編輯:關於Android編程
既然本節是學習如何使用多線程下載,那我們先要明白什麼是多線程下載,在搞明白什麼是多線程下載之前,需要先知道什麼是單線程下載。

上圖就是說明了單線程下載的原來,因此單線程下載速度很慢,因為只有一個任務在干活。
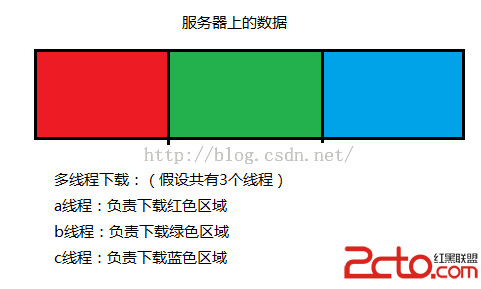
這樣的話,3個線程下載一個文件,總比1個線程一個文件的速度要快。所以多線程下載數據的速度就快。
既然知道了多線程的下載原理,那我們就分析多個線程是如何下載數據,以及如何保存數據的。
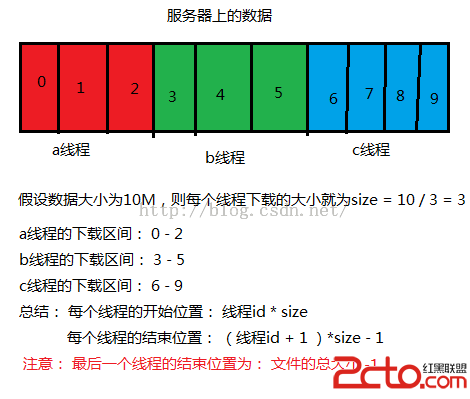
知道多線程下載的原理,以及每個線程如何存放數據後,那就開始寫代碼。
1: 當然先要獲取該數據的大小了,這樣才知道給每個線程分配多大的下載量
我在服務器上下載一個exe文件名為:wireshark.exe
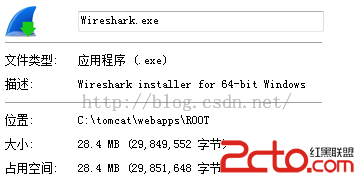
先從服務器上獲取該文件的大小,並計算每個線程應該下載的大小區間
public void downloade(View v)
{
Thread thread = new Thread()
{
//服務器地址
String path = http://192.168.1.123:8080/Wireshark.exe;
@Override
public void run() {
try {
URL url = new URL(path);
HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
conn.setRequestMethod(GET);
conn.setReadTimeout(5000);
conn.setReadTimeout(5000);
if(conn.getResponseCode() == 200)
{
//獲取數據的總大小
int length = conn.getContentLength();
//每個線程的大小
int size = length / threadCount;
for(int i = 0; i < threadCount; i++)
{
int startIndex = i * size;
int endIndex = (i + 1)*size - 1;
//最後一個線程的結束地址為文件總大小-1
if(i == threadCount - 1)
{
endIndex = length - 1;
}
System.out.println(線程 + i + 的下載區間為: + startIndex + --- + endIndex);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
thread.start();
}
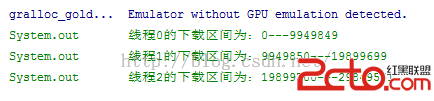
可以看到大小是正確的。總的大小為29849552大小
2: 既然已經給每個線程分好了下載區間,那我們就開始下載
在下載開始時,先要在存儲設備上分配一個個下載文件一樣大小的臨時文件,這樣可以避免下載過程中出現存儲不夠。
System.out.println(線程 + i + 的下載區間為: + startIndex + --- + endIndex); //開啟threadCount去下載數據 new downloadThread(startIndex, endIndex, i).start();
class downloadThread extends Thread{
int startIndex;//開始位置
int endIndex;//結束位置
int threadId;//線程Id
//構造方法
public downloadThread(int startIndex, int endIndex, int threadId) {
super();
this.startIndex = startIndex;
this.endIndex = endIndex;
this.threadId = threadId;
}
@Override
public void run() {
//這次需要請求要下載的數據了
URL url;
try {
url = new URL(path);
HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
conn.setRequestMethod(GET);
conn.setReadTimeout(5000);
conn.setReadTimeout(5000);
//設置本次HTTP請求數據的區間
conn.setRequestProperty(Range, bytes= + startIndex + - + endIndex);
//請求部分數據,返回碼為206
if(conn.getResponseCode() == 206)
{
//此時取到的流裡的數據只有上面給定區間的大小
InputStream is = conn.getInputStream();
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
int total = 0;
//再次打開臨時文件
File file = new File(Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory(), filename);
RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile(file, rwd);
//把文件的寫入位置指定到startindex
raf.seek(startIndex);
