編輯:關於Android編程
前言:從開始接觸rn到現在終於能寫出點東西了,的確得為自己好好地點個贊 ,不管咋樣,學習還是得繼續啊,廢話少說了,在rn中我們也需要對屏幕進行適配,但是rn中的適配貌似比android原生容易很多(不得佩服facebook那些大神哈,對android原生控件封裝的太屌!)。
我們先看看rn中的屏幕適配(作為一個android程序員去做rn確實比ios程序員考慮的東西多一點點哈,嘻嘻~~):
結合android的一些適配經驗,我在rn中也封裝了一個工具類
ScreenUtils.js:
/**
* 屏幕工具類
* ui設計基准,iphone 6
* width:750
* height:1334
*/
var ReactNative = require('react-native');
var Dimensions = require('Dimensions');
export var screenW = Dimensions.get('window').width;
export var screenH = Dimensions.get('window').height;
var fontScale = ReactNative.PixelRatio.getFontScale();
export var pixelRatio = ReactNative.PixelRatio.get();
const r2=2;
const w2 = 750/r2;``
const h2 = 1334/r2;
/**
* 設置text為sp
* @param size sp
* @returns {Number} dp
*/
export const DEFAULT_DENSITY=2;
export function setSpText(size:Number) {
var scaleWidth = screenW / w2;
var scaleHeight = screenH / h2;
var scale = Math.min(scaleWidth, scaleHeight);
size = Math.round((size * scale + 0.5) * pixelRatio / fontScale);
return size;
}
/**
* 屏幕適配,縮放size
* @param size
* @returns {Number}
* @constructor
*/
export function scaleSize(size:Number) {
var scaleWidth = screenW / w2;
var scaleHeight = screenH / h2;
var scale = Math.min(scaleWidth, scaleHeight);
size = Math.round((size * scale + 0.5));
return size/DEFAULT_DENSITY;
}
搞過rn的童鞋知道,rn中直接寫寬高都是dp的,所以我們要以一個美工設計的ui基准來計算我們的寬高,數學不好哈,不過大概是這樣的:
我們先定義好ui的設計基准:
/**
* 屏幕工具類
* ui設計基准,iphone 6
* width:750
* height:1334
*/
var ReactNative = require('react-native');
var Dimensions = require('Dimensions');
export var screenW = Dimensions.get('window').width;
export var screenH = Dimensions.get('window').height;
var fontScale = ReactNative.PixelRatio.getFontScale();
export var pixelRatio = ReactNative.PixelRatio.get();
const r2=2;
const w2 = 750/r2;``
const h2 = 1334/r2;
/**
* 設置text為sp
* @param size sp
* @returns {Number} dp
*/
export const DEFAULT_DENSITY=2;
然後獲取到我們自己手機的屏幕寬高,生成一個百分比,然後算出在iphone6上的100px,在我們手機上是多少px,最後轉換成dp設置在在我們布局的style中:
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
backgroundColor: 'white',
justifyContent: 'space-between',
flexDirection: 'row',
paddingTop: ScreenUtils.scaleSize(22),
paddingBottom: ScreenUtils.scaleSize(22),
paddingRight: ScreenUtils.scaleSize(12),
paddingLeft: ScreenUtils.scaleSize(12),
alignItems: 'center'
},
});
好啦~!!,rn上的適配就完啦,是不是soeasy呢???
