在Android開發中為了inflate一個布局文件,大體有2種方式,如下所示:
// 1. get a instance of LayoutInflater, then do whatever you want
LayoutInflater inflater = (LayoutInflater) context.getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
// 2. you're in some View class, then just call View's static inflate method
View.inflate(context, R.layout.xxx_xml, someViewGroup/null);
我們來看看這2種方式的具體源碼:
復制代碼
<!-- View.java -->
/**
* Inflate a view from an XML resource. This convenience method wraps the {@link
* LayoutInflater} class, which provides a full range of options for view inflation.
*
* @param context The Context object for your activity or application.
* @param resource The resource ID to inflate
* @param root A view group that will be the parent. Used to properly inflate the
* layout_* parameters.
* @see LayoutInflater
*/
public static View inflate(Context context, int resource, ViewGroup root) {
LayoutInflater factory = LayoutInflater.from(context);
return factory.inflate(resource, root);
}
<!-- LayoutInflater.java -->
/**
* Obtains the LayoutInflater from the given context.
*/
public static LayoutInflater from(Context context) {
LayoutInflater LayoutInflater =
(LayoutInflater) context.getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
if (LayoutInflater == null) {
throw new AssertionError("LayoutInflater not found.");
}
return LayoutInflater;
}
復制代碼
現在我們看到實質上都是方法1中的做法,View.inflate只是個helper方法而已(少敲幾行代碼)。那麼我們就先來看看
Context.getSystemService的具體實現,這裡我們直接去ContextImpl.java文件中的相關代碼:
復制代碼
/**
* Override this class when the system service constructor needs a
* ContextImpl. Else, use StaticServiceFetcher below.
*/
/*package*/ static class ServiceFetcher {
int mContextCacheIndex = -1;
/**
* Main entrypoint; only override if you don't need caching.
*/
public Object getService(ContextImpl ctx) {
ArrayList<Object> cache = ctx.mServiceCache;
Object service;
synchronized (cache) {
if (cache.size() == 0) {
// Initialize the cache vector on first access.
// At this point sNextPerContextServiceCacheIndex
// is the number of potential services that are
// cached per-Context.
for (int i = 0; i < sNextPerContextServiceCacheIndex; i++) {
cache.add(null);
}
} else {
service = cache.get(mContextCacheIndex); // 先從cache中找,
if (service != null) { // 如果已經存在了直接返回
return service;
}
}
service = createService(ctx); // 否則創建並加入到cache中,只會調用1次
cache.set(mContextCacheIndex, service);
return service;
}
}
/**
* Override this to create a new per-Context instance of the
* service. getService() will handle locking and caching.
*/
public Object createService(ContextImpl ctx) {
throw new RuntimeException("Not implemented");
}
}
/**
* Override this class for services to be cached process-wide.
*/
abstract static class StaticServiceFetcher extends ServiceFetcher {
private Object mCachedInstance;
@Override
public final Object getService(ContextImpl unused) {
synchronized (StaticServiceFetcher.this) {
Object service = mCachedInstance;
if (service != null) {
return service;
}
return mCachedInstance = createStaticService();
}
}
public abstract Object createStaticService(); // 它不需要ContextImpl參數
}
private static final HashMap<String, ServiceFetcher> SYSTEM_SERVICE_MAP =
new HashMap<String, ServiceFetcher>(); // 全局system service的map
private static int sNextPerContextServiceCacheIndex = 0;
private static void registerService(String serviceName, ServiceFetcher fetcher) {
if (!(fetcher instanceof StaticServiceFetcher)) {
fetcher.mContextCacheIndex = sNextPerContextServiceCacheIndex++;
}
SYSTEM_SERVICE_MAP.put(serviceName, fetcher); // 放到全局的靜態map中
}
// 還有很多registerService的調用,這裡都省略了,我們現在只關心LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE
registerService(LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE, new ServiceFetcher() {
public Object createService(ContextImpl ctx) { // 我們前一篇文章中提到過會new一個
return PolicyManager.makeNewLayoutInflater(ctx.getOuterContext()); // PhoneLayoutInflater的對象返回
}});
復制代碼
到這裡我們就清楚了Context.getSystemService方法的具體實現了,接下來我們將注意力轉移到LayoutInflater類。關鍵代碼如下:
復制代碼
/**
* Obtains the LayoutInflater from the given context.
