方法來發送Intent,在你應用中發送到其它組件的Intent是注冊過的。通過LocalBroadcastManager的getInstance()方法來實例化LocalBroadcastManager。
比如:
[java]
<span style="font-size:18px">public final class Constants {
...
// Defines a custom Intent action
public static final String BROADCAST_ACTION =
"com.example.android.threadsample.BROADCAST";
...
// Defines the key for the status "extra" in an Intent
public static final String EXTENDED_DATA_STATUS =
"com.example.android.threadsample.STATUS";
...
}
public class RSSPullService extends IntentService {
...
/*
* Creates a new Intent containing a Uri object
* BROADCAST_ACTION is a custom Intent action
*/
Intent localIntent =
new Intent(Constants.BROADCAST_ACTION)
// Puts the status into the Intent
.putExtra(Constants.EXTENDED_DATA_STATUS, status);
// Broadcasts the Intent to receivers in this app.
LocalBroadcastManager.getInstance(this).sendBroadcast(localIntent);
...
}
</span>
從IntentService接收廣播狀態
為了能夠接收Intent對象,需要定義一個BroadcastReciver的子類。在該類中,實現BroadcastReceiver的onReceive()回調方法,在接收到一個Intent時LocalBroadcastManager會引用它。LocalBroadcastManager將接收到的Intent傳遞到BroadcastReceiver的onRecive()方法中。
比如:
[java]
<span style="font-size:18px">// Broadcast receiver for receiving status updates from the IntentService
private class ResponseReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver
{
// Prevents instantiation
private DownloadStateReceiver() {
}
// Called when the BroadcastReceiver gets an Intent it's registered to receive
@
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
...
/*
* Handle Intents here.
*/
...
}
}
</span>
一旦你定義了BroadcastReceiver,你就可以通過指定動作、類別和數據等過濾信息來匹配它了。為了達到這種效果,你需要創建一個IntentFilter。下面的代碼向你展示了如何定義filter:
[java]
<span style="font-size:18px">// Class that displays photos
public class DisplayActivity extends FragmentActivity {
...
public void onCreate(Bundle stateBundle) {
...
super.onCreate(stateBundle);
...
// The filter's action is BROADCAST_ACTION
IntentFilter mStatusIntentFilter = new IntentFilter(
Constants.BROADCAST_ACTION);
// Adds a data filter for the HTTP scheme
mStatusIntentFilter.addDataScheme("http");
...
</span>
為了在系統中注冊BroadcastReceiver和IntentFilter,你需要實例化LocalBroadcastManager並調用其registerReceiver()方法。下例展示的是如何注冊BroadcastReceiver和其過濾器的過程:
[java]
<span style="font-size:18px">// Instantiates a new DownloadStateReceiver
DownloadStateReceiver mDownloadStateReceiver =
new DownloadStateReceiver();
// Registers the DownloadStateReceiver and its intent filters
LocalBroadcastManager.getInstance(this).registerReceiver(
mDownloadStateReceiver,
mStatusIntentFilter);
...
</span>
一個BroadcastReceiver可以操作多於一種類型的廣播Intent對象,每個類型都有自己的操作。這種特征允許你在不同的action中運行代碼,不需要為每個action都定義一個BroadcastReceiver。為了為同一個BroadcastReceiver定義其它的IntentFilter,創建IntentFilter並重復調用registerReceiver()。比如:
[java]
<span style="font-size:18px">/*
* Instantiates a new action filter.
* No data filter is needed.
*/
statusIntentFilter = new IntentFilter(Constants.ACTION_ZOOM_IMAGE);
...