但是在android原生中,我們寫布局大多數都是在xml中寫的,所以我們在寫布局的時候,壓根就不知道我要運行在什麼手機上,所以android官方建議我們使用dp啊,然後建很多layout文件啊,很多value文件啊,是的!我個人也是比較推崇官方的做法的,效率高,清晰明了,好啦!!除了android官方說的那種方法,我們是否也可以像rn一樣運行後再重新算出百分比,然後再布局呢?答案是肯定的,因為rn就是一個例子,它也是對原生控件封裝過的,所以才能用js輕易控制,在此之前鴻洋大神也對百分比布局做了封裝,也對齊做了很詳細的解析了,先貼上大神的博客鏈接:
好啦!我們今天要做的也就是在百分比布局的基礎上簡單封裝下,然後使得其能夠像rn一樣,直接寫上美工標的px就能完美適配大部分手機了。
先上張運行好的效果圖(效果還是很不錯的!):
布局文件:
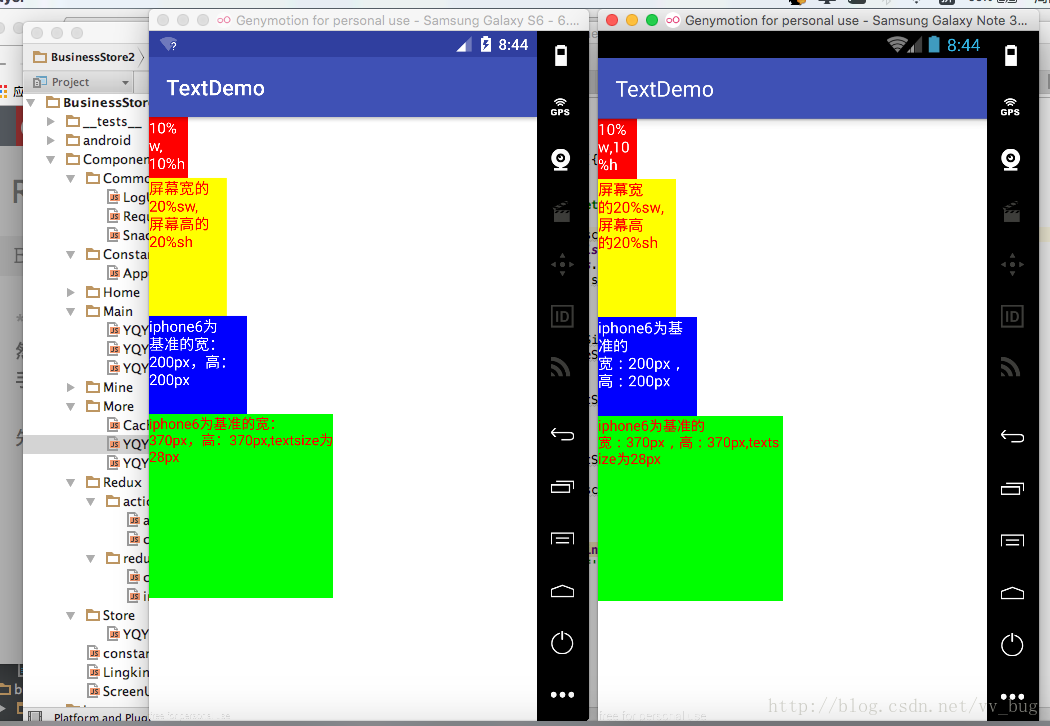
先走一遍百分比布,看它到底是咋實現適配的(以下是來自鴻洋大神封裝過後的代碼,我就直接拿走解析了,嘻嘻!!):
PercentLinearLayout.java:
package com.yasin.px_percent_layout;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.res.TypedArray;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.util.DisplayMetrics;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.view.WindowManager;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
import android.widget.ScrollView;
public class PercentLinearLayout extends LinearLayout {
private static final String TAG = "PercentLinearLayout";
private PercentLayoutHelper mPercentLayoutHelper;
public PercentLinearLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
mPercentLayoutHelper = new PercentLayoutHelper(this);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int tmpHeightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(heightSize, heightMode);
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int tmpWidthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(widthSize, widthMode);
//fixed scrollview height problems
if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED && getParent() != null && (getParent() instanceof ScrollView)) {
int baseHeight = 0;
Context context = getContext();
if (context instanceof Activity) {
Activity act = (Activity) context;
int measuredHeight = act.findViewById(android.R.id.content).getMeasuredHeight();
baseHeight = measuredHeight;
} else {
baseHeight = getScreenHeight();
}
tmpHeightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(baseHeight, heightMode);
}
mPercentLayoutHelper.adjustChildren(tmpWidthMeasureSpec, tmpHeightMeasureSpec);
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
if (mPercentLayoutHelper.handleMeasuredStateTooSmall()) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
}
private int getScreenHeight() {
WindowManager wm = (WindowManager) getContext().getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE);
DisplayMetrics outMetrics = new DisplayMetrics();
wm.getDefaultDisplay().getMetrics(outMetrics);
return outMetrics.heightPixels;
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