*/
public static LayoutInflater from(Context context) {
LayoutInflater LayoutInflater =
(LayoutInflater) context.getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
if (LayoutInflater == null) {
throw new AssertionError("LayoutInflater not found.");
}
return LayoutInflater;
}
/**
* Inflate a new view hierarchy from the specified xml resource. Throws
* {@link InflateException} if there is an error.
*
* @param resource ID for an XML layout resource to load (e.g.,
* <code>R.layout.main_page</code>)
* @param root Optional view to be the parent of the generated hierarchy.
* @return The root View of the inflated hierarchy. If root was supplied,
* this is the root View; otherwise it is the root of the inflated
* XML file.
*/
public View inflate(int resource, ViewGroup root) { // 實際上調用3個參數的版本,從這裡我們可以看出客戶端代碼
return inflate(resource, root, root != null); // 沒必要這樣寫(root!= null):inflate(resource, root, true);
}
/**
* Inflate a new view hierarchy from the specified xml node. Throws
* {@link InflateException} if there is an error. *
* <p>
* <em><strong>Important</strong></em> For performance
* reasons, view inflation relies heavily on pre-processing of XML files
* that is done at build time. Therefore, it is not currently possible to
* use LayoutInflater with an XmlPullParser over a plain XML file at runtime.
*
* @param parser XML dom node containing the description of the view
* hierarchy.
* @param root Optional view to be the parent of the generated hierarchy.
* @return The root View of the inflated hierarchy. If root was supplied,
* this is the root View; otherwise it is the root of the inflated
* XML file.
*/
public View inflate(XmlPullParser parser, ViewGroup root) { // 不太常用,我們一般使用layout文件的版本,但實質都一樣
return inflate(parser, root, root != null); // 下面的代碼中inflate一個include tag時調用了此版本
}
/**
* Inflate a new view hierarchy from the specified xml resource. Throws
* {@link InflateException} if there is an error.
*
* @param resource ID for an XML layout resource to load (e.g.,
* <code>R.layout.main_page</code>)
* @param root Optional view to be the parent of the generated hierarchy (if
* <em>attachToRoot</em> is true), or else simply an object that
* provides a set of LayoutParams values for root of the returned
* hierarchy (if <em>attachToRoot</em> is false.)
* @param attachToRoot Whether the inflated hierarchy should be attached to
* the root parameter? If false, root is only used to create the
* correct subclass of LayoutParams for the root view in the XML.
* @return The root View of the inflated hierarchy. If root was supplied and
* attachToRoot is true, this is root; otherwise it is the root of
* the inflated XML file.
*/
public View inflate(int resource, ViewGroup root, boolean attachToRoot) {
if (DEBUG) System.out.println("INFLATING from resource: " + resource);
XmlResourceParser parser = getContext().getResources().getLayout(resource);
try {
return inflate(parser, root, attachToRoot);
} finally {
parser.close();
}
}
/**
* Inflate a new view hierarchy from the specified XML node. Throws
* {@link InflateException} if there is an error.
* <p>
* <em><strong>Important</strong></em> For performance
* reasons, view inflation relies heavily on pre-processing of XML files
* that is done at build time. Therefore, it is not currently possible to
* use LayoutInflater with an XmlPullParser over a plain XML file at runtime.
*
* @param parser XML dom node containing the description of the view
* hierarchy.
* @param root Optional view to be the parent of the generated hierarchy (if
* <em>attachToRoot</em> is true), or else simply an object that
* provides a set of LayoutParams values for root of the returned
* hierarchy (if <em>attachToRoot</em> is false.)
* @param attachToRoot Whether the inflated hierarchy should be attached to
* the root parameter? If false, root is only used to create the
* correct subclass of LayoutParams for the root view in the XML.
* @return The root View of the inflated hierarchy. If root was supplied and
* attachToRoot is true, this is root; otherwise it is the root of
* the inflated XML file.