// Registers the receiver with the new filter
LocalBroadcastManager.getInstance(getActivity()).registerReceiver(
mDownloadStateReceiver,
mIntentFilter);
</span>
發送一個廣播Intent不會start或者resume一個窗口。即使你的窗口在後台,窗口中的BroadcastReceiver都是可以接收並處理Intent對象的,但並不會強制讓你的應用處於前台。當你的窗口處於後台時如果你想向用戶通知這個事件,你可以使用Notification。在接收一個廣播Intent時是絕不會啟動一個窗口的。
在後台加載數據
對於你需要顯示的數據,但有需要花時間去通過ContentProvider查詢時,如果你直接在窗口層面去執行查詢操作,可能會嚴重影響界面的響應速度,比如ANR。就算不會ANR,用戶也會明顯地感覺到卡頓的現象。為了避免這種問題,你應該在非UI線程裡面來初始化查詢操作,直到等待它結束後再窗口顯示結果。
你可以通過一個對象在後台執行查詢同步,待查詢結束後更新UI。這個對象就是CursorLoader。除了初始化後台查詢外,當查詢有變動時CursorLoader會自動地重新查詢數據。
本課將向你描述如何通過CursorLoader執行後台查詢操作。在課程中用到了V1-SupportLibrary版本的類,它支持V1.6及以上的版本執行此操作。
通過CursorLoader執行查詢操作
通過CursorLoader在後台執行同步查詢有別於ContentProvider,它會返回結果到調用它的Activity或者FragmentActivity。這樣就允許Activity或者FragmentActivity在後台查詢數據時可以和用戶交互。
定義一個使用CursorLoader的窗口
為了能夠在Activity或者FragmentActivity中使用CursorLoader,需要使用LoaderCallbacks<Cursor>接口,CursorLoader引用接口定義的回調和類進行交互;本課和下一課將詳細描述每一個回調。
比如,下面的實例向你展示如何使用依賴庫中的CursorLoader定義FragmentActivity。通過擴展FragmentActivity,可以達到通過Fragment使用CursorLoader一樣的效果。
[java]
<span style="font-size:18px">public class PhotoThumbnailFragment extends FragmentActivity implements
LoaderManager.LoaderCallbacks<Cursor> {
...
}
</span>
初始化查詢操作
為了初始化查詢操作,你需要調用LoadManager的initLoader()方法,它初始化後台框架,你可以在用戶進入查詢的數據後執行該操作,或者,如果你不需要任何數據,你可以在onCreate()或者onCreateView()中執行該操作,比如:
[java]
<span style="font-size:18px">// Identifies a particular Loader being used in this component
private static final int URL_LOADER = 0;
...
/* When the system is ready for the Fragment to appear, this displays
* the Fragment's View
*/
public View onCreateView(
LayoutInflater inflater,
ViewGroup viewGroup,
Bundle bundle) {
...
/*
* Initializes the CursorLoader. The URL_LOADER value is eventually passed
* to onCreateLoader().
*/
getLoaderManager().initLoader(URL_LOADER, null, this);
...
}</span>
注意:getLoaderManager()方法僅僅適用於Fragment類,為了能夠在FragmentActivity中獲取LoaderManager,需通過調用getSupportLoaderManager()。
開始查詢
為了能夠盡快地初始化後台框架,系統會調用你類中的onCreateLoader()方法,為了能夠開始查詢,需要從該方法中反饋一個CursorLoader對象。你可以初始化一個空的CursorLoader對象然後通過它來定義查詢操作,或者你可以在初始化對象的同時定義查詢操作。
[java]
<span style="font-size:18px">/*
* Callback that's invoked when the system has initialized the Loader and
* is ready to start the query. This usually happens when initLoader() is
* called. The loaderID argument contains the ID value passed to the
* initLoader() call.
*/
@Override
public Loader<Cursor> onCreateLoader(int loaderID, Bundle bundle)
{
/*
* Takes action based on the ID of the Loader that's being created
*/
switch (loaderID) {
case URL_LOADER:
// Returns a new CursorLoader
return new CursorLoader(
getActivity(), // Parent activity context
mDataUrl, // Table to query
mProjection, // Projection to return
null, // No selection clause
null, // No selection arguments
null // Default sort order
);
default:
// An invalid id was passed in
return null;
}
}
</span>
一旦生成了後台框架的對象,系統就會開始在後台執行查詢操作,當查詢操作執行完成後,後台框架會調用onLoadFinished()方法,這將在下一個作詳細討論。
處理查詢結果
正如前面課程所述,你應該在你所實現類的onCreateLoader()方法中通過CursorLoader加載你的數據,加載器會在你Acitivity或者FragmentActivity的LoaderCallbacks.onLoadFinished()方法中返回查詢結果。該方法的其中一個入參為包含查詢結果的游標。你可以使用這個對象來更新你的數據或者做其它操作。
除了onCreateLoader()和onLoadFinished()方法,你還需要實現onLoaderReset()方法,這個方法會在數據更新更新時被調用,當數據變化時,框架會重新執行當前的查詢操作。
處理查詢結果
為了顯示從CursorLoader返回的游標數據,你需要自定義一個繼承於AdapterView的視圖,並為這個視圖定義一個繼承於CursorAdapter的適配器。然後系統會自動地將數據從游標移到視圖。
在你顯示任何數據之前你可以為視圖和適配器建立連接,然後再onLoadFinished()方法中將游標移到適配器。當你將游標移到適配器後,系統會自動地更新視圖。在游標的數據有改動時同樣會更新視圖。
比如:
[java]
<span style="font-size:18px">public String[] mFromColumns = {
DataProviderContract.IMAGE_PICTURENAME_COLUMN
};
public int[] mToFields = {
R.id.PictureName
};
// Gets a handle to a List View
ListView mListView = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.dataList);
/*
* Defines a SimpleCursorAdapter for the ListView
*
*/
SimpleCursorAdapter mAdapter =
new SimpleCursorAdapter(
this, // Current context
R.layout.list_item, // Layout for a single row
null, // No Cursor yet
mFromColumns, // Cursor columns to use
mToFields, // Layout fields to use
0 // No flags
);
// Sets the adapter for the view
mListView.setAdapter(mAdapter);
...