while((len = is.read(b)) != -1)
{
raf.write(b, 0, len);
total += len;
System.out.println(線程 + threadId + 下載了 + total);
}
System.out.println(線程 + threadId + ---------------下載完畢-------------------);
raf.close();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
3: 既然下載東西,對用戶來說就的知道下載的進度。我們使用進度條顯示現在的進度
設置最大進度
//獲取數據的總大小 int length = conn.getContentLength(); //設置進度條的最大值 pBar.setMax(length); //每個線程的大小 int size = length / threadCount;
raf.write(b, 0, len); total += len; System.out.println(線程 + threadId + 下載了 + total); //設置當前進度,是3個線程的總和 currProgress += len; pBar.setProgress(currProgress);
Handler handler = new Handler()
{
public void handleMessage(android.os.Message msg)
{
//顯示下載比例,轉為為long型,int的時候有時候不夠大
tView.setText((long)pBar.getProgress() * 100 / pBar.getMax() + %);
};
};

接下來實現斷點續傳:
File bakFile = new File(Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory(), threadId + .txt);
try {
//判斷文件是否存在
if(bakFile.exists())
{
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(bakFile);
BufferedReader bReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(fis));
//從進度臨時文件中讀取出上一次下載的總進度,然後與原本的開始位置相加,得到新的開始位置
int lastProgress = Integer.parseInt(bReader.readLine());
startIndex += lastProgress;
//把上次下載的進度顯示至進度條
currProgress += lastProgress;
pBar.setProgress(currProgress);
//發送消息,讓主線程刷新文本進度
handler.sendEmptyMessage(1);
fis.close();
}
在下載時候,先需要創建配置文件,防止下載過程中某些原因導致停止下載,當後續接著下載時,還是會用上次下載的地方接著下載
while((len = is.read(b)) != -1)
{
raf.write(b, 0, len);
total += len;
System.out.println(線程 + threadId + 下載了 + total);
//設置當前進度,是3個線程的總和
currProgress += len;
pBar.setProgress(currProgress);
//通過發送消息,更新文本。而進度條不需要通過發消息刷新UI,因為進度條本身就是在別的任務中使用的
handler.sendEmptyMessage(1);
//將當前的下載進度保存到配置文件中
RandomAccessFile bakRaFile = new RandomAccessFile(bakFile, rwd);
bakRaFile.write((total + ).getBytes());
bakRaFile.close();
}
可以正常的支持斷點連續下載
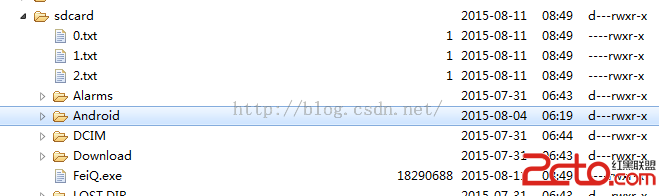
下載的文件可以正常運行,我將下載文件轉為feiq了,因為wireshark有點大
 小米5、榮耀V8、魅族PRO6和一加手機3哪個好 參數對比評測
小米5、榮耀V8、魅族PRO6和一加手機3哪個好 參數對比評測
國產手機的集體高潮,卻使消費者變的“煩惱了”,因為消費者在購買手機時變得越來越猶豫糾結。以2499元這個價位的手機來說,單國產手機就
 Activity實例詳解之啟動activity並返回結果
Activity實例詳解之啟動activity並返回結果
先給大家展示下效果展示圖:1 簡介如果想在Activity中得到新打開Activity 關閉後返回的數據,需要使用系統提供的startActivityForResult(
 View的事件分發機制學習筆記
View的事件分發機制學習筆記
好不容易周末有空,作為一個零基礎非計算機專業剛培訓出來7個月的小白,對付博大精深的Android源碼真的是心有余而力不足,但是東西還是要學滴,這不!找到Hongyang大
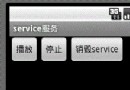 實例講解Android中的AIDL內部進程通信接口使用
實例講解Android中的AIDL內部進程通信接口使用
首先描述下我們想要實現的內容,我們希望在一個應用中通過點擊按鈕,去操作另一個進程中應用的音樂播放功能。如圖,我們點擊“播放”時,系統就會去遠程調用我們提供的一個servi