*/
public View inflate(XmlPullParser parser, ViewGroup root, boolean attachToRoot) { // 這是最終調用的版本
synchronized (mConstructorArgs) { // 進入同步塊
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "inflate");
final AttributeSet attrs = Xml.asAttributeSet(parser);
Context lastContext = (Context)mConstructorArgs[0];
mConstructorArgs[0] = mContext;
View result = root; // 此方法最後的返回值,初始化為傳入的root
try {
// Look for the root node.
int type;
while ((type = parser.next()) != XmlPullParser.START_TAG &&
type != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT) {
// Empty
}
// 能走到這裡,說明type是START_TAG 或 END_DOCUMENT
if (type != XmlPullParser.START_TAG) { // 如果一開始就是END_DOCUMENT,那說明xml文件有問題
throw new InflateException(parser.getPositionDescription()
+ ": No start tag found!");
}
// 能到這裡,那type一定是START_TAG,也就是xml文件裡的root node
final String name = parser.getName(); // 獲得當前start tag的name
if (DEBUG) {
System.out.println("**************************");
System.out.println("Creating root view: "
+ name);
System.out.println("**************************");
}
if (TAG_MERGE.equals(name)) { // 處理merge tag的情況
if (root == null || !attachToRoot) { // root必須非空且attachToRoot為true,否則拋異常結束
throw new InflateException("<merge /> can be used only with a valid "
+ "ViewGroup root and attachToRoot=true"); // 因為merge的xml並不代表某個具體的view,只是將它
} // 包起來的其他xml的內容加到某個上層ViewGroup中
rInflate(parser, root, attrs, false); // 遞歸的inflate
} else {
// Temp is the root view that was found in the xml
View temp; // xml文件中的root view
if (TAG_1995.equals(name)) {
temp = new BlinkLayout(mContext, attrs);
} else {
temp = createViewFromTag(root, name, attrs); // 根據tag節點創建view對象
}
ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = null;
if (root != null) {
if (DEBUG) {
System.out.println("Creating params from root: " +
root);
}
// Create layout params that match root, if supplied
params = root.generateLayoutParams(attrs); // 根據root生成合適的LayoutParams實例
if (!attachToRoot) { // 如果不attach的話就調用view的setLayoutParams方法
// Set the layout params for temp if we are not
// attaching. (If we are, we use addView, below)
temp.setLayoutParams(params);
}
}
if (DEBUG) {
System.out.println("-----> start inflating children");
}
// Inflate all children under temp
rInflate(parser, temp, attrs, true); // 遞歸inflate剩下的所有children
if (DEBUG) {
System.out.println("-----> done inflating children");
}
// We are supposed to attach all the views we found (int temp)
// to root. Do that now.
if (root != null && attachToRoot) { // root非空且指定了要attachToRoot
root.addView(temp, params); // 將xml文件的root view 加到用戶提供的root裡
}
// Decide whether to return the root that was passed in or the
// top view found in xml.
if (root == null || !attachToRoot) {
result = temp; // 否則我們將返回xml裡發現的root view:temp,而不是方法中傳遞進來的root對象
}
}
} catch (XmlPullParserException e) {
InflateException ex = new InflateException(e.getMessage());
ex.initCause(e);
throw ex;
} catch (IOException e) {
InflateException ex = new InflateException(
parser.getPositionDescription()
+ ": " + e.getMessage());
ex.initCause(e);
throw ex;
} finally {
// Don't retain static reference on context.
mConstructorArgs[0] = lastContext;
mConstructorArgs[1] = null;
}
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
return result; // 返回參數root或xml文件裡的root view
}
}
復制代碼
接下來我們看看inflate各種不同節點的方法:
復制代碼
/**
* Recursive method used to descend down the xml hierarchy and instantiate
* views, instantiate their children, and then call onFinishInflate().