/*
* Defines the callback that CursorLoader calls
* when it's finished its query
*/
@Override
public void onLoadFinished(Loader<Cursor> loader, Cursor cursor) {
...
/*
* Moves the query results into the adapter, causing the
* ListView fronting this adapter to re-display
*/
mAdapter.changeCursor(cursor);
}</span>
刪除舊的游標信息
當游標非法時CursorLoader會被重置,這多數情況發生在游標的數據有改動時,在重新執行查詢操作前,框架會調用你所實現的onLoaderReset()方法。在這個回調中,你應該刪除當前游標的所有信息來避免內存洩露。一旦結束回調onLoaderReset()方法後,CursorLoader會重新執行查詢操作。
比如:
[java]
<span style="font-size:18px">/*
* Invoked when the CursorLoader is being reset. For example, this is
* called if the data in the provider changes and the Cursor becomes stale.
*/
@Override
public void onLoaderReset(Loader<Cursor> loader) {
/*
* Clears out the adapter's reference to the Cursor.
* This prevents memory leaks.
*/
mAdapter.changeCursor(null);
}
</span>
管理設備的激活狀態
當一個android設備處於空閒狀態時,它首先會變暗,然後會關屏,最終會讓CPU停止工作。這樣處理是為了避免設備的電池被快速地耗盡,然而有些時候你的應用需要一些不同的表現:
(1)游戲或者電影應用可能需要保持屏幕常亮;
(2)有些應用雖然不需要屏幕常亮,但在CPU執行完核心操作之前同樣需要保持程序運行。
本課的目的是告訴你在避免電池被快速耗盡的情況下如何保持設備處於激活狀態。
保持設備處於激活狀態
為了避免電池被耗盡,android設備會在處於空閒狀態時立即切換到休眠狀態。然而,有些時候一個應用需要保持屏幕常亮或者CPU直到某些事情被處理完成。
你該采取什麼操作取決於你應用的需求。然而,通用的規則是你應該使用最輕量級的操作來處理你的應用程序,使你的應用減少對系統資源的占用。下面將向你描述通過怎樣地操作來使得你對應用的處理和系統默認的休眠行為相容。
保持屏幕常亮
某些應用需要保持屏幕常亮,比如游戲或者電影應用。最好的方式是在你的窗口中使用FLAG_KEEP_SCREEN_ON屬性(只在一個窗口,絕不是在一個服務或者其它應用組件中),比如:
[java]
<span style="font-size:18px">public class MainActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
getWindow().addFlags(WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_KEEP_SCREEN_ON);
}
</span>
這種先進的處理方式有別於喚醒鎖,它不需要特殊的權限,平台會正確地管理應用之間的切換,你不需要擔心自己的應用沒有釋放沒有使用的資源。
實現該功能的另一種思路是在你應用xml文件中使用android:keepScreenOn屬性:
[html]
<span style="font-size:18px"><RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:keepScreenOn="true">
...