super.onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b);
mPercentLayoutHelper.restoreOriginalParams();
}
@Override
public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
return new LayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
}
public static class LayoutParams extends LinearLayout.LayoutParams
implements PercentLayoutHelper.PercentLayoutParams {
private PercentLayoutHelper.PercentLayoutInfo mPercentLayoutInfo;
public LayoutParams(Context c, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(c, attrs);
mPercentLayoutInfo = PercentLayoutHelper.getPercentLayoutInfo(c, attrs);
}
@Override
public PercentLayoutHelper.PercentLayoutInfo getPercentLayoutInfo() {
return mPercentLayoutInfo;
}
@Override
protected void setBaseAttributes(TypedArray a, int widthAttr, int heightAttr) {
PercentLayoutHelper.fetchWidthAndHeight(this, a, widthAttr, heightAttr);
}
public LayoutParams(int width, int height) {
super(width, height);
}
public LayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams source) {
super(source);
}
public LayoutParams(MarginLayoutParams source) {
super(source);
}
}
}
代碼不要太簡單哈,就在構造方法中創建了一個mPercentLayoutHelper:
public PercentLinearLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
mPercentLayoutHelper = new PercentLayoutHelper(this);
}
我們待會再來說這個PercentLayoutHelper,
然後就是創建了一個自己的LayoutParams:
public static class LayoutParams extends LinearLayout.LayoutParams
implements PercentLayoutHelper.PercentLayoutParams {
private PercentLayoutHelper.PercentLayoutInfo mPercentLayoutInfo;
public LayoutParams(Context c, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(c, attrs);
mPercentLayoutInfo = PercentLayoutHelper.getPercentLayoutInfo(c, attrs);
}
@Override
public PercentLayoutHelper.PercentLayoutInfo getPercentLayoutInfo() {
return mPercentLayoutInfo;
}
@Override
protected void setBaseAttributes(TypedArray a, int widthAttr, int heightAttr) {
PercentLayoutHelper.fetchWidthAndHeight(this, a, widthAttr, heightAttr);
}
public LayoutParams(int width, int height) {
super(width, height);
}
public LayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams source) {
super(source);
}
public LayoutParams(MarginLayoutParams source) {
super(source);
}
}
其中也咩有啥代碼,創建了一個PercentLayoutInfo。
然後核心代碼就是onMeasure方法裡面了:
mPercentLayoutHelper.adjustChildren(tmpWidthMeasureSpec, tmpHeightMeasureSpec);
核心也就這一句。
終結下來就是:
1、先獲取到我們在布局文件中定義的屬性:
app:layout_widthPercent="10%w" app:layout_heightPercent="10%h" .......