*/
void rInflate(XmlPullParser parser, View parent, final AttributeSet attrs,
boolean finishInflate) throws XmlPullParserException, IOException { // 深度優先inflate,所有才能保證你在onFinish
// Inflate()裡可以通過findViewById找到已經創建完畢的孩子view
final int depth = parser.getDepth();
int type;
while (((type = parser.next()) != XmlPullParser.END_TAG ||
parser.getDepth() > depth) && type != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT) {
if (type != XmlPullParser.START_TAG) {
continue;
}
// 確保是一個START_TAG node
final String name = parser.getName(); // 拿到tagName
if (TAG_REQUEST_FOCUS.equals(name)) { // 處理REQUEST_FOCUS tag
parseRequestFocus(parser, parent);
} else if (TAG_INCLUDE.equals(name)) { // 處理include tag
if (parser.getDepth() == 0) { // include節點不能是根節點,否則就拋異常了。。。
throw new InflateException("<include /> cannot be the root element");
}
parseInclude(parser, parent, attrs);
} else if (TAG_MERGE.equals(name)) { // merge節點必須是xml文件裡的根節點,也就是說到這裡的時候不應該再出現merge節點了
throw new InflateException("<merge /> must be the root element");
} else if (TAG_1995.equals(name)) {
final View view = new BlinkLayout(mContext, attrs);
final ViewGroup viewGroup = (ViewGroup) parent;
final ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = viewGroup.generateLayoutParams(attrs);
rInflate(parser, view, attrs, true);
viewGroup.addView(view, params);
} else { // 一般情況,各種Android view、widget或用戶自定義的view節點
final View view = createViewFromTag(parent, name, attrs);
final ViewGroup viewGroup = (ViewGroup) parent;
final ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = viewGroup.generateLayoutParams(attrs);
rInflate(parser, view, attrs, true);
viewGroup.addView(view, params);
}
}
if (finishInflate) parent.onFinishInflate(); // parent的所有孩子節點都inflate完畢的時候,調用onFinishInflate回調
}
private void parseRequestFocus(XmlPullParser parser, View parent)
throws XmlPullParserException, IOException {
int type;
parent.requestFocus();
final int currentDepth = parser.getDepth();
while (((type = parser.next()) != XmlPullParser.END_TAG || // 忽略此節點剩下的所有內容,直到下一個新的START_TAG
parser.getDepth() > currentDepth) && type != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT) {
// Empty
}
}
private void parseInclude(XmlPullParser parser, View parent, AttributeSet attrs)
throws XmlPullParserException, IOException {
int type;
if (parent instanceof ViewGroup) {
final int layout = attrs.getAttributeResourceValue(null, "layout", 0); // include節點中必須指定layout屬性的值
if (layout == 0) {
final String value = attrs.getAttributeValue(null, "layout");
if (value == null) {
throw new InflateException("You must specifiy a layout in the"
+ " include tag: <include layout=\"@layout/layoutID\" />");
} else {
throw new InflateException("You must specifiy a valid layout "
+ "reference. The layout ID " + value + " is not valid.");
}
} else {
final XmlResourceParser childParser =
getContext().getResources().getLayout(layout);
try {
final AttributeSet childAttrs = Xml.asAttributeSet(childParser);
while ((type = childParser.next()) != XmlPullParser.START_TAG &&
type != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT) {
// Empty.
}
if (type != XmlPullParser.START_TAG) {
throw new InflateException(childParser.getPositionDescription() +
": No start tag found!");
}
final String childName = childParser.getName();
if (TAG_MERGE.equals(childName)) { // 處理include xml裡包含merge的情況
// Inflate all children.
rInflate(childParser, parent, childAttrs, false);
} else { // 處理一般的include layout文件,創建此xml文件的root view
final View view = createViewFromTag(parent, childName, childAttrs);
final ViewGroup group = (ViewGroup) parent;
// We try to load the layout params set in the <include /> tag. If
// they don't exist, we will rely on the layout params set in the
// included XML file.
// During a layoutparams generation, a runtime exception is thrown
// if either layout_width or layout_height is missing. We catch
// this exception and set localParams accordingly: true means we
// successfully loaded layout params from the <include /> tag,
// false means we need to rely on the included layout params.
ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = null;
try {
params = group.generateLayoutParams(attrs);
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
params = group.generateLayoutParams(childAttrs);
} finally {
if (params != null) {
view.setLayoutParams(params); // 設置其layoutParams
}
}
// Inflate all children.
rInflate(childParser, view, childAttrs, true); // 遞歸inflate剩下的節點
// Attempt to override the included layout's android:id with the
// one set on the <include /> tag itself.