</RelativeLayout>
</span>
使用andorid:keepScreenOn=”true”和使用FLAG_KEEP_SCREEN_ON是一樣的效果。你可以使用適合於你應用的任何一種方式。通過在程序中設置你窗口常亮狀態的優勢是:它可以清楚這個標志,從而可以關閉屏幕。
保持CPU持續工作
如果你希望在設備休眠之前CPU能夠完成需要處理的工作,你可以使用一個叫喚醒鎖的PowerManager系統服務。喚醒鎖允許你的應用可以控制主機設備電源的狀態。
創建和保持喚醒鎖會在一定程度上對電池的壽命有所影響,因此你應該只在非常有必要的情況下使用它,並盡量控制使用時間。比如,你絕不應該在一個窗口中使用喚醒鎖,正如上面所描述的那樣,如果你想保持當前窗口的屏幕常亮,你可以使用FLAG_KEEP_SCREEN_ON。
應該使用喚醒鎖的情況可能就是後台服務在屏幕關閉時需要通過喚醒鎖保持CPU持續工作。再次聲明,盡量限制它的使用時間,因為它會影響到電池的壽命。
為了使用喚醒鎖,首先需要在清單文件中添加WAKE_LOCK權限:
[html]
<span style="font-size:18px"><uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WAKE_LOCK" /></span>
如果你的應用包含一個使用服務處理某些事情的廣播接收器,你可以通過WakefulBroadcastReceiver來管理你的喚醒鎖,正如使用WakefulBroadcastReceiver一課中所描述的那樣,這是一個比較好的處理方式。如果你的應用沒有遵循這種方式,通過下面的代碼你可以直接設置喚醒鎖:
[java]
<span style="font-size:18px">PowerManager powerManager = (PowerManager) getSystemService(POWER_SERVICE);
Wakelock wakeLock = powerManager.newWakeLock(PowerManager.PARTIAL_WAKE_LOCK,
"MyWakelockTag");
wakeLock.acquire();
</span>
為了釋放喚醒鎖,你需要調用wakelock的release()方法。它將釋放你對CPU的聲明,在你的應用結束工作後盡快關閉喚醒鎖避免電池被耗盡。
使用WakefulBroadcastReceiver
使用廣播接收器和服務可以讓你很好地管理後台任務的生命周期。
一個WakefulBroadcastReceiver是廣播接收器的一個特殊類型,它可以創建和管理你應用的PARITAL_WAKE_LOCK。一個WakeBroadcastReceiver接收到廣播後將工作傳遞給Service(一個典型的IntentService),直到確保設備沒有休眠。如果你在交接工作給服務的時候沒有保持喚醒鎖,在工作還沒完成之前就允許設備休眠的話,將會出現一些你不願意看到的情況。
要使用WakefulBroadcastReceiver的第一步是在清單文件中添加它,和其它廣播接收器是一樣的:
[html]
<span style="font-size:18px"><receiver android:name=".MyWakefulReceiver"></receiver></span>
接下來是在代碼中通過startWakefulService()來啟動MyIntentService。和starService()方法相比,除了在服務啟動時可以保持喚醒鎖外,通過startWakefulService()方法傳遞的Intent可以保持一個額外的喚醒鎖:
[java]
<span style="font-size:18px">public class MyWakefulReceiver extends WakefulBroadcastReceiver {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
// Start the service, keeping the device awake while the service is
// launching. This is the Intent to deliver to the service.
Intent service = new Intent(context, MyIntentService.class);
startWakefulService(context, service);
}
}</span>
當服務執行完成後,系統會調用MyWakefulReceiver的completeWakefulIntent()方法來釋放喚醒鎖,completeWakefulIntent()方法攜帶的參數是從WakefulBroadcastReceiver傳遞過來的intent:
[java]
<span style="font-size:18px">public class MyIntentService extends IntentService {
public static final int NOTIFICATION_ID = 1;
private NotificationManager mNotificationManager;
NotificationCompat.Builder builder;
public MyIntentService() {
super("MyIntentService");
}
@Override
protected void onHandleIntent(Intent intent) {
Bundle extras = intent.getExtras();
// Do the work that requires your app to keep the CPU running.
// ...
// Release the wake lock provided by the WakefulBroadcastReceiver.
MyWakefulReceiver.completeWakefulIntent(intent);
}
}</span>
 無需root,教你智能電視和智能機頂盒系統大瘦身清緩存方法
無需root,教你智能電視和智能機頂盒系統大瘦身清緩存方法
 Android使用ViewDragHelper實現仿QQ6.0側滑界面(一)
Android使用ViewDragHelper實現仿QQ6.0側滑界面(一)
 Android——數據存儲(四種方式之二)讀寫SD卡
Android——數據存儲(四種方式之二)讀寫SD卡
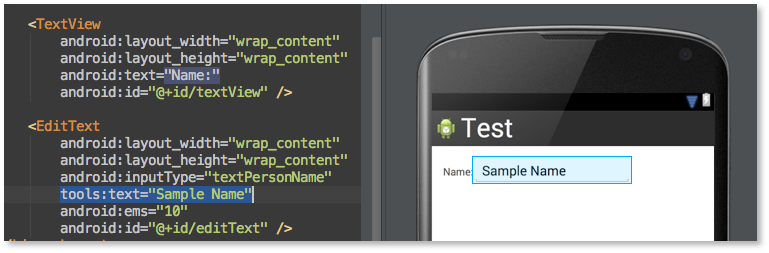 Android Studio使用小技巧:布局預覽時填充數據
Android Studio使用小技巧:布局預覽時填充數據