2、然後把獲取到的屬性封裝進一個叫PercentLayoutInfo的類中:
public LayoutParams(Context c, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(c, attrs);
mPercentLayoutInfo = PercentLayoutHelper.getPercentLayoutInfo(c, attrs);
}
3、在onMeasure方法中根據傳進的屬性對子控件進行重置大小:
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int tmpHeightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(heightSize, heightMode);
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int tmpWidthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(widthSize, widthMode);
//fixed scrollview height problems
if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED && getParent() != null && (getParent() instanceof ScrollView)) {
int baseHeight = 0;
Context context = getContext();
if (context instanceof Activity) {
Activity act = (Activity) context;
int measuredHeight = act.findViewById(android.R.id.content).getMeasuredHeight();
baseHeight = measuredHeight;
} else {
baseHeight = getScreenHeight();
}
tmpHeightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(baseHeight, heightMode);
}
mPercentLayoutHelper.adjustChildren(tmpWidthMeasureSpec, tmpHeightMeasureSpec);
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, hei }
}
看完是不是覺得很簡單呢? 是的,本來就不難哈,我們接著往下看:
先看看它是咋拿到我們在布局文件中寫的屬性的(怎麼封裝):
public static PercentLayoutInfo getPercentLayoutInfo(Context context,
AttributeSet attrs) {
PercentLayoutInfo info = null;
TypedArray array = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.PercentLayout_Layout);
info = setWidthAndHeightVal(array, info);
info = setMarginRelatedVal(array, info);
info = setTextSizeSupportVal(array, info);
info = setMinMaxWidthHeightRelatedVal(array, info);
info = setPaddingRelatedVal(array, info);
array.recycle();
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.DEBUG)) {
Log.d(TAG, "constructed: " + info);
}
return info;
}
獲取TypedArray數組中的數據(我們就只看setWidthAndHeightVal代碼了):
private static PercentLayoutInfo setWidthAndHeightVal(TypedArray array, PercentLayoutInfo info) {
PercentLayoutInfo.PercentVal percentVal = getPercentVal(array, R.styleable.PercentLayout_Layout_layout_widthPercent, true);
if (percentVal != null) {
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.VERBOSE)) {
Log.v(TAG, "percent width: " + percentVal.percent);
}
info = checkForInfoExists(info);
info.widthPercent = percentVal;
}
percentVal = getPercentVal(array, R.styleable.PercentLayout_Layout_layout_heightPercent, false);
if (percentVal != null) {
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.VERBOSE)) {
Log.v(TAG, "percent height: " + percentVal.percent);
}
info = checkForInfoExists(info);
info.heightPercent = percentVal;
}
return info;
}
獲取到heightPercent跟widthPercent信息然後賦給info對象,沒啥好看的,重點看看咋獲取到的widthPercent信息:
private static PercentLayoutInfo.PercentVal getPercentVal(TypedArray array, int index, boolean baseWidth) {
String sizeStr = array.getString(index);
PercentLayoutInfo.PercentVal percentVal = getPercentVal(sizeStr, baseWidth);
return percentVal;
}
也沒啥看的(繼續往下走):
private static PercentLayoutInfo.PercentVal getPercentVal(String percentStr, boolean isOnWidth) {
//valid param
if (percentStr == null) {
return null;
}
Pattern p = Pattern.compile(REGEX_PERCENT);
Matcher matcher = p.matcher(percentStr);
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(percentStr) ||
(!matcher.matches() && !(percentStr.toLowerCase().endsWith("px")))) {
throw new RuntimeException("the value of layout_xxxPercent invalid! ==>" + percentStr);
}
String floatVal;
String lastAlpha;
float percent;
int len = percentStr.length();
if (matcher.matches()) {
//extract the float value
floatVal = matcher.group(1);
lastAlpha = percentStr.substring(len - 1);
percent = Float.parseFloat(floatVal) / 100f;