TypedArray a = mContext.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs,
com.android.internal.R.styleable.View, 0, 0);
int id = a.getResourceId(com.android.internal.R.styleable.View_id, View.NO_ID);
// While we're at it, let's try to override android:visibility.
int visibility = a.getInt(com.android.internal.R.styleable.View_visibility, -1);
a.recycle();
if (id != View.NO_ID) {
view.setId(id); // override id,如果include節點提供了
}
switch (visibility) { // 同樣的,override visibility,如果include節點提供了
case 0:
view.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
break;
case 1:
view.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
break;
case 2:
view.setVisibility(View.GONE);
break;
}
group.addView(view); // 將include的xml文件裡的root view加到上層group中
}
} finally {
childParser.close();
}
}
} else { // include節點必須是某個ViewGroup的子節點
throw new InflateException("<include /> can only be used inside of a ViewGroup");
}
final int currentDepth = parser.getDepth();
while (((type = parser.next()) != XmlPullParser.END_TAG || // skip掉include節點剩下的內容
parser.getDepth() > currentDepth) && type != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT) {
// Empty
}
}
復制代碼
最後我們看看根據節點創建對應View的相關方法:
復制代碼
/*
* default visibility so the BridgeInflater can override it.
*/
View createViewFromTag(View parent, String name, AttributeSet attrs) {
if (name.equals("view")) {
name = attrs.getAttributeValue(null, "class");
}
if (DEBUG) System.out.println("******** Creating view: " + name);
try {
View view;
// 這裡我們忽略掉了各種factory的onCreateView,有興趣的讀者可自行研究
if (mFactory2 != null) view = mFactory2.onCreateView(parent, name, mContext, attrs);
else if (mFactory != null) view = mFactory.onCreateView(name, mContext, attrs);
else view = null;
if (view == null && mPrivateFactory != null) {
view = mPrivateFactory.onCreateView(parent, name, mContext, attrs);
}
if (view == null) {
if (-1 == name.indexOf('.')) { // 創建android.view.*裡的任何view,如TextView,ImageView等等
view = onCreateView(parent, name, attrs); // 其子類PhoneLayoutInflater override了此方法用來
} else { // 創建android.widget.*/android.webkit.*裡的任何對象
view = createView(name, null, attrs); // 創建用戶自定義的各種View(如com.xiaoweiz.browser.MyCustomView)
}
}
if (DEBUG) System.out.println("Created view is: " + view);
return view;
} catch (InflateException e) {
throw e;
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
InflateException ie = new InflateException(attrs.getPositionDescription()
+ ": Error inflating class " + name);
ie.initCause(e);
throw ie;
} catch (Exception e) {
InflateException ie = new InflateException(attrs.getPositionDescription()
+ ": Error inflating class " + name);
ie.initCause(e);
throw ie;
}
}
/**
* Low-level function for instantiating a view by name. This attempts to
* instantiate a view class of the given <var>name</var> found in this
* LayoutInflater's ClassLoader.
*
* <p>
* There are two things that can happen in an error case: either the
* exception describing the error will be thrown, or a null will be
* returned. You must deal with both possibilities -- the former will happen
* the first time createView() is called for a class of a particular name,
* the latter every time there-after for that class name.
*
* @param name The full name of the class to be instantiated.
* @param attrs The XML attributes supplied for this instance.
*
* @return View The newly instantiated view, or null.
*/
public final View createView(String name, String prefix, AttributeSet attrs) // 用戶自定義的view不需要prefix,因為
throws ClassNotFoundException, InflateException { // name中已經有所有需要的信息了;系統的prefix則是android.view.
Constructor<? extends View> constructor = sConstructorMap.get(name); // 或android.widget. 或 android.webkit.
Class<? extends View> clazz = null;
try {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, name);
if (constructor == null) {
// Class not found in the cache, see if it's real, and try to add it
clazz = mContext.getClassLoader().loadClass( // 加載class文件
prefix != null ? (prefix + name) : name).asSubclass(View.class);
if (mFilter != null && clazz != null) {
boolean allowed = mFilter.onLoadClass(clazz);
if (!allowed) {
failNotAllowed(name, prefix, attrs);
}
}
constructor = clazz.getConstructor(mConstructorSignature); // 拿到此類型的ctor
sConstructorMap.put(name, constructor);
} else {
// If we have a filter, apply it to cached constructor
if (mFilter != null) {
// Have we seen this name before?