} else {
//extract the float value
floatVal = percentStr.substring(0, percentStr.indexOf("px"));
lastAlpha = percentStr.substring(len - 1);
percent = Float.parseFloat(floatVal);
}
PercentLayoutInfo.PercentVal percentVal = new PercentLayoutInfo.PercentVal();
percentVal.percent = percent;
if (percentStr.endsWith(PercentLayoutInfo.BASEMODE.SW)) {
percentVal.basemode = PercentLayoutInfo.BASEMODE.BASE_SCREEN_WIDTH;
} else if (percentStr.endsWith(PercentLayoutInfo.BASEMODE.SH)) {
percentVal.basemode = PercentLayoutInfo.BASEMODE.BASE_SCREEN_HEIGHT;
} else if (percentStr.endsWith(PercentLayoutInfo.BASEMODE.PERCENT)) {
if (isOnWidth) {
percentVal.basemode = PercentLayoutInfo.BASEMODE.BASE_WIDTH;
} else {
percentVal.basemode = PercentLayoutInfo.BASEMODE.BASE_HEIGHT;
}
} else if (percentStr.endsWith(PercentLayoutInfo.BASEMODE.W)) {
percentVal.basemode = PercentLayoutInfo.BASEMODE.BASE_WIDTH;
} else if (percentStr.endsWith(PercentLayoutInfo.BASEMODE.H)) {
percentVal.basemode = PercentLayoutInfo.BASEMODE.BASE_HEIGHT;
} else if (percentStr.endsWith(PercentLayoutInfo.BASEMODE.PX)) {
percentVal.basemode = PercentLayoutInfo.BASEMODE.ABSOLUTE_PX;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("the " + percentStr + " must be endWith [%|w|h|sw|sh]");
}
return percentVal;
}
好啦,終於看到核心代碼了,不做太多解釋,相信都看得懂,簡單來說就是獲取到我們設置的值,然後判斷我們設置的值屬於哪種類型:
類型有:
private enum BASEMODE {
BASE_WIDTH, BASE_HEIGHT, BASE_SCREEN_WIDTH, BASE_SCREEN_HEIGHT, ABSOLUTE_PX;
/**
* width_parent
*/
public static final String PERCENT = "%";
/**
* width_parent
*/
public static final String W = "w";
/**
* height_parent
*/
public static final String H = "h";
/**
* width_screen
*/
public static final String SW = "sw";
/**
* height_screen
*/
public static final String SH = "sh";
/**
* absolute px
*/
public static final String PX = "px";
}
就是我們布局中寫的:
app:layout_widthPercent="10%w"
app:layout_heightPercent="10%h"
app:layout_widthPercent="20%sw"
app:layout_heightPercent="20%sh"
app:layout_widthPercent="200px"
app:layout_heightPercent="200px"
小伙伴是不是看懂了呢? 比如20%sw,就是把20跟sw取出來,然後封裝進類中。
好啦,我們已經拿到我們在布局中設置的屬性了,然後我們就得根據我們設置的值重新賦給子控件了。
在onMeasure中我們找到adjustChildren方法:
/**
* Iterates over children and changes their width and height to one calculated from percentage
* values.
*
* @param widthMeasureSpec Width MeasureSpec of the parent ViewGroup.
* @param heightMeasureSpec Height MeasureSpec of the parent ViewGroup.
*/
public void adjustChildren(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.DEBUG)) {
Log.d(TAG, "adjustChildren: " + mHost + " widthMeasureSpec: "
+ View.MeasureSpec.toString(widthMeasureSpec) + " heightMeasureSpec: "
+ View.MeasureSpec.toString(heightMeasureSpec));
}
int widthHint = View.MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightHint = View.MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.DEBUG))
Log.d(TAG, "widthHint = " + widthHint + " , heightHint = " + heightHint);
for (int i = 0, N = mHost.getChildCount(); i < N; i++) {
View view = mHost.getChildAt(i);
ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = view.getLayoutParams();
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.DEBUG)) {
Log.d(TAG, "should adjust " + view + " " + params);
}
if (params instanceof PercentLayoutParams) {
PercentLayoutInfo info =
((PercentLayoutParams) params).getPercentLayoutInfo();
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.DEBUG)) {
Log.d(TAG, "using " + info);
}
if (info != null) {
supportTextSize(widthHint, heightHint, view, info);
supportPadding(widthHint, heightHint, view, info);
supportMinOrMaxDimesion(widthHint, heightHint, view, info);
if (params instanceof ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams) {
info.fillMarginLayoutParams((ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams) params,
widthHint, heightHint);
} else {
info.fillLayoutParams(params, widthHint, heightHint);
}
}
}
}
}
遍歷我們的子控件,然後根據我們上面獲取到的info類,進行重新布局:
if (info != null) {
supportTextSize(widthHint, heightHint, view, info);
supportPadding(widthHint, heightHint, view, info);
supportMinOrMaxDimesion(widthHint, heightHint, view, info);
if (params instanceof ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams) {
info.fillMarginLayoutParams((ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams) params,
widthHint, heightHint);
} else {
info.fillLayoutParams(params, widthHint, heightHint);
}
}
demo中我們看到了:
我們有設置一個app:layout_textSizePercent:
看到這我們找到一個方法,沒錯!也就是這裡對textview設置的size大小的:
supportTextSize(widthHint, heightHint, view, info);
我們往下走:
private void supportTextSize(int widthHint, int heightHint, View view, PercentLayoutInfo info) {
//textsize percent support
PercentLayoutInfo.PercentVal textSizePercent = info.textSizePercent;
if (textSizePercent == null) return;
float textSize;
int base = getBaseByModeAndVal(widthHint, heightHint, textSizePercent.basemode);
if (textSizePercent.basemode == PercentLayoutInfo.BASEMODE.ABSOLUTE_PX) {
textSize = ViewUtils.scaleTextValue(mHost.getContext(), textSizePercent.percent);
} else {
textSize = (int) (base * textSizePercent.percent);
}
//Button 和 EditText 是TextView的子類
if (view instanceof TextView) {
((TextView) view).setTextSize(TypedValue.COMPLEX_UNIT_PX, textSize);
}
}
這裡如果我們是直接設置的px的話(如:app:layout_textSizePercent=”28px”),我們就需要根據ui基准,然後算出在我們手機上應該顯示多少:
int base = getBaseByModeAndVal(widthHint, heightHint, textSizePercent.basemode);
if (textSizePercent.basemode == PercentLayoutInfo.BASEMODE.ABSOLUTE_PX) {
textSize = ViewUtils.scaleTextValue(mHost.getContext(), textSizePercent.percent);
} else {
textSize = (int) (base * textSizePercent.percent);
}
如果是直接設置的20%w,20%h,20%sh這樣的值的話,我們就需要用父布局的寬、高、屏幕寬、高乘一個我們設置進去的百分比進行計算了:
textSize = (int) (base * textSizePercent.percent);
好啦!!!剩下的幾個方法也都差不多,我就不一一講了哈:
if (info != null) {
supportTextSize(widthHint, heightHint, view, info);
supportPadding(widthHint, heightHint, view, info);
supportMinOrMaxDimesion(widthHint, heightHint, view, info);
if (params instanceof ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams) {
info.fillMarginLayoutParams((ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams) params,
widthHint, heightHint);
} else {
info.fillLayoutParams(params, widthHint, heightHint);
}
}
嗯嗯~! 我們的百分比跟px布局差不多就講完啦~, 下面看看咋使用它哈:
如果要直接使用px布局的話(不用px布局可不需要做第一步與第二步):
1、在項目的manifest文件中定義好ui設計的基准(如iphone6):
2、在app中的application文件中,初始化布局:
package com.example.leo.textdemo;
import android.app.Application;
import android.content.Context;
import com.yasin.px_percent_layout.utils.PxAppConfig;
/**
* Created by leo on 17/2/9.
*/
public class BaseApplication extends Application {
@Override
protected void attachBaseContext(Context base) {
super.attachBaseContext(base);
PxAppConfig.init(base);
}
}
然後我們就可以在布局文件中用起來了:
好啦!!!文章有點長哈,最後附上項目的git鏈接:
https://github.com/913453448/PercentLayoutDemo
 Android基礎:HelloWorld之Toast用法
Android基礎:HelloWorld之Toast用法
一:看程序 二:改布局: 1:在res資源下面,找到layout,打開activity_main.xml 在Graphical Layout視圖下面,可以自定義
 Android開發之監聽手機來電
Android開發之監聽手機來電
TelephonyManager是一個管理手機通話狀態、電話網絡信息的服務類,該類提供了大量的getXxx(),方法獲取電話網絡的相關信息。關於TelephonyMana
 Android 組件Gallery和GridView示例講解
Android 組件Gallery和GridView示例講解
Android Gallery和GridView組件:Gallery 畫廊Gallery是一個內部元素可以水平滾動,並且可以把當前選擇的子元素定位在它中心的布局組件。我們
 Android Api Component---翻譯Fragment組件(一)
Android Api Component---翻譯Fragment組件(一)
Fragment代表了在Activity中的一種或者一部分行為,你可以在單個的activity中連接多個fragment來構建一個多面板的UI,並且在多個activit