Boolean allowedState = mFilterMap.get(name);
if (allowedState == null) {
// New class -- remember whether it is allowed
clazz = mContext.getClassLoader().loadClass(
prefix != null ? (prefix + name) : name).asSubclass(View.class);
boolean allowed = clazz != null && mFilter.onLoadClass(clazz);
mFilterMap.put(name, allowed);
if (!allowed) {
failNotAllowed(name, prefix, attrs);
}
} else if (allowedState.equals(Boolean.FALSE)) {
failNotAllowed(name, prefix, attrs);
}
}
}
Object[] args = mConstructorArgs; // 需要2個參數Context,AttributeSet的版本,所以如果你不打算動態inflate
args[1] = attrs; // 你的view,則沒必要提供此版本的ctor。
final View view = constructor.newInstance(args); // new一個View(可能是其子類)的對象,可能為null
if (view instanceof ViewStub) { // ViewStub的特殊處理
// always use ourselves when inflating ViewStub later
final ViewStub viewStub = (ViewStub) view;
viewStub.setLayoutInflater(this);
}
return view;
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
InflateException ie = new InflateException(attrs.getPositionDescription()
+ ": Error inflating class "
+ (prefix != null ? (prefix + name) : name));
ie.initCause(e);
throw ie;
} catch (ClassCastException e) {
// If loaded class is not a View subclass
InflateException ie = new InflateException(attrs.getPositionDescription()
+ ": Class is not a View "
+ (prefix != null ? (prefix + name) : name));
ie.initCause(e);
throw ie;
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// If loadClass fails, we should propagate the exception.
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
InflateException ie = new InflateException(attrs.getPositionDescription()
+ ": Error inflating class "
+ (clazz == null ? "<unknown>" : clazz.getName()));
ie.initCause(e);
throw ie;
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
}
}
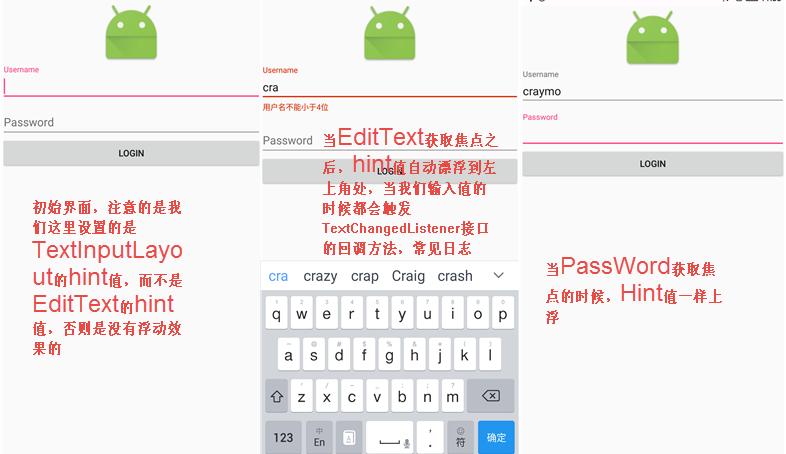 Android進階——Material Design新控件之TextInputLayout
Android進階——Material Design新控件之TextInputLayout
 android開發最常用例子整理----(1)自定義按鈕實現
android開發最常用例子整理----(1)自定義按鈕實現
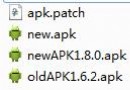 Android增量升級簡單實現(附源碼)
Android增量升級簡單實現(附源碼)
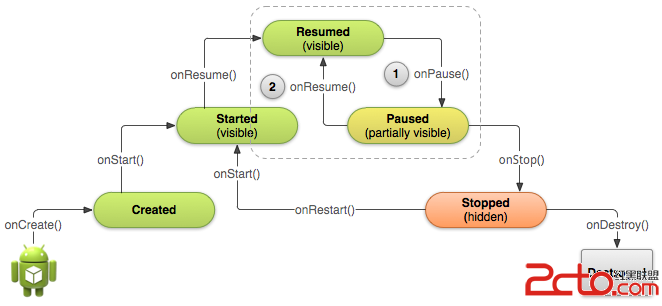 Android官方文檔翻譯 十八 4.2Pausing and Resuming an Activity
Android官方文檔翻譯 十八 4.2Pausing and Resuming an Activity